Portal:Viruses
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
The Viruses Portal
Welcome!
Viruses are small infectious agents that can replicate only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all forms of life, including animals, plants, fungi, bacteria and archaea. They are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most abundant type of biological entity, with millions of different types, although only about 6,000 viruses have been described in detail. Some viruses cause disease in humans, and others are responsible for economically important diseases of livestock and crops.
Virus particles (known as virions) consist of genetic material, which can be either DNA or RNA, wrapped in a protein coat called the capsid; some viruses also have an outer lipid envelope. The capsid can take simple helical or icosahedral forms, or more complex structures. The average virus is about 1/100 the size of the average bacterium, and most are too small to be seen directly with an optical microscope.
The origins of viruses are unclear: some may have evolved from plasmids, others from bacteria. Viruses are sometimes considered to be a life form, because they carry genetic material, reproduce and evolve through natural selection. However they lack key characteristics (such as cell structure) that are generally considered necessary to count as life. Because they possess some but not all such qualities, viruses have been described as "organisms at the edge of life".
Selected disease
Polio, also called poliomyelitis or infantile paralysis, was one of the most feared childhood diseases of the 20th century. Poliovirus, the causative agent, only naturally infects humans and spreads via the faecal–oral route. Most infections cause no or minor symptoms. In around 1% of cases, the virus enters the central nervous system, causing aseptic meningitis. There it can preferentially infect and destroy motor neurons, leading in 0.1–0.5% of cases to muscle weakness and acute flaccid paralysis. Spinal polio accounts for nearly 80% of paralytic cases, with asymmetric paralysis of the legs being typical; in a quarter of these cases permanent severe disability results. Bulbar involvement is rare, but in severe cases the virus can prevent breathing by affecting the phrenic nerve, so that patients require mechanical ventilation with an iron lung or similar device.
Depictions in ancient art show that the disease has existed for thousands of years. The virus was an endemic pathogen until the 1880s, when major epidemics began to occur in Europe and later the United States. Polio vaccines were developed in the 1950s and a global eradication campaign started in 1988. The annual incidence of wild-type disease fell from many hundreds of thousands to 22 in 2017, but has since resurged to a few hundreds.
Selected image
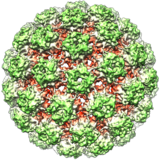
Megavirus chilensis is a very large DNA virus discovered in 2010. Until the discovery of Pandoravirus in 2013, it was the largest known virus, with its 440 nm diameter capsid being as large as some small bacteria. The capsid is enclosed in bacterial-like capsular material 75–100 nm thick.
Credit: Chantal Abergel (10 October 2011)
In the news
26 February: In the ongoing pandemic of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), more than 110 million confirmed cases, including 2.5 million deaths, have been documented globally since the outbreak began in December 2019. WHO
18 February: Seven asymptomatic cases of avian influenza A subtype H5N8, the first documented H5N8 cases in humans, are reported in Astrakhan Oblast, Russia, after more than 100,0000 hens died on a poultry farm in December. WHO
14 February: Seven cases of Ebola virus disease are reported in Gouécké, south-east Guinea. WHO
7 February: A case of Ebola virus disease is detected in North Kivu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. WHO
4 February: An outbreak of Rift Valley fever is ongoing in Kenya, with 32 human cases, including 11 deaths, since the outbreak started in November. WHO
21 November: The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gives emergency-use authorisation to casirivimab/imdevimab, a combination monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy for non-hospitalised people twelve years and over with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, after granting emergency-use authorisation to the single mAb bamlanivimab earlier in the month. FDA 1, 2
18 November: The outbreak of Ebola virus disease in Équateur Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo, which started in June, has been declared over; a total of 130 cases were recorded, with 55 deaths. UN
Selected article
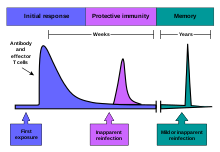
The immune system is a system of structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease. It must detect a wide variety of pathogens – from viruses to parasitic worms – distinguish them from the organism's own healthy tissue, and neutralise them. Simple unicellular organisms such as bacteria have enzymes that protect against bacteriophage infections. Other basic immune mechanisms, including phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides called defensins, and the complement system, evolved in ancient eukaryotes and are found in plants and invertebrates.
