History of Manhattan

The area of present-day Manhattan was originally part of Lenape territory.[1] European settlement began with the establishment of a trading post founded by colonists from the Dutch Republic in 1624 on Lower Manhattan; the post was named New Amsterdam in 1626. The territory and its surroundings came under English control in 1664 and were renamed New York after King Charles II of England granted the lands to his brother, the Duke of York.[2] New York, based in present-day Manhattan, served as the capital of the United States from 1785 until 1790.[3] The Statue of Liberty in New York Harbor greeted millions of immigrants as they came to America by ship in the late 19th century and is a world symbol of the United States and its ideals of liberty and peace.[4] Manhattan became a borough during the consolidation of New York City in 1898.
Etymology
[edit]The name Manhattan originated from the Lenapes language, Munsee, manaháhtaan (where manah- means "gather", -aht- means "bow", and -aan is an abstract element used to form verb stems). The Lenape word has been translated as "the place where we get bows" or "place for gathering the (wood to make) bows".
According to a Munsee tradition recorded by Albert Seqaqkind Anthony in the 19th century, the island was named so for a grove of hickory trees at its southern end that was considered ideal for the making of bows.[5] It was first recorded in writing as Manna-hata, in the 1609 logbook of Robert Juet, an officer on Henry Hudson's yacht Halve Maen (Half Moon).[6]
A 1610 map depicts the name Manna-hata twice, on both the east and west sides of the Mauritius River, later named the North River and ultimately the Hudson River. Alternative etymologies in folklore include "island of many hills",[7] "the island where we all became intoxicated" and simply "island", as well as a phrase descriptive of the whirlpool at Hell Gate.[8] It is thought that the term Manhattoe may originally have referred only to a location at the southern tip of the island before eventually signifying the entire island to the Dutch through pars pro toto.
Lenape settlement
[edit]Manhattan was historically part of the Lenapehoking territory inhabited by the Munsee Lenape[9] and Wappinger tribes.[10] There were several Lenape settlements in the area of Manhattan including Sapohanikan, Nechtanc, and Konaande Kongh that were interconnected by a series of trails. The primary trail on the island ran from what is now Inwood in the north to Battery Park in the south. There were various sites for fishing and planting established by the Lenape throughout Manhattan.[1] The 48-acre (19 ha) Collect Pond, which fed the fresh water streams and marshes around it, was also an important meeting and trading location for the people in the area.[11][12]
Colonial era
[edit]

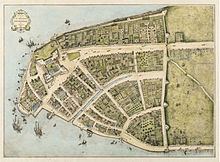

In 1524, Florentine explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano, sailing in service of King Francis I of France, became the first documented European to visit the area that would become New York City. Verrazzano entered the tidal strait now known as The Narrows and named the land around Upper New York Harbor New Angoulême, in reference to the family name of King Francis I that was derived from Angoulême in France; he sailed far enough into the harbor to sight the Hudson River, which he referred to in his report to the French king as a "very big river"; and he named the Bay of Santa Margarita – what is now Upper New York Bay – after Marguerite de Navarre, the elder sister of the king.[13][14]
Manhattan was first mapped during a 1609 voyage of Henry Hudson, an Englishman who worked for the Dutch East India Company.[15] Hudson came across Manhattan Island and the native people living there, and continued up the river that would later bear his name, the Hudson River, until he arrived at the site of present-day Albany.[16]
A permanent European presence in New Netherland began in 1624, with the founding of a Dutch fur trading settlement on Governors Island. In 1625, construction was started on the citadel of Fort Amsterdam on Manhattan Island, later called New Amsterdam (Nieuw Amsterdam), in what is now Lower Manhattan.[17][18] The 1625 establishment of Fort Amsterdam at the southern tip of Manhattan Island is recognized as the birth of New York City.[19]
According to a letter by Pieter Janszoon Schagen, Peter Minuit and Walloon colonists of the West India Company acquired the island of Manhattan on May 24, 1626, from unnamed native people, who are believed to have been Canarsee Indians of the Manhattoe, in exchange for traded goods worth 60 guilders,[20] often said to be worth US$24.[21] In actuality, 60 guilders in that time was worth 2,400 English pennies.[21] According to the writer Nathaniel Benchley, Minuit conducted the transaction with Seyseys, chief of the Canarsee, who were willing to accept valuable merchandise in exchange for the island that was mostly controlled by the Weckquaesgeeks, a band of the Wappinger.[22]
