APOA4
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
| APOA4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | APOA4, apolipoprotein A4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 107690 MGI: 88051 HomoloGene: 47927 GeneCards: APOA4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Apolipoprotein A-IV (also known as apoA-IV, apoAIV, or apoA4) is plasma protein that is the product of the human gene APOA4.[5][6]
Gene[edit]
APOA4 resides on chromosome 11 in close linkage to APOA1 and APOC3. APOA4 contains 3 exons separated by two introns, and is polymorphic, although most of the reported sequence polymorphisms occur in exon 3. The best validated and studied non-synonymous SNPs are a glutamine → histidine substitution at codon 360 and a threonine → serine substitution at codon 347; a sequence polymorphism has also been identified in the 3'UTR of the third exon.[7] Intra-species comparative gene sequence analysis suggests that the APOA4 gene arose from APOA1 by gene duplication approximately 270 MYA.[8]
Function[edit]
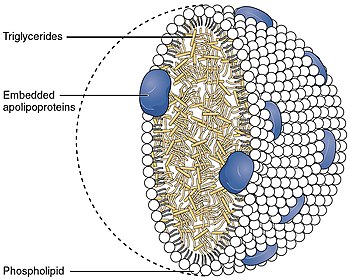
The primary translation product of the APOA4 gene is a 396-residue preprotein, which undergoes proteolytic processing to yield apo A-IV, a 376-residue mature O-linked glycoprotein. In most mammals, including humans, apo A-IV synthesis is confined to the intestine; however in mice and rats hepatic synthesis also occurs. Apo A-IV is secreted into circulation on the surface of newly synthesized chylomicron particles. Intestinal fat absorption dramatically increases the synthesis and secretion of apo A-IV. Although its primary function in human lipid metabolism has not been established, apo A-IV has been found to:
- activate lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase and cholesterylester transfer protein in vitro;
- play a role in the regulation of appetite and satiety in rodent models;
- display anti-oxidant and anti-atherogenic properties in vitro and in rodent models;
- modulate the efficiency of enterocyte and hepatic transcellular lipid transport in vitro.[7]
Human apo A-IV deficiency has not been reported.
Interactions[edit]
APOA4 has been shown to interact with GPLD1.[9]
Interactive pathway map[edit]
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
- ^ The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "Statin_Pathway_WP430".
References[edit]
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000110244 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000032080 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Karathanasis SK, Oettgen P, Haddad IA, Antonarakis SE (November 1986). "Structure, evolution, and polymorphisms of the human apolipoprotein A4 gene (APOA4)". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 83 (22): 8457–61. Bibcode:1986PNAS...83.8457K. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.22.8457. PMC 386949. PMID 3095836.
- ^ Elshourbagy NA, Walker DW, Paik YK, Boguski MS, Freeman M, Gordon JI, Taylor JM (June 1987). "Structure and expression of the human apolipoprotein A-IV gene". J. Biol. Chem. 262 (17): 7973–81. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)47513-8. PMID 3036793.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: APOA4 apolipoprotein A-IV".
- ^ Luo CC, Li WH, Moore MN, Chan L (February 1986). "Structure and evolution of the apolipoprotein multigene family". J. Mol. Biol. 187 (3): 325–340. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(86)90436-5. PMID 3084795.
- ^ Deeg, M A; Bierman E L; Cheung M C (March 2001). "GPI-specific phospholipase D associates with an apoA-I- and apoA-IV-containing complex". J. Lipid Res. 42 (3). United States: 442–51. doi:10.1016/S0022-2275(20)31669-2. ISSN 0022-2275. PMID 11254757.
Further reading[edit]
- von Eckardstein A, Funke H, Schulte M, et al. (1992). "Nonsynonymous polymorphic sites in the apolipoprotein (apo) A-IV gene are associated with changes in the concentration of apo B- and apo A-I-containing lipoproteins in a normal population". American Journal of Human Genetics. 50 (5): 1115–28. PMC 1682587. PMID 1349197.
- Kamboh MI, Williams ER, Law JC, et al. (1993). "Molecular basis of a unique African variant (A-IV 5) of human apolipoprotein A-IV and its significance in lipid metabolism". Genet. Epidemiol. 9 (6): 379–88. doi:10.1002/gepi.1370090602. PMID 1487136. S2CID 40107026.
- Lohse P, Kindt MR, Rader DJ, Brewer HB (1991). "Three genetic variants of human plasma apolipoprotein A-IV. apoA-IV-1(Thr347----Ser), apoA-IV-0(Lys167----Glu,Gln360----His), and apoA-IV-3(Glu165----Lys)". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (21): 13513–8. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)92728-6. PMID 1677358.
