List of COVID-19 vaccine authorizations
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
National regulatory authorities have granted full or emergency use authorizations for 40 COVID-19 vaccines.
Ten vaccines have been approved for emergency or full use by at least one stringent regulatory authority recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO): Pfizer–BioNTech, Oxford–AstraZeneca, Sinopharm BIBP, Moderna, Janssen, CoronaVac, Covaxin, Novavax, Convidecia, and Sanofi–GSK.[1] Seven others are under assessment by the WHO: Sputnik V, Sinopharm WIBP, Abdala, Zifivax, Corbevax, COVIran Barekat, and SCB-2019.[2]
Of the 40 vaccines, 16 have a full or emergency authorization in only one country, 12 in ten or fewer countries, and 12 in more than ten countries.
Note that in some countries, vaccines may be authorized solely for travel purposes. They may not be approved for the general population. For example, the CoronaVac, Covishield, BBIBP-CorV and Covaxin vaccines are not part of Australia's national vaccination program; however, they are recognized for the purpose of travel to Australia.[3][4][5]
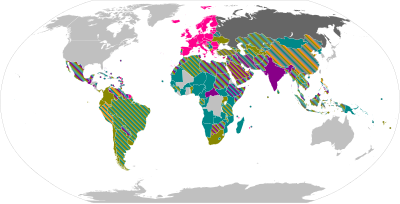
Overview maps[edit]
|
Oxford–AstraZeneca[edit]
Full authorization Emergency authorization Allowed for travel Eligible COVAX recipient Usage stopped | |||
The Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine, sold under the brand names Vaxzevria[6] and Covishield,[7] is a viral vector vaccine[8] produced by the British University of Oxford, British-Swedish company AstraZeneca, and the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations.[8][9][10] Finland, Denmark, and Norway suspended the use of the Oxford–AstraZeneca vaccine due to a small number of reports of a rare blood clot disorder.[11][12][13][14] Slovakia suspended its use after the death of a predisposed recipient.[15] South Africa suspended its use because a small trial found only minimal protection against mild to moderate disease from the locally predominant Beta variant.[16] Japan approved the vaccine for emergency use in May 2021, but did not plan to use them immediately because of rare cases of a blood clotting disorder reported overseas.[17] Later, Japan started to use the vaccine for people aged 40 or over to mitigate the surge of the Delta variant in August.[18] Finland ceased use of the vaccine as the last batch expired on 30 November 2021. Until then it was only offered for those aged 65 or more due to extremely rare coagulation disorders among younger recipients of the vaccine. After this Finland will not procure more of the vaccine.[19][20][21][22] The AstraZeneca vaccine is the most widely accepted internationally,[23] and the most popular in terms of total inoculated worldwide, over 1.3 billion.[24][25][26][27] The AstraZeneca vaccine is administered in more countries than any other vaccine.[28]
- Full (5)
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Emergency (170)
- Afghanistan[40][41]
- Albania[42]
- Algeria[43]
- Andorra[44]
- Angola[45]
- Argentina[46]
- Armenia[47]
- Azerbaijan[48]
- Bahrain[49]
- Bangladesh[50][51]
- Benin[48]
- Bhutan[52][53]
- Bolivia[48]
- Bosnia and Herzegovina[54]
- Botswana[55]
- Brunei[56]
- Burkina Faso[57]
- Cambodia[48]
- Cameroon[48]
- Cape Verde[58]
- Central African Republic[57]
- Chile[59]
- Colombia[60]
- Comoros[48]
- Congo-Brazzaville[48]
- Congo-Kinshasa[61]
- Costa Rica[62]
- Djibouti[48]
- Dominican Republic[63]
- East Timor[64]
- Ecuador[65]
- Egypt[66]
- El Salvador[67]
- Eswatini[68]
- Ethiopia[69][70][71]
- Fiji[48]
- Gambia[72]
- Georgia[73]
- Ghana[74]
- Guatemala[75]
- Guinea-Bissau[76]
- Guinea[57]
- Honduras[48]
- Indonesia[77]
- Iran[78]
- Iraq[79]
- Ivory Coast[80]
- Japan[81]
- Jordan[82]
- Kenya[83]
- Kiribati[57]
- Kosovo[84][85]
- Kuwait[86]
- Kyrgyzstan[57]
- Laos[57]
- Lebanon[87]
- Lesotho[88]
- Liberia[89]
- Libya[90][91]
- Madagascar[48]
- Malawi[92][93]
- Malaysia[94]
- Maldives[95]
- Mali[96]
- Mauritania[57]
- Mauritius[97]
- Mexico[98]
- Micronesia[57]
- Moldova[99]
- Mongolia[100]
- Montenegro[48]
- Morocco[101]
- Mozambique[48]
- Myanmar[102]
- Namibia[103]
- Nauru[104]
- Nepal[105]
- New Zealand[57]
- Nicaragua[48]
- Niger[48]
- Nigeria[106]
- North Macedonia[107]
- Oman[48]
- Pakistan[108]
- Palestine[48]
- Panama[48]
- Papua New Guinea[109][110]
- Paraguay[57]
- Peru[111]
- Philippines[112]
- Qatar[57]
- Rwanda[113]
- Samoa[104]
- São Tomé and Príncipe[48]
- Saudi Arabia[114]
- Senegal[57]
- Serbia[115]
- Seychelles[116]
- Sierra Leone[117]
- Singapore[118] (restricted)
- Solomon Islands[48]
- Somalia[119]
- South Korea[120][121]
- South Sudan[122]
- Sri Lanka[123]
- Sudan[124][125]
- Syria[57]
- Taiwan[126]
- Tajikistan[127]
- Thailand[128]
- Togo[129]
- Tonga[130][131][132]
- Tunisia[57]
- Turkmenistan[57]
- Tuvalu[104]
- Uganda[133]
- Ukraine[134]
- United Arab Emirates[48]
- United Kingdom[135][136][137]
- Uruguay[48]
- Uzbekistan[48]
- Vanuatu[57]
- Vietnam[138]
- Yemen[139]
- Zambia[140][141][142]
- Zimbabwe[57]
CARPHA countries and entities[143]
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Belize
- Dominica
- Grenada
- Guyana
- Haiti
- Jamaica
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Suriname[144]
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Anguilla
- Aruba
- British Virgin Islands
- Bermuda
- Caribbean Netherlands
- Cayman Islands
- Curaçao
- Montserrat
- Sint Maarten
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- Cook Islands[48]
- Falkland Islands[48]
- French Polynesia[48]
- Greenland[145]
- Guadeloupe[57]
- Guernsey[48]
- Isle of Man[48]
- Jersey[48]
- Northern Cyprus[146]
- Pitcairn[57]
- Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha[57]
- Wallis and Futuna[48]
- World Health Organization[147][2][148][149][150][151]
- Travel-only
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
Pfizer–BioNTech[edit]
| |||
The Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, sold under the brand name Comirnaty,[37] is an mRNA vaccine[156] produced by the German company BioNTech and the American company Pfizer.[156][157][158] In Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan, Comirnaty is distributed by Fosun Pharma.[159][160][161][162][163][164]
Original[edit]
- Full (39)
- Australia[165][166]
- Brazil[167]
- Canada[168][169]
- Marshall Islands[a][b]
- Micronesia[a][b]
- New Zealand[170]
- Palau[a][b]
- Saudi Arabia[173][145]
- Switzerland[174][175]