In 1647, Peter Stuyvesant was appointed as the last Dutch Director-General of the colony.[23] New Amsterdam was formally incorporated as a city on February 2, 1653.[24] In 1674, the English bought New Netherland, after Holland lost rentable sugar business in Brazil, and renamed it "New York" after the English Duke of York and Albany, the future King James II.[25] The Dutch, under Director General Stuyvesant, successfully negotiated with the English to produce 24 articles of provisional transfer, which sought to retain for the extant citizens of New Netherland their previously attained liberties (including freedom of religion) under their new English rulers.[26][18]
The Dutch Republic re-captured the city in August 1673, renaming it "New Orange". New Netherland was ultimately ceded to the English in November 1674 through the Treaty of Westminster.[27]
American Revolution and the early United States
[edit]
Manhattan was at the heart of the New York Campaign, a series of major battles in the early stages of the American Revolutionary War. The Continental Army was forced to abandon Manhattan after the Battle of Fort Washington on November 16, 1776. The city, greatly damaged by the Great Fire of New York during the campaign, became the British military and political center of operations in North America for the remainder of the war.[29] The military center for the colonists was established in neighboring New Jersey.[30][31] British occupation lasted until November 25, 1783, when George Washington returned to Manhattan, as the last British forces left the city.[32]
From January 11, 1785, to the fall of 1788, New York City was the fifth of five capitals of the United States under the Articles of Confederation, with the Continental Congress meeting at New York City Hall (then at Fraunces Tavern). New York was the first capital under the newly enacted Constitution of the United States, from March 4, 1789, to August 12, 1790, at Federal Hall.[33] Federal Hall was also the site where the United States Supreme Court met for the first time,[34] the United States Bill of Rights were drafted and ratified,[35] and where the Northwest Ordinance was adopted, establishing measures for adding new states to the Union.[36]
19th century
[edit]
New York grew as an economic center, first as a result of Alexander Hamilton's policies and practices as the first Secretary of the Treasury and, later, with the opening of the Erie Canal in 1825, which connected the Atlantic port to the vast agricultural markets of the Midwestern United States and Canada.[37][38] By 1810, New York City, then confined to Manhattan, had surpassed Philadelphia as the largest city in the United States.[39] The Commissioners' Plan of 1811 laid out the island of Manhattan in its familiar grid plan.
Tammany Hall, a Democratic Party political machine, began to grow in influence with the support of many of the immigrant Irish, culminating in the election of the first Tammany mayor, Fernando Wood, in 1854. Tammany Hall dominated local politics for decades. Central Park, which opened to the public in 1858, became the first landscaped public park in an American city.[40][41]
New York City played a complex role in the American Civil War. The city's strong commercial ties to the southern United States existed for many reasons, including the industrial power of the Hudson River, which allowed trade with stops such as the West Point Foundry, one of the great manufacturing operations in the early United States; and the city's Atlantic Ocean ports, rendering New York City the American powerhouse in terms of industrial trade between the northern and southern United States. Anger arose about conscription, with resentment at those who could afford to pay $300 to avoid service leading to resentment against Lincoln's war policies and fomenting paranoia about free Blacks taking the poor immigrants' jobs,[42] culminating in the three-day-long New York Draft Riots of July 1863. This was among the worst incidents of civil disorder in American history, with over 100 people killed by the rioters or by the military units that stopped the riot..[43]
The rate of immigration from Europe grew steeply after the Civil War, and Manhattan became the first stop for millions seeking a new life in the United States, a role acknowledged by the dedication of the Statue of Liberty on October 28, 1886, a gift from the people of France.[44][45] New York's growing immigrant population, which had earlier consisted mainly of German and Irish immigrants, began in the late 1800s to include waves of impoverished Italians and Central and Eastern European Jews flowing in en masse. This new European immigration brought further social upheaval. In a city of tenements packed with poorly paid laborers from dozens of nations, the city became a hotbed of revolution (including anarchists and communists among others), syndicalism, racketeering, and unionization.
