Lenguas asmat-kamoro

| Lenguas asmat-kamoro | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Países | | |||
| Familia | L. Asmat-Kamoro | |||
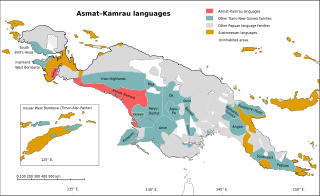 Las lenguas Asmat-Kamoro de Nueva Guinea:
| ||||
Las lenguas asmat-kamoro son una familia de una docena de lenguas trans-neoguineanas habladas por los asmat y otros pueblos relacionados de la provincia de Papúa. Se considera que estas lenguas son una expansión reciente hacia la costa sur, de pueblos procedentes del norte.
Clasificación
[editar]Las lenguas asmat-kamoro son:
- Rama asmat: Asmat de costa Casuarina, asmat de Yaosakor, asmat central, asmat septentrional, citak, citak de Tamnim.
- Rama sabakor: Buruwai (Asienara), Kamberau (Iria)
- Diuwe
- Kamoro
- Sempan
Comparación léxica
[editar]Los numerales en diferentes lenguas Asmat-Kamoro son:[1]
| GLOSA | Asmat | Kamoro | Sabakor | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asmat central | Asmat sept. | Citak | PROTO- ASMAT | Buruwai | Kamberau | PROTO- SABAKOR | ||
| '1' | taka | toko | takà | *taka | 'ɛna ow'aʔ | sasiábaɾa | a'banə | *ʤaba- |
| '2' | yamuk | yomnok | zamnèk | jaminak | yam'ina tí'ɛʔ | abómera | ábomə | *abomə- |
| '3' | manintep | mbemtiap | a zamnèk àtaka | *mbem-tiap | t'óːɾwáʔ | abomayébeɾa | obómdawə | *abome-ʤaba |
| '4' | eaktaka wapuk | ebràk tàka | binada | bemsídabə | *bemsi-ʤaba | |||
| '5' | ban taka | ban takanim | m'aiɾɛ pamɛɾé | mánbawɛta | maiyíbəʔə | *mairibə | ||
| '6' | maibɛɾábanə | |||||||
| '7' | ||||||||
| '8' | ||||||||
| '9' | ||||||||
| '10' | maiɛɾoa minɛtiaʔ | |||||||
Referencias
[editar]- ↑ «Asmat-Kamoro (E. Chan)». Archivado desde el original el 3 de diciembre de 2013. Consultado el 11 de abril de 2014.
Bibliografía
[editar]- Drabbe. 1953. Spraakkunst van de Kamoro-taal. The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff.
- Drabbe. 1963. Drie Asmat-dialecten. Verhandelingen van het Koninklijk Instituut voor Taal-, Land- en Volkenkunde, No. 42. The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff.
- Malcom Ross (2005). "Pronouns as a preliminary diagnostic for grouping Papuan languages." In: Andrew Pawley, Robert Attenborough, Robin Hide and Jack Golson, eds, Papuan pasts: cultural, linguistic and biological histories of Papuan-speaking peoples, 15-66. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics.
- Voorhoeve, C.L. 1965. The Flamingo Bay Dialect of the Asmat language. Verhandelingen van het Koninklijk Instituut voor Taal-, Land- en Volkenkunde, No. 46. The Hague.
- Voorhoeve, C.L. 1968. "The Central and South New Guinea Phylum: a report on the language situation in south New Guinea." Pacific Linguistics, Series A, No. 16: 1-17. Canberra: The Australian National University.
- Voorhoeve, C.L. 1975. Languages of Irian Jaya: Checklist, Preliminary Classification, Language Maps, Wordlists. Pacific Linguistics, Series B, No. 31. Canberra: The Australian National University.
- Voorhoeve, C.L. 1980. The Asmat Languages of Irian Jaya.< Pacific Linguistics, Series B, No. 64. Canberra: The Australian National University.
- Wurm, Stephan Adolphe. 1983. The Papuan Languages of Oceania. Ars Linguistica 7. Tübingen: Narr.