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Emergency (145)
- Afghanistan[48]
- Albania[178]
- Algeria[179]
- Andorra[180]
- Argentina[181]
- Armenia[182]
- Azerbaijan[57]
- Bahrain[183][184]
- Bangladesh[185]
- Benin[57]
- Bhutan[57]
- Bolivia[48]
- Bosnia and Herzegovina[54]
- Botswana[186]
- Brunei[56]
- Cambodia[57]
- Cameroon[57]
- Cape Verde[48]
- Chile[187]
- China (For German citizens)[188]
- Colombia[189]
- Congo-Kinshasa[190]
- Costa Rica[191]
- Djibouti[57]
- Dominican Republic[192]
- East Timor[57]
- Ecuador[193]
- Egypt[57]
- El Salvador[48][194]
- Eswatini[57]
- Fiji[195]
- Gabon[57]
- Georgia[57]
- Ghana[196]
- Guatemala[75]
- Guinea[57]
- Honduras[57]
- Indonesia[197]
- Iraq[198]
- Israel[199]
- Ivory Coast[57]
- Japan[81][200][201]
- Jordan[202]
- Kazakhstan[57]
- Kenya[203]
- Kosovo[57]
- Kuwait[204]
- Kyrgyzstan[57]
- Laos[57]
- Lebanon[205]
- Libya[48]
- Malawi[206]
- Malaysia[207]
- Maldives[208]
- Mexico[209][210]
- Moldova[99]
- Monaco[211]
- Mongolia[212]
- Montenegro[57]
- Morocco[57]
- Namibia[57]
- Nepal[213]
- Nicaragua[57]
- Nigeria[214]
- North Macedonia[215]
- Oman[216]
- Pakistan[217]
- Palestine[48]
- Panama[218]
- Papua New Guinea[219]
- Paraguay[220][221]
- Peru[222]
- Philippines[223]
- Qatar[224]
- Rwanda[48]
- Samoa[57]
- San Marino[48]
- Serbia[225][226]
- Singapore[227]
- Somalia[57]
- South Africa[228][229]
- South Korea[230][231]
- Sri Lanka[232]
- Sudan[48]
- Syria[57]
- Taiwan[163][164]
- Tajikistan[57]
- Tanzania[57]
- Thailand[233]
- Tonga[57]
- Tunisia[145]
- Turkey[234]
- Uganda[57]
- Ukraine[235]
- United Arab Emirates[236]
- United Kingdom[237][238][239]
- Uruguay[240]
- Uzbekistan[241]
- Vatican City[242][243]
- Vietnam[244]
- Yemen[57]
- Zambia[245]
CARPHA countries and entities[246][247]
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Belize
- Dominica
- Grenada
- Guyana
- Haiti
- Jamaica
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Suriname
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Anguilla
- Aruba
- British Virgin Islands
- Bermuda
- Caribbean Netherlands
- Cayman Islands
- Curaçao
- Montserrat
- Sint Maarten
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- American Samoa[57]
- Cook Islands[57]
- Faroe Islands[248]
- French Polynesia[57]
- Gibraltar[48]
- Greenland[249]
- Guadeloupe[57]
- Guam[57]
- Guernsey[48]
- Isle of Man[48]
- Jersey[48]
- Macau[250]
- Martinique[57]
- New Caledonia[48]
- Niue[57]
- Northern Cyprus[146]
- Northern Mariana Islands[57]
- Puerto Rico[57]
- Tokelau[57]
- World Health Organization[147][2][251][252]
Bivalent original–BA.1[edit]
- Japan[citation needed]
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
Bivalent original–BA.4/5[edit]
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Hong Kong[255]
- Macau[256]
- World Health Organization[147]
XBB.1.5[edit]
- United States[257]
Janssen[edit]
Full authorization Full authorization, not used Emergency authorization Allowed for travel Eligible COVAX recipient Usage stopped | |||
The Janssen COVID-19 vaccine[258] is a viral vector vaccine[259] produced by Janssen Pharmaceutica (a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson) and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.[260][261] It is also known as Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 Vaccine and as COVID-19 Vaccine Janssen.[262] Three countries, Denmark, Finland, and Norway, discontinued the use of the Janssen vaccine in favor of other available vaccines due to a possible link between the vaccine and a rare blood clot disorder.[263][19][264] The use of the Janssen adenovirus vector vaccine began in Finland in October 2021. It is only offered for those aged 65 and over because of a very rare risk of thrombosis in younger age groups.[20][22][21] The United States began use of the Janssen vaccine in March 2021,[265] but discouraged use in favor of other available vaccines in December 2021 due to the risk of a rare clotting disorder.[266] The Janssen vaccine became unavailable in the United States in May 2023 after all existing doses expired.[267]
- Full (3)
- Emergency (133)
- Afghanistan[57]
- Andorra[44]
- Argentina[274]
- Bahamas[275]
- Bahrain[276][277]
- Bangladesh[278][279]
- Benin[57]
- Bolivia[57]
- Botswana[280]
- Brazil[281]
- Brunei[57]
- Burkina Faso[57]
- Cambodia[57]
- Cameroon[57]
- Central African Republic[245]
- Chile[282]
- Colombia[283]
- Congo-Kinshasa[190]
- Djibouti[57]
- Egypt[57]
- Eswatini[57]
- Ethiopia[57]
- Gabon[245]
- Ghana[284]
- Guinea[57]
- Honduras[48]
- India[285]
- Indonesia[286]
- Iran[245]
- Iraq[57]
- Ivory Coast[57]
- Jordan[57]
- Kenya[203]
- Kuwait[287]
- Laos[57]
- Lebanon[57]
- Lesotho[57]
- Liberia[245]
- Libya[48]
- Madagascar[57]
- Malawi[57]
- Malaysia[288]
- Maldives[289]
- Mali[245]
- Marshall Islands[a]
- Mauritania[245]
- Mexico[290][291]
- Micronesia[a]
- Moldova[292]
- Monaco[57]
- Morocco[57]
- Mozambique[57]
- Namibia[57]
- Nepal[293]
- New Zealand[57]
- Nicaragua[57]
- Nigeria[294]
- Oman[57]
- Pakistan[57]
- Palau[a]
- Palestine[57]
- Papua New Guinea[57]
- Peru[295]
- Philippines[296]
- Qatar[57]
- Rwanda[57]
- Saudi Arabia[57]
- Senegal[57]
- Singapore[118] (restricted)
- Somalia[57]
- South Africa[297]
- South Korea[298]
- South Sudan[57]
- Sudan[57]
- Syria[57]
- Taiwan (not used)[299]
- Tanzania[57]
- Thailand[300]
- Tunisia[301]
- Uganda[57]
- Ukraine[57]
- United Arab Emirates[57]
- United Kingdom[302]
- United States[265][303] (no longer available as of May 7, 2023 [267])
- Vanuatu[57]
- Vietnam[304][305]
- Yemen[57]
- Zambia[140][141][142]
- Zimbabwe[306]
EMA countries[262][38][307][1]
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
CARPHA countries and entities[308]
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Belize
- Dominica
- Grenada
- Guyana
- Haiti
- Jamaica
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines[309]
- Suriname
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Anguilla
- Aruba
- British Virgin Islands
- Bermuda
- Caribbean Netherlands
- Cayman Islands
- Curaçao
- Montserrat
- Sint Maarten
- Turks and Caicos Islands
Non-country entities
- American Samoa[57]
- French Polynesia[57]
- Greenland[145]
- Guam[57]
- New Caledonia[57]
- Northern Cyprus[310]
- Northern Mariana Islands[57]
- Puerto Rico[57]
- Africa Regulatory Taskforce[311]
- World Health Organization[147][312][313]
- Travel-only
- Hong Kong[152]
- Japan[314]
- Turkey[315][unreliable source?]