In 1883, the opening of the Brooklyn Bridge established a road connection to Brooklyn, across the East River. In 1874, the western portion of the present Bronx County was transferred to New York County from Westchester County, and in 1895 the remainder of the present Bronx County was annexed.[46] In 1898, when New York City consolidated with three neighboring counties to form "the City of Greater New York", Manhattan and the Bronx, though still one county, were established as two separate boroughs. On January 1, 1914, the New York State Legislature created Bronx County and New York County was reduced to its present boundaries.[47]
20th century
[edit]
The construction of the New York City Subway, which opened in 1904, helped bind the new city together, as did additional bridges to Brooklyn. In the 1920s Manhattan experienced large arrivals of African-Americans as part of the Great Migration from the southern United States, and the Harlem Renaissance, part of a larger boom time in the Prohibition era that included new skyscrapers competing for the skyline. New York City became the most populous city in the world in 1925, overtaking London, which had reigned for a century.[48] Manhattan's majority white ethnic group declined from 98.7% in 1900 to 58.3% by 1990.[49]
On March 25, 1911, the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire in Greenwich Village killed 146 garment workers. The disaster eventually led to overhauls of the city's fire department, building codes, and workplace regulations.
The period between the World War I and World War II saw the election of reformist mayor Fiorello La Guardia and the fall of Tammany Hall after 80 years of political dominance.[50] As the city's demographics stabilized, labor unionization brought new protections and affluence to the working class, the city's government and infrastructure underwent a dramatic overhaul under La Guardia.

Despite the Great Depression, some of the world's tallest skyscrapers were completed in Manhattan during the 1930s, including numerous Art Deco masterpieces that are still part of the city's skyline, most notably the Empire State Building, the Chrysler Building, and the 30 Rockefeller Plaza.[51]
Returning World War II veterans created a postwar economic boom, which led to the development of huge housing developments targeted at returning veterans, the largest being Peter Cooper Village-Stuyvesant Town, which opened in 1947.[52] In 1951–1952, the United Nations relocated to a new headquarters the East Side of Manhattan.[53][54]
The Stonewall riots were a series of spontaneous, violent protests by members of the gay community against a police raid that took place in the early morning hours of June 28, 1969, at the Stonewall Inn in the Greenwich Village neighborhood of Lower Manhattan. They are widely considered to constitute the single most important event leading to the gay liberation movement[55][56] and the modern fight for LGBT rights.[57][58]
In the 1970s, job losses due to industrial restructuring caused New York City, including Manhattan, to suffer from economic problems and rising crime rates.[59] While a resurgence in the financial industry greatly improved the city's economic health in the 1980s, New York's crime rate continued to increase through the decade and into the beginning of the 1990s.[60]
The 1980s saw a rebirth of Wall Street, and Manhattan reclaimed its role at the center of the worldwide financial industry. The 1980s also saw Manhattan at the heart of the AIDS crisis, with Greenwich Village at its epicenter. The organizations Gay Men's Health Crisis (GMHC) and AIDS Coalition to Unleash Power (ACT UP) were founded to advocate on behalf of those stricken with the disease.
By the 1990s, crime rates started to drop dramatically due to revised police strategies, improving economic opportunities, gentrification, and new residents, both American transplants and new immigrants from Asia and Latin America. Murder rates that had reached 2,245 in 1990 plummeted to 537 by 2008, and the crack epidemic and its associated drug-related violence came under greater control.[61] The outflow of population turned around, as the city once again became the destination of immigrants from around the world, joining with low interest rates and Wall Street bonuses to fuel the growth of the real estate market.[62] Important new sectors, such as Silicon Alley, emerged in Manhattan's economy.
- The newly completed Singer Building towering above the city, 1909
- A construction worker atop the Empire State Building as it was being built in 1930; to the right is the Chrysler Building
- Aerial view of the tip of Lower Manhattan, 1931
- Lower East Side and Lower Manhattan skyline photographed using Agfacolor, 1938
- V-J Day in Times Square in Times Square, 1945
- The Stonewall Inn in Greenwich Village, a designated U.S. National Historic Landmark and National Monument, as the site of the June 1969 Stonewall riots and the cradle of the modern gay rights movement[55][63][64]
21st century
[edit]

On September 11, 2001, two of four hijacked planes were flown into the Twin Towers of the original World Trade Center, and the towers subsequently collapsed in the September 11 attacks launched by al-Qaeda terrorists. 7 World Trade Center collapsed due to fires and structural damage caused by heavy debris falling from the collapse of the Twin Towers. The other buildings within the World Trade Center complex were damaged beyond repair and soon after demolished. The collapse of the Twin Towers caused extensive damage to other surrounding buildings and skyscrapers in Lower Manhattan, and resulted in the deaths of 2,606 people, in addition to those on the planes. Many rescue workers and residents of the area developed several life-threatening illnesses that have led to some of their subsequent deaths.[66]
Since 2001, most of Lower Manhattan has been restored, although there has been controversy surrounding the rebuilding. A memorial at the site was opened to the public on September 11, 2011, and the museum opened in 2014. In 2014, the new One World Trade Center, at 1,776 feet (541 m) and formerly known as the Freedom Tower, became the tallest building in the Western Hemisphere,[67] while other skyscrapers were under construction at the site.
The Occupy Wall Street protests in Zuccotti Park in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan began on September 17, 2011, receiving global attention and spawning the Occupy movement against social and economic inequality worldwide.[68]
On October 29 and 30, 2012, Hurricane Sandy caused extensive destruction in the borough, ravaging portions of Lower Manhattan with record-high storm surge from New York Harbor,[69] severe flooding, and high winds, causing power outages for hundreds of thousands of city residents[70] and leading to gasoline shortages[71] and disruption of mass transit systems.[72][73][74][75] The storm and its profound impacts have prompted the discussion of constructing seawalls and other coastal barriers around the shorelines of the borough and the metropolitan area to minimize the risk of destructive consequences from another such event in the future.[76] Around 15 percent of the borough is considered to be in flood-risk zones.[77]
On October 31, 2017, a terrorist took a rental pickup truck and deliberately drove down a bike path alongside the West Side Highway in Lower Manhattan, killing eight people and injuring a dozen others before crashing into a school bus.[78]
See also
[edit]- History of education in New York City
- History of New York City
- Timeline of Brooklyn
- Timeline of the Bronx
- Timeline of Queens
- Timeline of Staten Island
References
[edit]- ^ a b Burrows, Edwin G.; Wallace, Mike (1998). Gotham : a history of New York City to 1898. Mike Wallace. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 6–7. ISBN 978-0-585-36462-9. OCLC 47011419.
- ^ "KINGSTON Discover 300 Years of New York History DUTCH COLONIES". National Park Service, U.S. Department of the Interior. Archived from the original on November 23, 2008. Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ "The Nine Capitals of the United States". United States Senate. Archived from the original on March 20, 2016. Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ "Statue of Liberty". World Heritage. UNESCO World Heritage Centre 1992–2011. Archived from the original on August 28, 2012. Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ Goddard, Ives (2010). "The Origin and Meaning of the Name "Manhattan"". New York History. 91 (4): 277–293. hdl:10088/16790. ISSN 0146-437X – via Smithsonian Research Online.
- ^ Juet, Robert (2006) [1625]. Juet's Journal of Hudson's 1609 Voyage, from the 1625 Edition of Purchas His Pilgrimes. Translated by Brea Barthel. p. 16. Archived from the original on July 3, 2016. Retrieved May 11, 2020.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ Holloway, Marguerite (May 16, 2004). "Urban tactics; I'll Take Mannahatta". The New York Times. Archived from the original on October 7, 2010. Retrieved June 30, 2009. "He could envision what Henry Hudson saw in 1609 as he sailed along Mannahatta, which in the Lenape dialect most likely meant island of many hills."
- ^ Goddard, Ives (2010). "The Origin and Meaning of the Name "Manhattan"" (PDF). The New York State Historical Association. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 26, 2018. Retrieved May 25, 2018.
- ^ Magazine, Smithsonian. "The True Native New Yorkers Can Never Truly Reclaim Their Homeland". Smithsonian Magazine. Retrieved June 29, 2022.
- ^ "The $24 Swindle", Nathaniel Benchley, American Heritage, 1959, Vol. 11, Issue 1
- ^ Cooke, Hope (1995). Seeing New York : history walks for armchair and footloose travelers. Philadelphia: Temple University Press. p. 63. ISBN 978-1-4399-0486-2. OCLC 646067836.
- ^ Aronson, Marc (2021). Four streets and a square : a history of Manhattan and the New York idea. Somerville. p. 22. ISBN 978-1-5362-0593-0. OCLC 1284998504.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ R. J. Knecht: Renaissance Warrior and Patron: The Reign of Francis I; p. 372. Cambridge University Press (1996) ISBN 0-521-57885-X
- ^ Seymour I. Schwartz: The Mismapping of America. p. 42; The University of Rochester Press (2008) ISBN 978-1-58046-302-7
- ^ Rankin, Rebecca B.; Cleveland Rodgers (1948). New York: the World's Capital City, Its Development and Contributions to Progress. Harper.
- ^ "Henry Hudson and His Exploration" Archived January 18, 2012, at the Wayback Machine Scientific American, September 25, 1909. Accessed May 1, 2007. "This was a vain hope however, and the conviction must finally have come to the heart of the intrepid adventurer that once again he was foiled in his repeated quest for the northwest passage ... On the following day the Half Moon let go her anchor inside of Sandy Hook. The week was spent in exploring the bay with a shallop, or small boat, and "they found a good entrance between two headlands" (the Narrows) "and thus entered on September 12 into as fine a river as can be found""
- ^ Dutch Colonies Archived May 19, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, National Park Service. Accessed May 19, 2007. "Sponsored by the West India Company, 30 families arrived in North America in 1624, establishing a settlement on present-day Manhattan."
- ^ a b GovIsland Park-to-Tolerance: through Broad Awareness and Conscious Vigilance Archived August 24, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, Tolerance Park. Accessed November 20, 2016. See Legislative Resolutions Senate No. 5476 and Assembly No. 2708.
- ^ City Seal and Flag Archived April 28, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, New York City. Accessed November 20, 2016. "Date: Beneath the horizontal laurel branch the date 1625, being the year of the establishment of New Amsterdam."
- ^ "Peter Schaghen Letter with transcription". New Netherland Institute. November 7, 1626. Archived from the original on March 24, 2016. Retrieved February 16, 2015.
- ^ a b Davis, Kenneth C. (2003). Don't Know Much About History: Everything You Need to Know About American History but Never Learned (1st ed.). New York: HarperCollins. p. 37. ISBN 978-0-06-008381-6.
- ^ Benchley, Nathaniel. "The $24 Swindle: The Indians who sold Manhattan were bilked, all right, but they didn't mind — the land wasn't theirs anyway." Archived November 28, 2018, at the Wayback Machine American Heritage, Vol. 11, no. 1 (December 1959).
- ^ Journal of New Netherland 1647. Written in the Years 1641, 1642, 1643, 1644, 1645, and 1646., Library of Congress. Accessed August 6, 2023. "The West India Company removed Kieft from his post in 1647 and replaced him with Peter Stuyvesant, the last director-general of New Netherland before the colony was taken over by the English in 1664."
- ^ About the Council Archived February 12, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, New York City Council. Accessed May 18, 2007.
- ^ New York State History Archived April 22, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, New York Department of State. Accessed June 29, 2009. "...named New York in honor of the Duke of York."
- ^ Griffis, William Elliot. "The Story of New Netherland" Chapter XV: The Fall of New Netherland, Houghton Mifflin Company, 1909. "In religious matters, Article VIII of the capitulation read, "The Dutch shall enjoy the liberty of their consciences in Divine worship and in Church government.""
- ^ Scheltema, Gajus and Westerhuijs, Heleen (eds.),Exploring Historic Dutch New York. Museum of the City of New York/Dover Publications, New York (2011). ISBN 978-0-486-48637-6
- ^ "The Inauguration of George Washington, 1789". Eyewitness to History. Ibis Communications, Inc. 2005. Archived from the original on January 10, 2013. Retrieved January 6, 2013.
- ^ Fort Washington Park Archived July 8, 2009, at the Wayback Machine, New York City Department of Parks and Recreation. Accessed May 18, 2007.
- ^ About Morristown Archived June 24, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, Town of Morristown. Accessed April 3, 2013. "Morristown became characterized as 'the military capital of the American Revolution' because of its strategic role in the war for independence from Great Britain."
- ^ Weig, Melvin J.; and Craig, Vera B. Morristown: A Military Capital of the American Revolution Archived July 7, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, National Park Service, 1950, reprinted 1961. Accessed July 19, 2011.
- ^ "Happy Evacuation Day" Archived October 5, 2008, at the Wayback Machine, New York City Department of Parks and Recreation, November 23, 2005. Accessed May 18, 2007.
- ^ The Nice Capitals of the United States Archived March 20, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. United States Senate Historical Office. Accessed June 9, 2005. Based on Fortenbaugh, Robert, The Nine Capitals of the United States, York, Pennsylvania: Maple Press, 1948...
- ^ "Birthplace of American Government". National Park Service. Archived from the original on September 12, 2014. Retrieved September 21, 2014.
- ^ Lynch, Jack. "Debating the Bill of Rights". Colonial Williamsburg Foundation. Archived from the original on July 5, 2014. Retrieved September 21, 2014.
- ^ "History & Culture – Federal Hall National Memorial". National Park Service. Archived from the original on August 31, 2014. Retrieved September 21, 2014.
- ^ Bridges, William (1811). Map of the City of New York and Island of Manhattan with Explanatory Remarks and References.
- ^ Lankevich (1998), pp. 67–68.
- ^ Dunlap, David W. (December 2010). "Last Time New York Had Just 27 House Seats? The City Was on the Rise". The New York Times. Archived from the original on September 24, 2014. Retrieved September 21, 2014.
- ^ Blair, Cynthia. "1858: Central Park Opens", Newsday. Accessed May 29, 2007. "Between 1853 and 1856, city commissioners purchased more than 700 acres (280 ha) from 59th Street to 106th Street between Fifth and Eighth Avenues to create Central Park, the nation's first public park [sic] as well as its first landscaped park." In actuality, Boston Common is the nation's first public park. Boston Common Archived December 26, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Thefreedomtrail.org.
- ^ Rybczynski, Witold. "Olmsted's Triumph" Archived December 26, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Smithsonian (magazine), July 2003. Accessed November 20, 2016. "By 1876, landscape designer Frederick Law Olmsted and architect Calvert Vaux had transformed the swampy, treeless 50 blocks between Harlem and midtown Manhattan into the first landscaped park in the United States."
- ^ Harris, Leslie M. "The New York City Draft Riots of 1863" excerpted from In the Shadow of Slavery: African Americans in New York City, 1626–1863 Archived June 29, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, University of Chicago Press. Accessed November 20, 2016.
- ^ Ward, Geoffrey C. "Gangs of New York" Archived July 16, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, a review of Paradise Alley by Kevin Baker, The New York Times, October 6, 2002. Accessed June 30, 2009. "The New York draft riots remain the worst civil disturbance in American history: according to the historian Adrian Cook, 119 people are known to have been killed, mostly rioters or onlookers who got too close when federal troops, brought back from the battlefield to restore order, started shooting."
- ^ Statue of Liberty Archived March 16, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, National Park Service. Accessed May 17, 2007.
- ^ "New Jerseyans' Claim To Liberty I. Rejected" Archived March 28, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, October 6, 1987. Accessed June 30, 2009. "The Supreme Court today refused to strip the Statue of Liberty of its status as a New Yorker. The Court, without comment, turned away a move by a two New Jerseyans to claim jurisdiction over the landmark for their state."
- ^ Macy Jr., Harry. Before the Five-Borough City: The Old Cities, Towns, and Villages That Came Together to Form "Greater New York" Archived September 27, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, New York Genealogical and Biographical Society from The NYG&B Newsletter, Winter 1998. Accessed April 29, 2007. "In 1683, when the Province of New York was first divided into counties, the City of New York also became New York County... In 1874, to accommodate this growth, New York City and County annexed from Westchester County what is now the western Bronx... In 1895 New York City annexed the eastern Bronx."
- ^ Gary Hermalyn and Ultan, Lloyd. Bronx History: A General Survey Archived July 2, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, New York Public Library. Accessed April 26, 2007.