- Tenkanen H, Koskinen P, Metso J, et al. (1992). "A novel polymorphism of apolipoprotein A-IV is the result of an asparagine to serine substitution at residue 127". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1138 (1): 27–33. doi:10.1016/0925-4439(92)90147-f. PMID 1737067.
- Lohse P, Kindt MR, Rader DJ, Brewer HB (1990). "Human plasma apolipoproteins A-IV-0 and A-IV-3. Molecular basis for two rare variants of apolipoprotein A-IV-1". J. Biol. Chem. 265 (21): 12734–9. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)38406-6. PMID 1973689.
- Tenkanen H, Lukka M, Jauhiainen M, et al. (1991). "The mutation causing the common apolipoprotein A-IV polymorphism is a glutamine to histidine substitution of amino acid 360". Arterioscler. Thromb. 11 (4): 851–6. doi:10.1161/01.atv.11.4.851. PMID 2065039.
- de Temmerman P, Visvikis S, Boerwinkle E, Siest G (1990). "Study of the sequence tagged site (STS) in the beginning of human apo A4 gene region". Nucleic Acids Res. 18 (18): 5576. doi:10.1093/nar/18.18.5576. PMC 332267. PMID 2216752.
- Wei S, Rocchi M, Archidiacono N, et al. (1990). "Physical mapping of the human chromosome 11q23 region containing the ataxia-telangiectasia locus". Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 46 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1016/0165-4608(90)90002-R. PMID 2331673.
- Lohse P, Kindt MR, Rader DJ, Brewer HB (1990). "Genetic polymorphism of human plasma apolipoprotein A-IV is due to nucleotide substitutions in the apolipoprotein A-IV gene". J. Biol. Chem. 265 (17): 10061–4. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)38779-4. PMID 2351649.
- Yang CY, Gu ZW, Chong IS, et al. (1989). "The primary structure of human apolipoprotein A-IV". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1002 (2): 231–7. doi:10.1016/0005-2760(89)90292-0. PMID 2930771.
- Elshourbagy NA, Walker DW, Boguski MS, et al. (1986). "The nucleotide and derived amino acid sequence of human apolipoprotein A-IV mRNA and the close linkage of its gene to the genes of apolipoproteins A-I and C-III". J. Biol. Chem. 261 (5): 1998–2002. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)35888-X. PMID 3080432.
- Bisgaier CL, Sachdev OP, Lee ES, et al. (1987). "Effect of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase on distribution of apolipoprotein A-IV among lipoproteins of human plasma". J. Lipid Res. 28 (6): 693–703. doi:10.1016/S0022-2275(20)38666-1. PMID 3611972.
- Karathanasis SK, Yunis I, Zannis VI (1986). "Structure, evolution, and tissue-specific synthesis of human apolipoprotein AIV". Biochemistry. 25 (13): 3962–70. doi:10.1021/bi00361a034. PMID 3755616.
- Karathanasis SK (1985). "Apolipoprotein multigene family: tandem organization of human apolipoprotein AI, CIII, and AIV genes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 82 (19): 6374–8. Bibcode:1985PNAS...82.6374K. doi:10.1073/pnas.82.19.6374. PMC 390718. PMID 3931073.
- Gordon JI, Bisgaier CL, Sims HF, et al. (1984). "Biosynthesis of human preapolipoprotein A-IV". J. Biol. Chem. 259 (1): 468–74. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)43684-2. PMID 6706947.
- Menzel HJ, Dieplinger H, Sandholzer C, et al. (1995). "Apolipoprotein A-IV polymorphism in the Hungarian population: gene frequencies, effect on lipid levels, and sequence of two new variants". Hum. Mutat. 5 (1): 58–65. doi:10.1002/humu.1380050108. PMID 7728150. S2CID 3063305.
- Duverger N, Tremp G, Caillaud JM, et al. (1996). "Protection against atherogenesis in mice mediated by human apolipoprotein A-IV". Science. 273 (5277): 966–8. Bibcode:1996Sci...273..966D. doi:10.1126/science.273.5277.966. PMID 8688083. S2CID 30484255.
- Deeb SS, Nevin DN, Iwasaki L, Brunzell JD (1997). "Two novel apolipoprotein A-IV variants in individuals with familial combined hyperlipidemia and diminished levels of lipoprotein lipase activity". Hum. Mutat. 8 (4): 319–25. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1996)8:4<319::AID-HUMU4>3.0.CO;2-2. PMID 8956036. S2CID 19100488.
External links[edit]
- Apolipoprotein+A-IV at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Human APOA4 genome location and APOA4 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.