Moderna[edit]
| |||
The Moderna COVID-19 vaccine, also known as Spikevax,[316] is an mRNA vaccine[317] produced by the American company Moderna, the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the U.S. Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, and the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations.[318][319] The Moderna vaccine is not offered for men under 30 years of age in Finland as a precaution to reduce a very rare risk of myocarditis.[320][22]
Original[edit]
- Full (34)
EMA countries[316][38][328][1]
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Emergency (116)
- Andorra[44]
- Argentina[329]
- Armenia[57]
- Bahrain[57]
- Bangladesh[330]
- Bhutan[57]
- Botswana[331]
- Bolivia[332]
- Brazil[333]
- Brunei[57]
- Cape Verde[57]
- Chile[334]
- Colombia[335]
- Congo-Brazzaville[48]
- Congo-Kinshasa[190]
- Djibouti[57]
- Egypt[336]
- El Salvador[57]
- Fiji[57]
- Ghana[337]
- Guatemala[75]
- Honduras[338]
- India[339]
- Indonesia[340]
- Iran[57]
- Iraq[57]
- Israel[341]
- Japan[81][342]
- Jordan[57]
- Kenya[343]
- Kuwait[344]
- Kyrgyzstan[57]
- Lebanon[57]
- Libya[48]
- Malawi[206]
- Malaysia[345]
- Maldives[346]
- Marshall Islands[a]
- Mexico[347][348]
- Micronesia[a]
- Moldova[292]
- Monaco[57]
- Mongolia[100]
- Morocco[57]
- Nepal[349]
- Nigeria[350]
- Oman[57]
- Pakistan[57]
- Palau[a]
- Palestine[48]
- Paraguay[57]
- Peru[351]
- Philippines[352]
- Qatar[353]
- Rwanda[48]
- Saudi Arabia[114]
- Serbia[354]
- Singapore[355]
- South Korea[356]
- Sri Lanka[57]
- Sudan[57]
- Syria[57]
- Taiwan[357]
- Tajikistan[358]
- Thailand[359]
- Tunisia[57]
- Uganda[57]
- Ukraine[360]
- United Arab Emirates[361]
- Uzbekistan[362]
- Vietnam[363][364]
- Yemen[57]
CARPHA countries and entities[246][308]
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Belize
- Dominica
- Grenada
- Guyana
- Haiti
- Jamaica
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Suriname
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Anguilla
- Aruba
- British Virgin Islands
- Bermuda
- Caribbean Netherlands
- Cayman Islands
- Curaçao
- Montserrat
- Sint Maarten
- Turks and Caicos Islands
Non-country entities
- American Samoa[57]
- Faroe Islands[48]
- Greenland[48]
- Guadeloupe[57]
- Guam[57]
- Guernsey[48]
- Isle of Man[57]
- Jersey[48]
- Northern Mariana Islands[57]
- Puerto Rico[57]
- Wallis and Futuna[57]
- World Health Organization[147][365][366]
- Travel-only
Bivalent original–BA.1[edit]
- Australia[368]
- Canada[322][369]
- Japan[citation needed]
- Singapore[370]
- Switzerland[371]
- Taiwan[372][373]
- United Kingdom[374]
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
Bivalent original–BA.4/5[edit]
- Taiwan[376]
XBB.1.5[edit]
- United States[377]
Sinopharm BIBP[edit]
| |||
The Sinopharm BIBP COVID-19 vaccine is an inactivated virus vaccine produced by the China National Pharmaceutical Group (Sinopharm) and its Beijing Institute of Biological Products.[378][379]
- Full (4)
- Emergency (111)
- Afghanistan[385]
- Algeria[386]
- Angola[387]
- Argentina[388]
- Armenia[57]
- Bangladesh[389]
- Belarus[390]
- Bhutan[391]
- Bolivia[392]
- Bosnia and Herzegovina[393]
- Brazil[333]
- Brunei[394]
- Burkina Faso[57]
- Burundi[57]
- Cambodia[395]
- Cameroon[48]
- Cape Verde[57]
- Chad[396]
- Comoros[48]
- Congo-Brazzaville[48]
- Cuba[397]
- Djibouti[48]
- Dominican Republic[398]
- Egypt[399]
- El Salvador[57]
- Equatorial Guinea[400]
- Ethiopia[401]
- Gabon[402]
- Gambia[57]
- Georgia[403]
- Guinea-Bissau[48]
- Guinea[57]
- Hungary[404][405]
- Indonesia[406]
- Iran[407]
- Iraq[79]
- Ivory Coast[57]
- Jordan[408]
- Kazakhstan[409]
- Kenya[343]
- Kiribati[57]
- Kuwait[48]
- Kyrgyzstan[410]
- Laos[411]
- Lebanon[412]
- Lesotho[57]
- Libya[413]
- Madagascar[57]
- Malawi[414]
- Malaysia[415]
- Maldives[416]
- Mauritania[417]
- Mauritius[48]
- Mexico[418][419]
- Moldova[420]
- Mongolia[421]
- Montenegro[422]
- Morocco[423]
- Mozambique[424]
- Myanmar[425]
- Namibia[426]
- Nepal[427]
- Nicaragua[428]
- Niger[429]
- Nigeria[430]
- North Korea[431]
- North Macedonia[432]
- Oman[48]
- Pakistan[433]
- Palestine[434]
- Papua New Guinea[435]
- Paraguay[57]
- Peru[436]
- Philippines[437]
- Qatar[48]
- Rwanda[438]
- Senegal[439]
- Serbia[440]
- Sierra Leone[441]
- Singapore[442]
- Solomon Islands[443]
- Somalia[444]
- South Sudan[445]
- Sri Lanka[446]
- Sudan[447][448]
- Syria[57]
- Tanzania[57]
- Thailand[449]
- Tunisia[450]
- Turkmenistan[451]
- Vanuatu[452]
- Venezuela[453]
- Vietnam[454]
- Yemen[48]
- Zambia[455]
- Zimbabwe[456]
CARPHA countries and entities[457]
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Belize
- Dominica
- Grenada
- Guyana
- Haiti
- Jamaica
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Suriname
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Anguilla
- Aruba
- British Virgin Islands
- Bermuda
- Caribbean Netherlands
- Cayman Islands
- Curaçao
- Montserrat
- Sint Maarten
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- Travel-only
- Andorra[461]
- Australia[462][463]
- Austria[464] (only for entry)
- Bulgaria[465]
- Canada[466]
- Chile[467]
- Costa Rica[468]
- Croatia[469]
- Cyprus[470]
- Czech Republic[471] (only for Hungarian citizens and EU nationals vaccinated in Hungary)
- Estonia[472] (only if approved in a person's country of origin)
- Finland[473]
- Greece[474]
- Grenada[475]
- Hong Kong[152]
- Iceland[476]
- Ireland[477]
- Japan[314]
- Latvia[478]
- Liechtenstein[479]
- New Zealand[367]
- Oman[480]
- Panama[481]
- Portugal[482] (only in Madeira)
- Qatar[483]
- Saudi Arabia (for short visits, Hajj and Umrah only)[484]
- Slovakia[485]
- Slovenia[486]
- South Korea[487]
- Spain[488]
- St. Kitts and Nevis[489]
- St. Lucia[490]
- St. Vincent and the Grenadines[491]
- Sweden[492]
- Switzerland[493]
- The Netherlands[494]
- Turkey[495]
- Ukraine[496]
- United Kingdom[497]
- United States[498]
- Uruguay[499] (only if approved in a person's country of origin)
Sputnik V[edit]
Full authorization Emergency authorization Authorization expired Allowed for travel Rejected | |||
The Sputnik V COVID-19 vaccine is a viral vector vaccine[500] produced by the Russian Gamaleya Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology.
- Full (3)
- Emergency (76)
- Albania[42]
- Algeria[506]
- Angola[507]
- Antigua and Barbuda[508]
- Argentina[509]
- Armenia[510]
- Azerbaijan[511][512]
- Bahrain[513]
- Bangladesh[514]
- Belarus[515]
- Bolivia[516]
- Bosnia and Herzegovina[517]
- Brazil[518] (restricted)
- Cambodia[519]
- Cameroon[520]
- Chile[521]
- Congo-Brazzaville[507]
- Djibouti[507]
- Ecuador[522]
- Egypt[66]
- Gabon[523]
- Gambia[524]
- Ghana[525]
- Guatemala[526]
- Guinea[527]
- Guyana[528]
- Honduras[529]
- Hungary[530][517][405]
- India[531]
- Indonesia[532]
- Iran[533]
- Iraq[534]
- Ivory Coast[57]
- Jordan[535]
- Kazakhstan[536]
- Kenya[537]
- Kyrgyzstan[538]
- Laos[411]
- Lebanon[539]
- Libya[90][91]
- Maldives[540]
- Mali[541]
- Mauritius[542]
- Mexico[543]
- Moldova[99]
- Mongolia[544]
- Montenegro[545]
- Morocco[546]
- Myanmar[547]
- Namibia[548]
- Nepal[549]
- Nicaragua[550]
- Nigeria[551]
- North Macedonia[552]
- Oman[553]
- Pakistan[554]
- Palestine[555]
- Panama[556]
- Paraguay[557]
- Peru[558]
- Philippines[559]
- Rwanda[57]
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines[309]
- San Marino[560][561]
- Serbia[562]
- Seychelles[563]
- Sri Lanka[564]
- Syria[565]
- Tajikistan[57]
- Tanzania[566]
- Tunisia[567]
- Turkey (limited use)[568][569]
- United Arab Emirates[570]
- Venezuela[571]
- Vietnam[572]
- Zimbabwe[573]
- Expired
- Rejected
- Travel-only
CoronaVac[edit]
| |||
The CoronaVac COVID-19 vaccine is an inactivated virus vaccine[590] produced by the Chinese company Sinovac Biotech.[590][591][592]
- Full (1)
- China[593]
- Emergency (71)
- Afghanistan[48]
- Albania[42]
- Algeria[57]
- Argentina[245]
- Armenia[595]
- Azerbaijan[596]
- Bangladesh[597]
- Benin[598]
- Bolivia[599]
- Bosnia and Herzegovina[600]
- Botswana[601]
- Brazil[602]
- Cambodia[603]
- Chile[604]
- Colombia[605]
- Djibouti[606]
- Dominica[145]
- Dominican Republic[607]
- East Timor[608]
- Ecuador[609]
- Egypt[610]
- El Salvador[611]
- Equatorial Guinea[57]
- Fiji[612]
- Gabon[145]
- Georgia[613]
- Guinea[614]
- Guyana[145]
- Hungary[57]
- Indonesia[615][616]
- Iraq[48]
- Jordan[48]
- Kazakhstan[617]
- Kuwait[48]
- Laos[593]
- Lebanon[48]
- Libya[618]
- Malawi[414]
- Malaysia[619]
- Maldives[57]
- Mexico[620]
- Moldova[621]
- Morocco[145]
- Myanmar[622]
- Nepal[623]
- North Macedonia[624]
- Oman[553]
- Pakistan[625]
- Palestine[57]
- Panama[626]
- Paraguay[627]
- Philippines[628]
- Qatar[48]
- Rwanda[57]
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines[145]
- Saudi Arabia[629]
- Singapore[630]
- Somalia[48]
- South Africa[631]
- Sri Lanka[632]
- Sudan[48]
- Syria[57]
- Tajikistan[633]
- Tanzania[634]
- Thailand[635]
- Togo[636]
- Trinidad and Tobago[637]
- Tunisia[638]
- Turkey[639]
- Turkmenistan[640]
- Uganda[57]
- Ukraine[641]
- United Arab Emirates[48]
- Uruguay[593]
- Uzbekistan[642]
- Venezuela[643]
- Yemen[57]
- Zimbabwe[573]
- Travel-only
- Andorra[461]
- Australia[462][647]
- Austria[464] (only for entry)
- Canada[466]
- Costa Rica[468]
- Croatia[469]
- Cyprus[470]
- Estonia[472] (only if approved in a person's country of origin)
- Finland[473]
- Greece[474]
- Grenada[475]
- Iceland[476]
- Ireland[477]
- Japan[314]
- Liechtenstein[479]
- Norway[648]
- New Zealand[367]
- Norway[649]
- Palau[650]
- Panama[481]
- Portugal[482] (only in Madeira)
- Slovakia[485]
- Slovenia[486]
- South Korea[487]
- Spain[488]
- St. Kitts and Nevis[489]
- St. Lucia[490]
- St. Vincent and the Grenadines[491]
- Sweden[492]
- Switzerland[493]
- The Netherlands[494]
- Ukraine[496]
- United Arab Emirates[651]
- United Kingdom[497]
- United States[498]
- Vietnam[652]
Novavax[edit]
| |||
The Novavax COVID-19 vaccine, sold under the brand names Nuvaxovid and Covovax, is a subunit COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Novavax and the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations.[653][654]
- Full (4)
- Emergency (57)
- Bangladesh[660]
- India[661]
- Indonesia[662]
- Monaco[57]
- New Zealand[663]
- Philippines[664]
- Singapore[665]
- South Africa[245]
- Switzerland[666]
- Thailand[667]
- Taiwan[668]
- United Kingdom[669]
- United States[670][671]
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
CARPHA countries and entities[245][673]
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Belize
- Dominica
- Grenada
- Guyana
- Haiti
- Jamaica
- Saint Kitts and Nevis[489]
- Saint Lucia[490]
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines[491]
- Suriname
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Anguilla
- Aruba
- British Virgin Islands
- Bermuda
- Caribbean Netherlands
- Cayman Islands
- Curaçao
- Montserrat
- Sint Maarten
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- Travel-only
Covaxin[edit]
| |||
Covaxin is an inactivated virus vaccine produced by the Indian company Bharat Biotech in collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research–National Institute of Virology.
- Full (1)
- India[34]
- Emergency (50)
- Afghanistan[48]
- Bahrain[48][676]
- Botswana[48][677]
- Central African Republic[48]
- Comoros[48]
- Egypt[48]
- Ethiopia[48][57]
- Guatemala[677] (not used)[678]
- Iran[48][679]
- Iraq[48]
- Jordan[48]
- Kuwait[48]
- Lebanon[48]
- Libya[48]
- Malaysia[680]
- Mauritius[681]
- Mexico[682] (not used)[678]
- Morocco[48]
- Myanmar[683]
- Nepal[48][684]
- Nicaragua[677] (not used)[678]
- Oman[48]
- Pakistan[48]
- Paraguay[48][685][686]
- Philippines[687][688]
- Qatar[48]
- Somalia[48]
- Sudan[48]
- Syria[48]
- Tunisia[48]
- United Arab Emirates[48]
- Venezuela[677] (not used)[678]
- Vietnam[689]
- Yemen[48]
- Zimbabwe[690]
CARPHA countries and entities[245][673]
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Belize
- Dominica
- Grenada[475]
- Guyana[677] (not used)[678]
- Haiti
- Jamaica
- Saint Kitts and Nevis[489]
- Saint Lucia[490]
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines[491]
- Suriname
- Trinidad and Tobago[637]
- Anguilla
- Aruba
- British Virgin Islands
- Bermuda
- Caribbean Netherlands
- Cayman Islands
- Curaçao
- Montserrat
- Sint Maarten
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- Travel-only
- Andorra[461]
- Australia[462][463]
- Austria[464] (only for entry)
- Canada[466]
- Costa Rica[468]
- Croatia[469]
- Cyprus[470]
- Estonia[472] (only if approved in a person's country of origin)
- Finland[473]
- Greece[474]
- Hong Kong[152]
- Iceland[476]
- Ireland[477]
- Japan[314]
- Kyrgyzstan[681]
- Liechtenstein[479]
- Mongolia[681]
- New Zealand[367]
- Norway[649]
- Oman[480]
- Palestine[681]
- Palau[650]
- Panama[481]
- Portugal[482] (only in Madeira)
- Saudi Arabia[693]
- Singapore[118]
- Slovakia[485]
- Slovenia[486]
- South Korea[487]
- Spain[488]
- Sri Lanka[694]
- Sweden[492]
- Switzerland[493]
- Thailand[695]
- The Netherlands[494]
- Turkey[495]
- Ukraine[496]
- United Kingdom[497]
- United States[498]
VLA2001[edit]
Full authorization Emergency authorization Allowed for travel | |||
VLA2001 is an inactivated vaccine developed by Valneva SE and Dynavax Technologies.
- Full (1)
- United Kingdom[696]
- Emergency (32)
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Travel-only
Sanofi–GSK[edit]
The Sanofi–GSK COVID-19 vaccine, sold under the brand name VidPrevtyn Beta, is a subunit vaccine developed by Sanofi Pasteur and GSK plc. It is based on the SARS-CoV-2 Beta variant.
EMA countries (as booster only)[700]
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
Sputnik Light[edit]
Full authorization Emergency authorization Allowed for travel | |||
Sputnik Light is a viral vector vaccine,[701] produced by the Russian Gamaleya Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology. It consists of the first dose of the Sputnik V vaccine, which is based on the Ad26 vector.[702]
- Full (0)
- Emergency (28)
- Angola[703]
- Argentina[704]
- Armenia[705]
- Bahrain[706]
- Belarus[707]
- Benin[708]
- Cambodia[519]
- Congo-Brazzaville[709]
- Egypt[710]
- Iran[245]
- India[711]
- Kazakhstan[712]
- Kyrgyzstan[713]
- Laos[57]
- Mauritius[714]
- Mongolia[715]
- Nicaragua[716]
- Palestine[717]
- Philippines[718]
- Russia[719]
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines[57]
- San Marino[720]
- Syria[721]
- Tanzania[245]
- Tunisia[245]
- Turkmenistan[245][722]
- United Arab Emirates[723]
- Venezuela[724]
Non-country entities
- Travel-only
Convidecia[edit]
Full authorization Emergency authorization Allowed for travel | |||
Convidecia is a viral vector vaccine[727] produced by the Chinese company CanSino Biologics and the Beijing Institute of Biotechnology of the Academy of Military Medical Sciences.