- ^ Chase-Dunn, Christopher and Manning, Susan. "City systems and world-systems: Four millennia of city growth and decline" Archived July 16, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, University of California, Riverside Institute for Research on World-Systems. Accessed May 17, 2007. "New York, which became the largest city in the world by 1925, beating out London..."
- ^ "New York – Race and Hispanic Origin for Selected Cities and Other Places: Earliest Census to 1990". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on August 12, 2012. Retrieved May 6, 2012.
- ^ Allen, Oliver E. (1993). "Chapter 9: The Decline". The Tiger – The Rise and Fall of Tammany Hall. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0-201-62463-2.
- ^ "Skyscraper boom tied to market crash". Real Estate Weekly. February 19, 2014. Archived from the original on April 12, 2018. Retrieved April 11, 2018.
- ^ "Stuyvesant Town to Get Its First Tenants Today", The New York Times, August 1, 1947. p. 19
- ^ Associated Press (January 8, 1951). "UN MOVES INTO NEW BUILDING IN NYC TODAY" (PDF). Cortland Standard. p. 1. Retrieved December 21, 2017 – via Fultonhistory.com.
- ^ Rosenthal, A.M. (May 19, 1951). "U.N. Vacates Site at Lake Success; Peace Building Back to War Output" (PDF). The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved December 26, 2017.
- ^ a b Julia Goicichea (August 16, 2017). "Why New York City Is a Major Destination for LGBT Travelers". The Culture Trip. Archived from the original on April 28, 2019. Retrieved February 2, 2019.
- ^ "Brief History of the Gay and Lesbian Rights Movement in the U.S." University of Kentucky. Archived from the original on April 28, 2019. Retrieved September 2, 2017.
- ^ U.S. National Park Service (October 17, 2016). "Civil Rights at Stonewall National Monument". Department of the Interior. Archived from the original on May 27, 2019. Retrieved August 31, 2017.
- ^ "Obama inaugural speech references Stonewall gay-rights riots". North Jersey Media Group. January 21, 2013. Archived from the original on May 30, 2013. Retrieved July 20, 2014.
- ^ Allan Tannenbaum. "New York in the 70s: A Remembrance". The Digital Journalist. Archived from the original on March 20, 2012. Retrieved July 20, 2014.
- ^ Christopher Effgen (September 11, 2001). "New York Crime Rates 1960–2009". Disastercenter.com. Archived from the original on June 29, 2014. Retrieved July 20, 2014.
- ^ Harris, Paul. "How the mean streets of New York were tamed" Archived May 8, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, The Guardian, January 15, 2006. Accessed June 29, 2009. "Alongside the changed tactics came a fall in the crack epidemic that had swept the city in the Eighties. By the Nineties police had driven dealers off the streets, thus reducing drug-related violence.... The figures speak for themselves. In 1990, 2,245 New Yorkers were murdered. Last year the number was 537, the lowest for 40 years."
- ^ Hevesi, Dennis. "In Much of the City, A Robust Market" Archived March 28, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, March 16, 1997. Accessed June 29, 2009.
- ^ "Workforce Diversity The Stonewall Inn, National Historic Landmark National Register Number: 99000562". National Park Service, U.S. Department of the Interior. Archived from the original on March 6, 2016. Retrieved May 1, 2011.
- ^ Eli Rosenberg (June 24, 2016). "Stonewall Inn Named National Monument, a First for the Gay Rights Movement". The New York Times. Archived from the original on April 12, 2019. Retrieved June 25, 2016.
- ^ Mary Johnson (October 29, 2012). "VIDEO: Dramatic Explosion at East Village Con Ed Plant". DNA Info. Archived from the original on December 3, 2012. Retrieved December 2, 2012.
- ^ 9/11 World Trade Center Health Program: Toxins and Health Impacts, Centers for Disease Control. Accessed August 6, 2023. "These contaminants remained in Lower Manhattan and parts of Brooklyn for an undetermined amount of time after 9/11. Responders, local workers, residents, students, and others had potential for acute exposures in the early days and continuing exposure from residual materials—indoors and outside—as well as exposure to toxic gases, smoke, vapors, and combustion by-products from continuing fires."
- ^ Katia Hetter (November 12, 2013). "It's official: One World Trade Center to be tallest U.S. skyscraper". CNN. Archived from the original on November 12, 2013. Retrieved November 12, 2013.
- ^ "OccupyWallStreet — About". The Occupy Solidarity Network, Inc. Archived from the original on July 22, 2014. Retrieved July 20, 2014.
- ^ Long, Colleen & Peltz, Jennifer (October 30, 2012). "Water, fire and darkness: NYC after the superstorm". Associated Press. Archived from the original on December 27, 2012. Retrieved September 19, 2014.
- ^ "Gas Lines Pop Up Citywide As Relief Efforts Continue". NY1. November 3, 2012. Archived from the original on November 4, 2012. Retrieved November 4, 2012.
- ^ "Free Gas Draws Crowds In New York City; Gas Rationing Starts In New Jersey". NPR. November 3, 2012. Archived from the original on November 5, 2012. Retrieved November 5, 2012.
- ^ "Tracking Storm Sandy Recovery". Reuters. October 30, 2012. Archived from the original on October 30, 2012. Retrieved October 30, 2012.
- ^ Bhasin, Kim (October 30, 2012). "MTA: In 108 Years, The NYC Subway System Has Never Faced A Disaster As Devastating As This". Business Insider. Archived from the original on October 24, 2013. Retrieved September 19, 2014.
- ^ "Hurricane Sandy forces mass transit closure, evacuations". MyFoxNY. November 12, 2012. Archived from the original on October 29, 2012. Retrieved September 19, 2014.
- ^ Raw: Sandy Leaves NYC Subways Flooded on YouTube
- ^ Robert S. Eshelman (November 15, 2012). "Adaptation: Political support for a sea wall in New York Harbor begins to form". E&E Publishing. Archived from the original on February 5, 2013. Retrieved December 2, 2012.
- ^ "Irma spared America, but still had a big effect on it". The Economist. Archived from the original on September 26, 2017. Retrieved September 26, 2017.
- ^ "New York Terrorist Attack: Truck Driver Kills Eight in Lower Manhattan" Archived April 29, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, NBC News, November 1, 2017. Accessed November 1, 2017.
Further reading
[edit]- Burrows, Edwin G. and Wallace, Mike (1999). Gotham: A History of New York City to 1898. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-195-11634-8., The standard scholarly history, 1390pp onlibe review; Pulitzer Prize; excerpt
- Wallace, Mike. Greater Gotham: A History of New York City from 1898 to 1919 (2017) excerpt
- Burns, Ric, and James Sanders. New York: An Illustrated History (2003), book version of 17-hour Burns PBS documentary, "NEW YORK: A Documentary Film"
- Jackson, Kenneth T., ed. (1995). The Encyclopedia of New York City. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 0300055366.; second edition 2010
- Jackson, Kenneth T. and Roberts, Sam (eds.) The Almanac of New York City (2008)
- Jaffe, Steven H. New York at War: Four Centuries of Combat, Fear, and Intrigue in Gotham (2012) Excerpt and text search
- Lankevich, George J. New York City: A Short History (2002)
- Lockwood, Charles. Manhattan moves uptown: an illustrated history (Courier, 2014).
- Munn, Nancy D. "The "becoming-past" of places: Spacetime and memory in nineteenth-century, pre-Civil War New York: The Edward Westermarck Lecture, 2003." HAU: Journal of Ethnographic Theory 3.2 (2013): 359–380. online
- Roman, James. Chronicles of Old New York: Exploring Manhattan's Landmark Neighborhoods (Museyon, 2010).
- Rosner, David. A once charitable enterprise: Hospitals and health care in Brooklyn and New York 1885–1915 (Cambridge University Press, 2004).
- Scherzer, Kenneth A. The unbounded community: neighborhood life and social structure in New York City, 1830–1875 (Duke University Press, 1992).
- Taylor, Dorceta E. "Central Park as a model for social control: Urban parks, social class and leisure behavior in nineteenth-century America." Journal of leisure research 31.4 (1999): 420–477. online





![The Stonewall Inn in Greenwich Village, a designated U.S. National Historic Landmark and National Monument, as the site of the June 1969 Stonewall riots and the cradle of the modern gay rights movement[55][63][64]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/ce/Stonewall_Inn_5_pride_weekend_2016.jpg/180px-Stonewall_Inn_5_pride_weekend_2016.jpg)