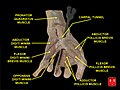
Flexor pollicis brevis muscle

| Flexor pollicis brevis muscle | |
|---|---|
 Superficial muscles of the left hand, palmar view. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Trapezium, flexor retinaculum |
| Insertion | Thumb, proximal phalanx |
| Artery | Superficial palmar arch |
| Nerve | Recurrent branch of the median nerve, deep branch of ulnar nerve (medial head) |
| Actions | Flexes the thumb at the first metacarpophalangeal joint |
| Antagonist | Extensor pollicis longus and brevis |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus flexor pollicis brevis |
| TA98 | A04.6.02.055 |
| TA2 | 2522 |
| FMA | 37378 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The flexor pollicis brevis is a muscle in the hand that flexes the thumb. It is one of three thenar muscles.[1][2] It has both a superficial part and a deep part.
Origin and insertion
[edit]The muscle's superficial head arises from the distal edge of the flexor retinaculum and the tubercle of the trapezium, the most lateral bone in the distal row of carpal bones.[1] It passes along the radial side of the tendon of the flexor pollicis longus.
The deeper (and medial) head "varies in size and may be absent."[3] It arises from the trapezoid and capitate bones on the floor of the carpal tunnel, as well as the ligaments of the distal carpal row.[3]
Both heads become tendinous and insert together into the radial side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb;[2] at the junction between the tendinous heads there is a sesamoid bone.[4]
Innervation
[edit]The superficial head is usually innervated by the lateral terminal branch of the median nerve.[1] The deep part is often innervated by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve (C8, T1).[2][3]
Blood supply
[edit]The flexor pollicis brevis receives its blood supply from the superficial palmar branches of radial artery.[5]
Action
[edit]The flexor pollicis brevis flexes the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal joint,[1] as well as flexion and medial rotation of the 1st metacarpal bone at the carpometacarpal joint.[3]
Pathology
[edit]Flexor pollicis brevis can, rarely, be completely absent at birth due to a congenital issue (as can the other muscles of the thenar eminence).[6]
Additional images
[edit]- The muscles of the left hand. Palmar surface. (Flexor pollicis brevis visible at center right, near thumb.)
- Caput profundum of the Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
- Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
- Bones of the left hand. Volar surface.
- Front of the left forearm. Deep muscles.
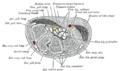
- Transverse section across the wrist and digits.
- Superficial palmar nerves.
- Deep palmar nerves.
- Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
- Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
- Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
- Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
- Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
- Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
- Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
- Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
- Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
- Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
- Muscles of hand. Cross section.
References
[edit]![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 461 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 461 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b c d Fernández-de-las-Peñas, César; Iglesias, Javier González; Gröbli, Christian; Weissmann, Ricky (2012-01-01), Dommerholt, Jan; Fernández-de-las-Peñas, César (eds.), "8 - Deep dry needling of the arm and hand muscles", Trigger Point Dry Needling, Oxford: Churchill Livingstone, pp. 107–118, doi:10.1016/b978-0-7020-4601-8.00008-6, ISBN 978-0-7020-4601-8, retrieved 2020-10-25
- ^ a b c Strickland, James W. (2006-01-01), Henderson, Anne; Pehoski, Charlane (eds.), "Chapter 2 - Anatomy and Kinesiology of the Hand", Hand Function in the Child (Second Edition), Saint Louis: Mosby, pp. 21–44, doi:10.1016/b978-032303186-8.50005-8, ISBN 978-0-323-03186-8, retrieved 2020-10-25
- ^ a b c d Gray's 37th British Edition, p. 630"
- ^ Gray's Anatomy 1918, see infobox
- ^ "Brachium to Hand Musculature". PTCentral. Archived from the original on 4 February 2012.
- ^ Iyer, K. M.; Stanley, J. K. (2017-07-18). "Congenital Absence of Flexor Pollicis Brevis and Abductor Pollicis Brevis". Hand. 14 (3): 313–316. doi:10.1016/S0072-968X(82)80067-3. PMID 7152382. S2CID 41628800.