- Full (1)
- China[728]
- Emergency (9)
- Argentina[729]
- Chile[730]
- Ecuador[731]
- Hungary[732][405]
- Indonesia[286]
- Malaysia[733]
- Mexico[620]
- Moldova[292]
- Pakistan[734]
- Travel-only
Sinopharm WIBP[edit]
Full authorization Emergency authorization Allowed for travel | |||
The Sinopharm WIBP COVID-19 vaccine is an inactivated virus vaccine produced by the China National Pharmaceutical Group (Sinopharm) and its Wuhan Institute of Biological Products.
- Full (1)
- China[736]
- Emergency (5)
- Travel-only
Abdala[edit]
Full authorization Emergency authorization Allowed for travel | |||
Abdala is a subunit vaccine developed by the Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology in Cuba.
- Full (0)
- Emergency (6)
- Cuba[738][739]
- Mexico[740]
- Nicaragua[741]
- St. Vincent and the Grenadines[742][743]
- Venezuela[744]
- Vietnam[145]
- Travel-only
- Cambodia[745]
- Colombia[746]
- Guyana[747][748]
- Malaysia[585]
- New Zealand[367]
- St. Lucia[490]
- Turkey[315]
- Uruguay[499] (only if accepted in the country of the person's origin)
EpiVacCorona[edit]
Full authorization Emergency authorization Allowed for travel | |||
EpiVacCorona is a peptide vaccine produced by the Russian State Research Center of Virology and Biotechnology VECTOR.[749]
- Full (1)
- Emergency (4)
- Travel-only
Zifivax[edit]
Full authorization Emergency authorization Allowed for travel | |||
Zifivax is a subunit vaccine produced by the Chinese company Anhui Zhifei Longcom Biopharmaceutical.[755]
- Full (0)
- Emergency (5)
- Travel-only
Soberana 02[edit]
Full authorization Emergency authorization Allowed for travel | |||
Soberana 02, is a conjugate vaccine developed by the Finlay Institute in Cuba.[761]
- Full (0)
- Emergency (4)
- Travel-only
CoviVac[edit]
Full authorization Emergency authorization Allowed for travel | |||
CoviVac is an inactivated virus vaccine[701] produced by the Chumakov Centre at the Russian Academy of Sciences.[765]
- Full (0)
- Emergency (3)
- Travel-only
QazCovid-in[edit]
Full authorization Emergency authorization Allowed for travel | |||
QazCovid-in, also known as QazVac, is an inactivated virus vaccine developed by the Research Institute for Biological Safety Problems in Kazakhstan.[768]
- Full (0)
- Emergency (2)
- Travel-only
Minhai[edit]
Full authorization Emergency authorization Allowed for travel | |||
Minhai COVID-19 vaccine, is an inactivated virus vaccine developed by Minhai Biotechnology Co. and Shenzhen Kangtai Biological Products Co. Ltd. in China.[772]
- Full (0)
- Emergency (2)
- Travel-only
Medigen[edit]
Full authorization Emergency authorization Allowed for travel | |||
MVC-COV1901, is a protein subunit vaccine developed by Taiwan's Medigen Vaccine Biologics and Dynavax Technologies.[774]
- Full (0)
- Emergency (3)
- Non-country entities
1. Somaliland[776]
- Travel-only
Corbevax[edit]
Corbevax is a protein subunit vaccine developed by Texas Children's Hospital at the Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, and licensed to Indian biopharmaceutical firm Biological E. Limited (BioE) for development and production.[661][780]
- Full (0)
- Emergency (2)
- Travel-only
COVIran Barekat[edit]
COVIran Barekat, is an inactivated virus vaccine developed by Shifa Pharmed Industrial Co. in Iran.[782]
- Full (0)
- Emergency (2)
- Travel-only
Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences[edit]
Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences COVID-19 vaccine, is an inactivated virus vaccine developed by Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences.[786]
- Full (0)
- Emergency (1)
- China[786]
- Travel-only
ZyCoV-D[edit]
ZyCoV-D, is a DNA plasmid based COVID-19 vaccine developed by the Indian pharmaceutical company Cadila Healthcare with support from the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council.[787]
- Full (0)
- Emergency (1)
- India[787]
- Travel-only
FAKHRAVAC[edit]
FAKHRAVAC (or MIVAC), is an inactivated virus vaccine developed in Iran by the Organization of Defensive Innovation and Research, an organization of Iran's Ministry of Defense.[788]
- Full (0)
- Emergency (1)
- Iran[788]
- Travel-only
COVAX-19[edit]
COVAX-19, also known as SpikoGen, is a protein subunit vaccine jointly developed by Australian-based company Vaxine and Iran-based company CinnaGen.[789]
- Full (0)
- Emergency (1)
- Iran[789]
- Travel-only
Razi Cov Pars[edit]
Razi Cov Pars is a protein subunit vaccine developed by Razi Vaccine and Serum Research Institute.[790]
- Full (0)
- Emergency (1)
- Iran[790]
- Travel-only
Turkovac[edit]
Turkovac is an inactivated vaccine developed by Health Institutes of Turkey and Erciyes University.[791]
- Full (0)
- Emergency (1)
- Turkey[791]
- Travel-only
Sinopharm CNBG[edit]
Sinopharm CNBG COVID-19 vaccine (NVSI) is a recombinant protein subunit vaccine developed by the National Vaccine & Serum Institute (NVSI, 中生研究院), a subsidiary of China National Biotec Group (CNBG), which in turn is a subsidiary of Sinopharm.[792]
- Full (0)
- Emergency (1)
- United Arab Emirates[792]
- Travel-only
Soberana Plus[edit]
Soberana Plus is a single-dose of conjugate vaccine developed by the Finlay Institute in Cuba.[793]
- Full (0)[793]
- Emergency (2)
- Travel-only
CoVLP[edit]
CoVLP is a virus-like particle vaccine grown in an Australian weed, Nicotiana benthamiana. It was developed by Medicago, and is marketed under the name Covifenz Archived 24 February 2022 at the Wayback Machine.
- Full (1)
- Canada[796]
- Emergency (0)
- Travel-only
Noora[edit]
Noora is a protein-based vaccine developed by the Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences.
- Full (0)
- Emergency (1)
- Iran[797]
- Travel-only
SKYCovione[edit]
SKYCovione is a protein subunit vaccine developed by SK Bioscience.
- Full (0)
- Emergency (1)
- South Korea[798]
Walvax[edit]
Walvax COVID-19 vaccine is an RNA vaccine developed by Walvax Biotechnology, Suzhou Abogen Biosciences, and the PLA Academy of Military Science.[799]
- Full (0)
- Emergency (1)
- Indonesia[800]
iNCOVACC[edit]
iNCOVACC, also called BBV154 is an adenovirus vector vaccine developed by Bharat Biotech, Precision Virologics, and Washington University School of Medicine.
- Full (0)
- Emergency (1)
Gemcovac[edit]
Gemcovac, or GEMCOVAC-19, is a self-amplifying mRNA vaccine manufactured by Gennova Biopharmaceuticals.
- Full (0)
- Emergency (1)
V-01[edit]
V-01 is a protein subunit vaccine developed by Livzon Mabpharm.
- Full (0)
- Emergency (1)
IndoVac[edit]
IndoVac is a protein subunit vaccine developed by Indonesian pharmaceutical company Bio Farma and Baylor College of Medicine.
- Full (0)
- Emergency (1)
- Indonesia[245]
Notes[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c "Status of COVID-19 Vaccines within WHO EUL/PQ evaluation process". World Health Organization (WHO).
- ^ "International COVID-19 vaccines recognised by Australia". Therapeutic Goods Administration. Australian Government Department of Health. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ "COVID-19 and the border - Vaccinated travellers". Department of Home Affairs. Australian Government Department of Home Affairs. Archived from the original on 14 March 2022. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ "COVID-19 vaccinations". Smartraveller. Australian Government Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ a b "Vaxzevria (previously COVID-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca) EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 25 January 2021.
- ^ "Covishield and Covaxin: What we know about India's Covid-19 vaccines". BBC News. 4 March 2021. Archived from the original on 7 March 2021. Retrieved 8 March 2021.
- ^ a b "Investigating a Vaccine Against COVID-19". ClinicalTrials.gov. United States National Library of Medicine. 26 May 2020. NCT04400838. Archived from the original on 11 October 2020. Retrieved 14 July 2020.
- ^ "A Phase 2/3 study to determine the efficacy, safety and immunogenicity of the candidate Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) vaccine ChAdOx1 nCoV-19". EU Clinical Trials Register. European Union. 21 April 2020. EudraCT 2020-001228-32. Archived from the original on 5 October 2020. Retrieved 3 August 2020.
- ^ O'Reilly P (26 May 2020). "A Phase III study to investigate a vaccine against COVID-19". ISRCTN. doi:10.1186/ISRCTN89951424. ISRCTN89951424.
- ^ "THL temporarily suspends the use of the AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine - Press release - THL". Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare (THL), Finland. Retrieved 5 December 2021.
- ^ "Denmark continues its vaccine rollout without the COVID-19 vaccine from AstraZeneca". Danish Health Authority. 14 April 2021. Retrieved 31 July 2021.
That is why it is important to emphasise that it is still an approved vaccine.
- ^ Peltier E (14 April 2021). "Denmark says it's permanently stopping use of the AstraZeneca vaccine". The New York Times.
- ^ omsorgsdepartementet Ho (12 May 2021). "AstraZeneca-vaksinen tas ut av koronavaksinasjons-programmet". Regjeringen.no (in Norwegian). Retrieved 12 May 2021.
- ^ "Slovakia suspends use of AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine as a recipient dies". Reuters. 11 May 2021. Retrieved 23 June 2021.
- ^ "South Africa sells AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccines to other African countries". Reuters. 21 March 2021. Retrieved 23 June 2021.
- ^ "Japan to donate millions more AstraZeneca vaccine doses across Asia". Kyodo News. 25 June 2021.
- ^ "Japan to give COVID-19 emergency areas AstraZeneca vaccine". The Japan Times. 4 August 2021. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 28 August 2021.
- ^ a b "Suspension of AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccines for those under the age of 65 extended – THL evaluating how it affects the vaccination programme - Press release - THL". Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare (THL), Finland. Retrieved 5 December 2021.
- ^ a b "Adenovirus vaccines: FAQ - THL". Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare (THL), Finland. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ a b c "Getting vaccinated against COVID-19: how, why and when? - THL". Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare (THL), Finland. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ "Which covid-19 vaccine is the most widely accepted for international travel?". The Economist. 23 July 2021. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- ^ "India celebrates 1 billion COVID-19 vaccine doses with song and dance". Reuters. 21 October 2021. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- ^ "Oxford vaccine reaches one billion doses released". University of Oxford. 29 July 2021. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- ^ "Two billion doses of AstraZeneca's COVID-19 vaccine supplied to countries across the world less than 12 months after first approval". AstraZeneca. 16 November 2021. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- ^ "Vaxzevria COVID-19 Vaccine (AstraZeneca)". precisionvaccinations.com. 8 June 2022. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- ^ a b "Where are Vaccines (Company and Brand) Administered Globally?". CDC Covid Data Tracker. 9 June 2022. Retrieved 13 June 2022.
- ^ "AstraZeneca coronavirus vaccine approved for use in Australia by TGA". ABC News (Australia). 16 February 2021. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ "TGA provisionally approves AstraZeneca's COVID-19 vaccine". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 16 February 2021. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ "Brazil grants full approval to Oxford vaccine, orders Sputnik". Brasilia: France 24. Agence France-Presse. 12 March 2021. Retrieved 13 March 2021.
- ^ "AstraZeneca Vaxzevria COVID-19 vaccine". Health Canada. 7 June 2022. Retrieved 30 October 2022.
- ^ "Regulatory Decision Summary - Vaxzevria". Health Canada. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ a b Sharma M, Mordani S (27 January 2022). "Covaxin, Covishield granted market approval in India but conditions apply". India Today. Retrieved 29 January 2022.
- ^ "Israel to offer AstraZeneca vaccines starting Thursday". The Times of Israel. 18 October 2021. Retrieved 13 June 2022.
- ^ "Vaccines "Three vaccines have been approved for use in Israel for protection from coronavirus, by Pfizer, Moderna and AstraZeneca."". Vaccines - Corona Traffic Light Model (Ramzor) Website. 31 May 2022. Retrieved 13 June 2022.
- ^ a b "Comirnaty EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Retrieved 23 December 2020.
- ^ "Comirnaty". Union Register of medicinal products. 21 December 2020. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ Sediqi AQ (7 February 2021). "First doses of COVID-19 vaccine arrive in Afghanistan from India". Reuters. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ^ "India donates 500,000 COVID vaccines to Afghanistan". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ^ a b c Semini L. "Albania starts mass COVID vaccinations before tourist season". ABC News. Retrieved 29 March 2021.
- ^ Kreo. "البلاد الوطني / وزارة الصناعات الصيدلانية ترخص باستعمال لقاح "أسترا زينيكا -أوكسفورد " المضاد لكورونا". elbilad.net (in Arabic). Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ a b c "Informació en relació amb la vacunació contra la COVID-19" (PDF) (in Catalan). Govern d'Andorra. Retrieved 14 March 2021.
- ^ AfricaNews (3 March 2021). "Angola begins Covid immunization fight with COVAX vaccines". Africanews. Event occurs at CET13:13:37+01:00. Retrieved 14 April 2021.
- ^ "Argentine regulator approves AstraZeneca/Oxford COVID-19 vaccine". Reuters. 30 December 2020. Retrieved 30 December 2020.
- ^ Ghalechian N (27 April 2021). "Armenia Scraps Restrictions For AstraZeneca Vaccine". «Ազատ Եվրոպա/Ազատություն» ռադիոկայան (in Armenian).
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf cg ch ci cj ck cl cm cn co cp cq cr cs ct cu cv "COVID Data Tracker". U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 28 March 2020.
- ^ "Bahrain approves Oxford/AstraZeneca coronavirus vaccine produced in India". Saudigazette. 25 January 2021. Retrieved 30 January 2021.
- ^ "Oxford University-Astrazeneca vaccine: Bangladesh okays it for emergency use". The Daily Star. 4 January 2021. Retrieved 6 January 2021.
- ^ "Bangladesh approves Oxford-AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine". aa.com.tr. Retrieved 6 January 2021.
- ^ "Bhutan receives 400,000 doses of COVID-19 vaccine from India". Xinhuanet. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ "Bhutan begins biggest vaccination drive against COVID-19". CNA. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ a b "Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccines shipped by COVAX arrive in Bosnia and Herzegovina". United Nations. Retrieved 14 April 2021.
- ^ "Botswana starts COVID-19 vaccine rollout". Xinhuanet. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ a b "COVID-19: Brunei to begin mass vaccination on April 3". TheScoop. 2 April 2021. Retrieved 6 April 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf cg ch ci cj ck cl cm cn co cp cq cr cs ct cu cv cw cx cy cz da db dc dd de df dg dh di dj dk dl dm dn do dp dq dr ds dt du dv dw dx dy dz ea eb ec ed ee ef eg eh ei ej ek el em en eo ep eq er es et eu ev ew ex ey ez fa fb fc fd fe ff fg fh fi fj fk fl fm fn fo fp fq fr "WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard". World Health Organization (WHO).
- ^ "COVID-19 vaccines sent by COVAX arrive in Cabo Verde". ReliefWeb. 15 March 2021. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ "Instituto de Salud Pública de Chile" (in Spanish). Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ "Colombia approves emergency use of AstraZeneca coronavirus vaccine". Reuters. 23 February 2021. Retrieved 22 March 2021.
- ^ "More than 1.7 million COVID-19 vaccines arrive in the Democratic Republic of Congo". www.unicef.org. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ^ "Costa Rica approves use of AstraZeneca's COVID-19 vaccine". Q COSTA RICA. 9 April 2021.
- ^ "La República Dominicana aprueba la vacuna de AstraZeneca contra la covid-19". Agencia EFE (in Spanish). 31 December 2020.
- ^ "First vaccines for East Timor arrive in Dili on Monday – LUSA". COVID-19 Timor-Leste Dashboard. 1 April 2021. Archived from the original on 2 April 2021.
- ^ "Ecuador approves use of AstraZeneca vaccine for COVID-19". Reuters. 24 January 2021. Retrieved 30 January 2021.
- ^ a b "COVID-19: Egypt authorises Sputnik V, AstraZeneca virus jabs". Gulf News. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ^ "El Salvador greenlights AstraZeneca, Oxford University COVID-19 vaccine". Reuters. 30 December 2020.
- ^ "Eswatini launches nationwide COVID-19 vaccination campaign". World Health Organization (WHO). 24 March 2021. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ "Ethiopia begins COVID-19 vaccine rollout". aa.com.tr. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ "Ethiopia introduces COVID-19 vaccine in a national launching ceremony". World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ "Ethiopia says it has secured 9 million doses of COVID-19 vaccines till April". Reuters. 9 February 2021. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ "The Arrival of COVAX vaccines Raises Hope in The Gambia". World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ "Georgia to receive first doses of COVID-19 vaccine in early March instead of February". Agenda.ge. Retrieved 22 March 2021.
- ^ "Welcome to Ghana Food And Drug Authority". fdaghana.gov.gh. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ a b c "COVID-19 Information". U.S. Embassy in Guatemala. 25 February 2020. Archived from the original on 7 May 2021. Retrieved 14 April 2021.
- ^ "Today, 28,800 doses of COVID-19 vaccine arrive in Bissau". www.unicef.org.
- ^ "BPOM Terbitkan Izin Penggunaan Darurat Vaksin Covid-19 AstraZeneca". Kompas. Retrieved 10 February 2021.
- ^ "Iran issues permit for emergency use for three other COVID-19 vaccines: Official". IRNA English. 17 February 2021. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ a b "Iraq approves Sinopharm, AstraZeneca vaccines". Big News Network. Retrieved 30 January 2021.
- ^ "Covax: Ivory Coast and Ghana begin mass Covid vaccination rollouts". BBC News. 1 March 2021. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ a b c "Japan Approves Moderna, AstraZeneca Coronavirus Vaccines". Bloomberg. 20 May 2021. Retrieved 2 July 2021.
- ^ "COVAX roll-out - Jordan". www.gavi.org. Retrieved 14 May 2021.
- ^ "Kenya Receives 1M Vaccine Doses, Will Distribute to Health Workers First". Voice of America. 3 March 2021. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ "Kosovo receives first COVID-19 vaccines through Covax scheme". euronews. 29 March 2021. Retrieved 14 April 2021.
- ^ "Kosovo PM Becomes Nation's First Person To Receive COVID-19 Vaccine". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 29 March 2021. Retrieved 14 April 2021.
- ^ Godinho V (31 January 2021). "Kuwait authorises emergency use of Oxford-AstraZeneca Covid-19 vaccine". Gulf Business. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ "Lebanon Received 33600 Doses of The AstraZeneca Vaccine as First Batch". Ministry of Public Health of Lebanon.
- ^ "Lesotho receives 1st batch of COVID-19 vaccines". aa.com.tr. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ "96,000 Doses of COVID-19 Vaccine Arrives in Liberia". World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 11 April 2021.
- ^ a b "Libya kicks off delayed COVID-19 vaccination drive". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ^ a b "57,600 COVID-19 vaccine doses received today in Tripoli, Libya". ReliefWeb. 8 April 2021. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ^ "Malawi to receive COVID-19 vaccines in late February – Xinhua". Xinhuanet. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ "Malawi Sticks to AstraZeneca Despite Concerns Over Efficacy". Voice of America. 8 February 2021. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ Sipalan J, Donovan K (3 March 2021). "Malaysia approves Sinovac, AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccines for use". Reuters. Retrieved 7 March 2021.
- ^ "Maldives starts training healthcare workers on COVID-19 vaccine distribution – Xinhua". Xinhuanet. Retrieved 19 February 2021.
- ^ AfricaNews (6 March 2021). "Mali receives first batch of COVID-19 vaccines". Africanews. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ AfricaNews (26 January 2021). "Mauritius begins vaccinating frontline health workers against covid-19". Africanews. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ^ "Mexico approves AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine, minister says". Reuters. 5 January 2021. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ^ a b c "Moldova approves Russia's Sputnik V vaccine as political row simmers". Thomson Reuters Foundation. Archived from the original on 3 April 2021. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ a b "Mongolia approved three Covid-19 vaccines". News.MN. 11 January 2021. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ "Morocco approves AstraZeneca/Oxford COVID-19 vaccine – Minister". Reuters. 7 January 2021. Retrieved 22 March 2021.
- ^ "Myanmar launches nationwide COVID-19 vaccination program". Xinhua News. 27 January 2021.
- ^ "Importation of COVID-19 Vaccines into Namibia for Public Use and Guidance on Administration of Vaccines by Private Health Care Providers". Republic of Namibia Ministry of Health and Social Services. 31 March 2021. Archived from the original on 22 April 2021. Retrieved 14 April 2021. Public Notice No.: 05/032021
- ^ a b c "Samoa receives 24,000 doses of COVID-19 vaccines through the COVAX facility - Samoa". ReliefWeb. 14 April 2021. Retrieved 7 June 2021.
- ^ "Nepal approves AstraZeneca COVID vaccine for emergency use – government statement". Reuters. 15 January 2021.
- ^ "Wetin we sabi about NAFDAC approval of Oxford AstraZeneca vaccine use for Nigeria". BBC News Pidgin. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ^ "Сѐ за вакцините". Официјална веб-страница за вакцинација против КОВИД19 (in Macedonian).
- ^ "Pakistan approves AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine for emergency use". 16 January 2021.
- ^ "PNG prime minister first to be vaccinated with Australian-supplied doses 'to show it's safe'". The Guardian. 30 March 2021. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ "Australia gives Covid-19 vaccine doses to hard-hit Papua New Guinea". France 24. 17 March 2021. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ "DIGEMID". www.digemid.minsa.gob.pe (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 7 May 2021. Retrieved 2 May 2021.
- ^ "Philippine regulator approves emergency use of AstraZeneca vaccine". Reuters. 28 January 2021. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- ^ "Rwanda receives COVID-19 Vaccines through COVAX". World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ a b "AstraZeneca and Moderna vaccines to be administered in Saudi Arabia". Gulf News. 18 January 2021. Retrieved 19 January 2021.
- ^ "Serbia receives first shipment of AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine". Reuters. 21 February 2021. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ Bhattacherjee K (22 January 2021). "Coronavirus | Myanmar, Mauritius, Seychelles receive Covishield vaccine". The Hindu. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ "COVID-19 vaccines shipped by COVAX arrive in Sierra Leone". World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ a b c "Those who opt for Sinovac, other vaccines under WHO emergency list to be considered fully vaccinated". CNA. 6 August 2021. Retrieved 6 August 2021.
- ^ "Somalia Receives Its First Batch of COVID-19 Vaccines". Voice of America. 15 March 2021. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ Kim Hj (10 February 2021). "S. Korea approves AstraZeneca's COVID-19 vaccine for all adults". Yonhap News. Retrieved 10 February 2021.
- ^ Maresca T (10 February 2021). "South Korea approves AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine". United Press International. Retrieved 10 February 2021.
- ^ "COVID-19 vaccination kicks-off in South Sudan". World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 14 April 2021.
- ^ "Sri Lanka approves vaccine amid warnings of virus spread". Associated Press. 22 January 2021. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ^ "COVID-19 vaccination in Sudan". UNICEF. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ "Sudan receives first delivery of COVID-19 vaccines with over 800,000 doses". UNICEF. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ "Taiwan grants emergency authorisation for AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine". Reuters. 20 February 2021. Retrieved 13 March 2021.
- ^ "Tajikistan becomes first country in Central Asia to receive COVID-19 vaccine through COVAX Facility". unicef.org. Retrieved 14 April 2021.
- ^ "Thai Food and Drug registers COVID-19 vaccine developed by AstraZeneca". Pattaya Mail. 23 January 2021.
- ^ First T. "Covid-19: First vaccination campaign to soon begin". togofirst. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ "Over 500 people given first COVID-19 vaccine shot in Tonga – Xinhua". xinhuanet. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ^ "Tonga's Princess takes the lead on Covid-19 vaccination". RNZ. 16 April 2021. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ^ "Kingdom of Tonga receives 24,000 doses of COVID-19 vaccines through the COVAX facility". World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ^ AfricaNews (10 March 2021). "Uganda starts COVID-19 vaccinations". Africanews. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ "COVID-19: AstraZeneca vaccine certified for use in Ukraine". covid.unian.info. Retrieved 10 March 2021.
- ^ "Information for Healthcare Professionals on COVID-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca". Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA). 30 December 2020. Retrieved 4 January 2021.
- ^ "Oxford University/AstraZeneca vaccine authorised by UK medicines regulator" (Press release). Department of Health and Social Care. 30 December 2020. Retrieved 30 December 2020.
- ^ "Conditions of Authorisation for COVID-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca". Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA). 30 December 2020. Retrieved 4 January 2021.
- ^ "Vietnam approves AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine, cuts short Communist Party congress". CNA. Retrieved 5 February 2021.
- ^ "Yemen receives 360,000 COVID-19 vaccine doses through the COVAX Facility". www.unicef.org. Retrieved 7 June 2021.
- ^ a b "Zambia sets out plans to vaccinate all people over 18 against COVID-19". Reuters. 25 March 2021. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ a b "Zambia launches the COVID-19 vaccination". ReliefWeb. 16 April 2021. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ a b "Zambia gets 1st 228,000 vaccine doses from COVAX". aa.com.tr. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ "CARPHA Issues its First Emergency Use Recommendation for a COVID-19 Vaccine". Caribbean Public Health Agency.
- ^ "Suriname begins coronavirus vaccination campaign with donated doses". Reuters. 23 February 2021. Retrieved 28 February 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Zimmer C, Corum J, Wee SL (10 June 2020). "Coronavirus Vaccine Tracker". The New York Times.
- ^ a b c Psyllides G (31 March 2021). "Coronavirus: 10,000 vaccines handed over to north". cyprus-mail.com/. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "COVID-19 Vaccines with WHO Emergency Use Listing". World Health Organization (WHO). 3 November 2021. Archived from the original on 21 December 2021. Retrieved 30 October 2022.
- ^ "Interim recommendations for use of the AZD1222 (ChAdOx1-S (recombinant)) vaccine against COVID-19 developed by Oxford University and AstraZeneca". World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 27 February 2021.
- ^ "AstraZeneca/Oxford Covid-19 Vaccine Gets Emergency Approval From WHO". Forbes. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ "WHO Recommendation AstraZeneca/SKBio - COVID-19 Vaccine (ChAdOx1-S [recombinant])". World Health Organization (WHO). 15 February 2021. Archived from the original on 4 July 2021. Retrieved 8 May 2021.
- ^ "WHO recommendation Serum Institute of India Pvt Ltd - COVID-19 Vaccine (ChAdOx1-S [recombinant]) - Covishield". World Health Organization (WHO). 15 February 2021. Archived from the original on 6 July 2021. Retrieved 8 May 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "List of COVID-19 Vaccines Recognised for Specified Purposes" (PDF). Hong Kong Department of Health. Retrieved 24 November 2021.
- ^ FOPH FO. "Coronavirus: Entering Switzerland". www.bag.admin.ch. Archived from the original on 24 July 2020. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ^ "COVID-19 and Your Health". U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 11 February 2020. Retrieved 17 November 2021.
- ^ "Vaxzevria". Union Register of medicinal products. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ a b "Regulatory Decision Summary – Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine". Health Canada, Government of Canada. 9 December 2020. Retrieved 9 December 2020.
- ^ "Study to Describe the Safety, Tolerability, Immunogenicity, and Efficacy of RNA Vaccine Candidates Against COVID-19 in Healthy Adults". ClinicalTrials.gov. United States National Library of Medicine. 30 April 2020. NCT04368728. Archived from the original on 11 October 2020. Retrieved 14 July 2020.
- ^ "A Multi-site Phase I/II, 2-Part, Dose-Escalation Trial Investigating the Safety and Immunogenicity of four Prophylactic SARS-CoV-2 RNA Vaccines Against COVID-19 Using Different Dosing Regimens in Healthy Adults". EU Clinical Trials Register. European Union. 14 April 2020. EudraCT 2020-001038-36. Archived from the original on 22 April 2020. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
- ^ "BioNTech and China partner, not Pfizer, to produce HK shots". The Standard.
- ^ "Pfizer and BioNTech's overlooked third partner will distribute the vaccine in China – and it's facing some resistance". Retrieved 18 April 2021.
- ^ Burger L (16 March 2020). "BioNTech in China alliance with Fosun over potential coronavirus vaccine". Reuters. Retrieved 18 April 2021.
- ^ "BioNTech, Fosun start Phase II trial of COVID-19 vaccine in China". Reuters. 25 November 2020. Retrieved 18 April 2021.
- ^ a b Kemp R (11 July 2021). "Fosun says it has struck deal to send Taiwan vaccines". RTHK. Retrieved 11 July 2021.
- ^ a b "10 Million Doses of mRNA-based COVID-19 Vaccine to be supplied to Taiwan Region". BioNTech (Press release). 12 July 2021. Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ "Comirnaty". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 25 January 2021. Retrieved 25 January 2021.
- ^ Australian Public Assessment Report for BNT162b2 (mRNA) (PDF) (Report). Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). Retrieved 25 January 2021.
- ^ "Vacina da Pfizer é a 1ª a obter registro definitivo no Brasil" (in Brazilian Portuguese). G1. 23 February 2021. Retrieved 23 February 2021.
- ^ a b "Pfizer-BioNTech Comirnaty COVID-19 vaccine". Health Canada. 21 October 2022. Retrieved 30 October 2022.
- ^ a b Osman L (16 September 2021). "Goodbye Pfizer, hello Comirnaty: Top COVID-19 vaccines given brand names in Canada". CBC News. Retrieved 16 September 2021.
- ^ "Robust assessment ahead of Medsafe approval of vaccine". Ministry of Health. 3 February 2021. Retrieved 6 February 2021.
- ^ "Interior Applauds Inclusion of Insular Areas through Operation Warp Speed to Receive COVID-19 Vaccines" (Press release). United States Department of the Interior (DOI). 12 December 2020. Retrieved 13 January 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ^ Dorman B (6 January 2021). "Asia Minute: Palau Administers Vaccines to Keep Country Free of COVID". Hawaii Public Radio. Retrieved 13 January 2021.
- ^ "Coronavirus: Saudi Arabia approves Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine for use". Al Arabiya English. 10 December 2020. Retrieved 10 December 2020.
- ^ "Comirnaty Product information" (in German). Retrieved 31 January 2021. [Due to incomplete clinical data at the time of the assessment of the authorization application, the Comirnaty medicinal product is authorized for a limited period (Art. 9a Medicinal Products Act).]
- ^ "Use of vaccine approved". Government of Hong Kong. 25 January 2021. Retrieved 15 February 2021.
- ^ a b "COVID-19 vaccines supplied by two drug manufacturers registered as pharmaceutical products in Hong Kong". Government of Hong Kong. 20 December 2022. Retrieved 23 December 2022.
- ^ "Albania to start COVID-19 immunisation with Pfizer vaccine in January – report". Seenews.
- ^ "Canada allows Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine for children aged 12-15". Reuters. 5 May 2021. Retrieved 19 August 2021.
- ^ "Andorra COVID-19". govern.ad. Retrieved 19 February 2021.
- ^ "Coronavirus en la Argentina: La ANMAT aprobo el uso de emergencia de la vacuna Pfizer". La Nación (in Spanish). Retrieved 23 December 2020.
- ^ "Dashboard: Vaccinating Eurasia- June". Eurasianet. 30 June 2021. Retrieved 4 August 2021.
- ^ "Bahrain becomes second country to approve Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 5 December 2020.
- ^ "The Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine Was Granted Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) & Bahrain National Health Regulatory Authority (NHRA)". cvdvaccine. Retrieved 18 April 2021.
- ^ "Bangladesh approves Pfizer Covid-19 vaccine for emergency use". Dhaka Tribune. 27 May 2021. Retrieved 27 May 2021.
- ^ "Botswana expects to welcome multiple COVID-19 vaccines". Xinhuanet. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ "Chile approves Pfizer-BioNTech Covid-19 vaccine for emergency use". The Straits Times. 17 December 2020. Retrieved 17 December 2020.
- ^ a b "BioNTech ships COVID shots to China for use by Germans". Reuters. 22 December 2022. Retrieved 23 December 2022.
- ^ "Colombia regulator approves Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine for emergency use". Reuters. 6 January 2021. Retrieved 6 January 2021.
- ^ a b c "Covid-19 en RDC: des officiers et agents de la Police se font vacciner après échanges avec le ministre de la Santé". Actualite.cd (in French). 7 December 2021. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ "Costa Rica authorizes Pfizer-BioNTech coronavirus vac