Humans and most other vertebrates have more sophisticated defence mechanisms, including the ability to adapt over time to recognise specific pathogens more efficiently. Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leading to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that same pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination. Viruses and other pathogens can rapidly evolve to evade immune detection, and some viruses, notably HIV, cause the immune system to function less effectively.
Selected outbreak
The last recorded smallpox death occurred during the 1978 smallpox outbreak in Birmingham, UK. The outbreak resulted from accidental exposure to the Abid strain of Variola major, from a laboratory, headed by Henry Bedson, at the University of Birmingham Medical School – also associated with an outbreak in 1966. Bedson was investigating strains of smallpox known as whitepox, considered a potential threat to the smallpox eradication campaign, then in its final stages.
A medical photographer who worked on the floor above the laboratory showed smallpox symptoms in August and died the following month; one of her contacts was also infected but survived. The government inquiry into the outbreak concluded that she had been infected in late July, possibly via ducting, although the precise route of transmission was subsequently challenged. The inquiry criticised the university's safety procedures. Bedson committed suicide while under quarantine. Radical changes in UK research practices for handling dangerous pathogens followed, and all known stocks of smallpox virus were concentrated in two laboratories.
Selected quotation
| “ | ...getting rid of the last 1 percent has been like trying to squeeze Jell-O to death. As the vaccination fist closes in one country, the virus bursts out in another... | ” |
—Donald McNeil on the campaign to eradicate polio
Recommended articles
Viruses & Subviral agents: bat virome • elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus • HIV • introduction to viruses![]() • Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus
• Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus![]() • virus
• virus![]()
Diseases: colony collapse disorder • common cold • croup • dengue fever![]() • gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza
• gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza![]() • meningitis
• meningitis![]() • myxomatosis • polio
• myxomatosis • polio![]() • pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
• pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
Epidemiology & Interventions: 2007 Bernard Matthews H5N1 outbreak • Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations • Disease X • 2009 flu pandemic • HIV/AIDS in Malawi • polio vaccine • Spanish flu • West African Ebola virus epidemic
Virus–Host interactions: antibody • host • immune system![]() • parasitism • RNA interference
• parasitism • RNA interference![]()
Methodology: metagenomics
Social & Media: And the Band Played On • Contagion • "Flu Season" • Frank's Cock![]() • Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa
• Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa![]() • social history of viruses
• social history of viruses![]() • "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
• "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
People: Brownie Mary • Macfarlane Burnet![]() • Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C
• Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C![]() • HIV-positive people
• HIV-positive people![]() • Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock
• Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock![]() • poliomyelitis survivors
• poliomyelitis survivors![]() • Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White
• Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White![]()
Selected virus
Papillomaviruses are small non-enveloped DNA viruses that make up the Papillomaviridae family. Their circular double-stranded genome is around 8000 nucleotides long. The icosahedral capsid is 55–60 nm in diameter. They infect humans, other mammals and some other vertebrates including birds, snakes, turtles and fish. Around a hundred species are classified into 53 genera. All papillomaviruses replicate exclusively in epithelial cells of stratified squamous epithelium, which forms the skin and some mucosal surfaces, including the lining of the mouth, airways, genitals and anus.
Infection by most papillomaviruses is either asymptomatic or causes small benign tumours known as warts or papillomas. Francis Peyton Rous showed in 1935 that the Shope papilloma virus could cause skin cancer in rabbits – the first time that a virus was shown to cause cancer in mammals – and papillomas caused by some virus types, including human papillomavirus 16 and 18, carry a risk of becoming cancerous if the infection persists. Papillomaviruses are associated with cancers of the cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, oropharynx and anus in humans.
Did you know?
- ...that the greenbug (pictured) is the vector of several plant viruses?
- ...that during the West African Ebola virus epidemic as many as 15 different vaccines were in development?
- ...that in 1978, populations of the gulf sea star in the Gulf of California were devastated by starfish wasting disease and had not fully recovered twenty years later?
- ...that virologist Stephen Straus, first head of the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine, said he did not use alternative medicine?
- ...that Looking for Madonna, meant to raise awareness of HIV/AIDS in Papua, used shots of a green bra to symbolise sex?
Selected biography
Ali Maow Maalin (1954 – 22 July 2013) was a hospital cook and health worker from Merca, Somalia, who is the last person in the world known to be infected with naturally occurring smallpox. Although he worked in the local smallpox eradication programme, he had not been successfully vaccinated. In October 1977, he was infected with the Variola minor strain of the virus while driving two children with smallpox symptoms to quarantine. He did not experience complications and made a full recovery. An aggressive containment campaign was successful in preventing an outbreak, and smallpox was declared to have been eradicated globally by the World Health Organization (WHO) two years later.
In later life, Maalin volunteered for the successful poliomyelitis eradication campaign in Somalia. He worked for WHO as a local coordinator with responsibility for social mobilisation, and spent several years travelling across Somalia, vaccinating children and educating communities. He encouraged people to be vaccinated by sharing his experiences with smallpox. He died of malaria while carrying out polio vaccinations after the reintroduction of poliovirus to the country in 2013.
In this month
1 April 1911: Peyton Rous showed that a cell-free isolate could transmit sarcoma in chickens, an early demonstration of cancer caused by a virus
7 April 1931: First electron micrograph taken by Ernst Ruska and Max Knoll
8 April 1976: Bacteriophage MS2 (pictured) sequenced by Walter Fiers and coworkers, first viral genome to be completely sequenced
8 April 1990: Death from AIDS of Ryan White, haemophiliac teenager for whom the Ryan White Care Act is named
8 April 1992: Tennis player Arthur Ashe announced that he had been infected with HIV from blood transfusions
9 April 1982: Stanley Prusiner proposed proteinaceous prions as the cause of scrapie
12 April 1955: Success of trial of Jonas Salk's polio vaccine announced
12 April 2013: New order of double-stranded DNA bacteriophages, Ligamenvirales, announced
15 April 1957: André Lwoff proposes a concise definition of a virus
21 April 1989: Discovery of hepatitis C virus by Qui-Lim Choo and colleagues
28 April 1932: First yellow fever vaccine announced at an American Societies for Experimental Biology meeting by Wilbur Sawyer
29 April 2015: PAHO and WHO declared the Americas region free from rubella transmission
30 April 1937: Discovery of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus, later a model for multiple sclerosis research
Selected intervention
Several human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccines, including Cervarix and Gardasil, have been approved to protect against infections with particular types of HPV, associated with cervical and other cancers. All vaccines protect against the high-risk HPV types 16 and 18. Gardasil is a quadrivalent vaccine that additionally protects against low-risk HPV-6 and -11, which are associated with most cases of genital warts. A second-generation nine-valent Gardasil vaccine protects against five additional high-risk HPV types. It is estimated that the vaccines may prevent 70% of cervical cancer, 80% of anal cancer, 60% of vaginal cancer, 40% of vulvar cancer and possibly some oropharyngeal cancers. Protection lasts for at least 8–9 years. Some advocate giving Gardasil to men and boys with the primary aim of protecting their female sexual partners; others consider vaccinating only women and girls to be more cost effective. The licensed vaccines are subunit vaccines, containing only the L1 capsid protein of the virus, which self-assembles into virus-like particles. They are not effective in people already infected with HPV. Research is ongoing into therapeutic HPV vaccines including the viral oncoproteins, E6 and E7, but none has yet been licensed.
Subcategories
Subcategories of virology:
Topics
Things to do
- Comment on what you like and dislike about this portal
- Join the Viruses WikiProject
- Tag articles on viruses and virology with the project banner by adding {{WikiProject Viruses}} to the talk page
- Assess unassessed articles against the project standards
- Create requested pages: red-linked viruses | red-linked virus genera
- Expand a virus stub into a full article, adding images, citations, references and taxoboxes, following the project guidelines
- Create a new article (or expand an old one 5-fold) and nominate it for the main page Did You Know? section
- Improve a B-class article and nominate it for Good Article
 or Featured Article
or Featured Article status
status - Suggest articles, pictures, interesting facts, events and news to be featured here on the portal
WikiProjects & Portals
 WikiProject Viruses Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Viruses Related WikiProjects Medicine • Microbiology • Molecular & Cellular Biology • Veterinary Medicine
Related PortalsAssociated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
- Commons
Free media repository - Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals - Wikidata
Free knowledge base - Wikinews
Free-content news - Wikiquote
Collection of quotations - Wikisource
Free-content library - Wikispecies
Directory of species - Wikiversity
Free learning tools - Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus