1 South African Infantry Battalion
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
This article may contain an excessive amount of intricate detail that may interest only a particular audience. (November 2020) |
| 1 South African Infantry Battalion | |
|---|---|
 1 SAI emblem | |
| Founded | 26 January 1951 |
| Country | |
| Branch | |
| Type | Infantry |
| Role | Mechanised infantry |
| Size | Battalion |
| Part of | South African Infantry Formation |
| Garrison/HQ | Tempe, Bloemfontein |
| Motto(s) | Sevire parati |
| Equipment | Ratel |
| Engagements | |
| Insignia | |
| Company level Insignia |  |
| SA Mechanised Infantry beret bar c. 1992 |  |
1 South African Infantry Battalion is a mechanized infantry unit of the South African Army.
History
[edit]Oudtshoorn origin
[edit]With its establishment as 1 SA Infantry Training Battalion at Oudtshoorn on 26 January 1951, the unit became part of the infantry corps.
In 1953, the unit consisted of:
- a headquarters with companies at:
- 1 SAI itself in Oudsthoorn as A Company,
- 1 SSB in Bloemfontein as B Company;
- 4 Field Regiment in Potchefstroom as C Company;
and
- a supply & transport company, an attempt at all arms training.

The unit was reconstituted as 1 SA Infantry Battalion in November 1967 and moved to its current base at Tempe near Bloemfontein, in November 1973.[1]
1 SAI in the development of modern mechanised infantry
[edit]By 1976, infantry operations had transformed drastically when the Ratel Infantry Fighting Vehicle (IFV) was introduced, with the first Ratel course presented by then Major Roland de Vries in November at 1 SAI.
In 1977, 1 SAI received its first consignment of 42 Ratel IFVs, along with a redesigned shoulder flash, depicting a wild honey badger.
For the next four years, mechanised infantry leadership students shared the same lines as 1 SAI's conventional companies, but were required to wear a nutria brassard on the right arm with a green and yellow embroidered honey badger insignia in order to stand out and ensure Espirit de Corps. The training wing, identified as the T&D Wing, was where all students attended the same course until the Section Leaders Phase had been completed, where they were then awarded their Lance Corporal stripes and then placed with regular rifle companies. The rest of the future NCOs also received their stripes and future Officers received their white Candidate Officer's tabs. These students were then evaluated and split into the Mechanised Platoon Commanders Course and Specialist Instructors Course. These platoon commanders were destined to either become future leaders of 1 SAIs rifle companies or instructors at the Training Wing, while the Specialist Instructors would become Officers and NCOs responsible for training Ratel gunners and drivers. The Platoon NCOs were responsible for the support of the vehicles, platoon weapons and signal equipment of a specific platoon. Platoon sergeants were responsible for the training and discipline of an allocated platoon.
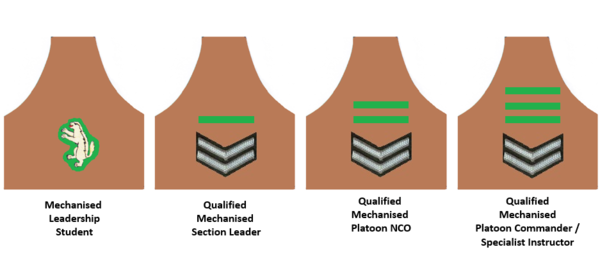
By January 1981, the training wing had been renamed to the Mechanised Leadership Wing and moved to the Akkedisdorp premises outside the lines of 1 SAI and next to 1 SSB. The distinctive honey badger student brassard was discontinued during this period.
The mechanised techniques developed at 1 SAI was transferred to two additional mechanised infantry battalions under development at that time, namely 4 SAI and 8 SAI.
Battalion Pioneer Platoon
[edit]1 SAI also had an assault pioneer capability in the 1980s, usually designated Oscar Company. Assault pioneers were the integral combat engineering component of the battalion. Assault pioneers were trained in tasks such as:
- Field defences and obstacles
- Mine detection and removal
- Primary demolitions
- Non standard bridging
- Anchorages and suspension traverses
The Pioneer Platoon provided small tasks and close support capabilities to the battalion ensuring immediacy of response and decreasing the workload of the engineer squadrons. By the 1990s this function was retired to the Engineering Corps however.
Bushwar
[edit]Operations
[edit]By 1978, 1 SAI took part in Operation Reindeer. 1 SAI was also later involved in:
Honouris Crux recipients
[edit]The following 1 SAI members were awarded the Honoris Crux decoration
Operation Sceptic;
- Lt. J.J. du Toit
- LCpl A.T. Rutherford
Operation Protea;
- Cpl A.D. Burgers
Relationship with 61 Mech
[edit]1 SAI was also the main feeder unit for mechanised infantry companies for 61 Mechanised Battalion Group during this period.[2]


Post 1994
[edit]Assimilation of 151 Battalion
[edit]Peled writes that after January 1993, 151 Battalion, formed from the Southern Sothos in the Orange Free area, was assimilated into 1 SAI.[3]

Murder at 1 SAI
[edit]In September 1999, Lt. S. Madubela from 1 SAI went on a shooting spree through the unit, killing seven personnel and injuring five, before being stopped and killed by his colleagues.[4]
Freedom of Entry
[edit]1 SAI received the freedom of entry to Bloemfontein in 1981.
Insignia
[edit]Previous Dress Insignia
[edit]
Current Dress Insignia
[edit]
Ordnance
[edit]Current
[edit]Vehicle mounted weapons
[edit]1 SAI is equipped with Ratel 20 Infantry Fighting Vehicles,[5] Ratel 60 mm (2.4 in) Mortar Platform Vehicles, Ratel Command Vehicles with mounted 12.7 mm (0.50 in) machine guns, Kwevoel 100 Armoured Trucks for IFV Recovery, field maintenance, fuel bunkers and water provision,[6] Samil 50 and 100 logistics trucks, Samil 20 trucks for its organic field workshops, Casspir APCs for its forward artillery observation party,[citation needed] and Rinkhals Field Ambulance.[7] 1 SAI has also used Buffel IFVs and Mambas at certain stages in its history. Ratel mounted weapons include the Denel Land Systems GI-2 20 mm (0.79 in) Quick Firing Cannon (QFC) (Ratel mounted), 60 mm (2.4 in) breech-loading mortar (Ratel mounted), Browning M1919[8] Machine gun and the Browning M2 12.75 mm (0.502 in) Machine gun.[8]



Lighter and personal weapons
[edit]1 SAI is equipped with the Vektor SS77 Squad Automatic Machine gun, Fabrique Nationale 7.62 mm (0.300 in) Light Machine gun, Vektor R4 5.56 mm (0.219 in) assault rifle, 40 mm (1.6 in) Multiple Grenade Launcher (MGL), Rocket Propelled grenade launcher (RPG-7),[citation needed] M26 Fragmentation grenade,[9] M4 60 mm (2.4 in) patrol mortar (PATMOR), and the Denel 99 mm (3.9 in) FT5 rocket launcher.[10]
Future
[edit]Under Project Hoefyster, the SANDF will eventually replace the Ratel family of vehicles with the Badger system.[11][12][13] Nine versions are contemplated of which three are earmarked for mechanized Infantry Battalions such as 1 SAI:[14][15][16]
- Command (mech infantry)
- Mortar (turreted 60mm breech loading long-range mortar) ( mech infantry)
- Missile (turreted Denel ZT3 Ingwe)
- Section (turreted 30mm cannon) (mech infantry)
- Fire Support (turreted 30mm cannon, but with more ammunition than the section vehicle)
- Signal variant
- Ambulance variant
- Artillery variant
1 SAI Mechanised Fleet early 1990s
[edit]Fighting Echelon Vehicles
[edit]1 Ratel 20 per section, 3 sections per platoon, 1 Ratel 60 per platoon, 3 platoons per company. 2 Ratel 12,7 per company.
A Echelon Vehicles
[edit]Unit Song
[edit]In 1 SAI wil ek bly,
dis die eenheid net vir my,
slaggereed en kommer vry,
met ons ratels veg ons ver,
onder die al en suider ster 1 SAI Bataljon,
1 SAI! Servire, servire, servire parati is ons lese as jy vra, 1 SAI Bataljon, 1 SAI!
From the shores of Cape Agulhas,
to the Northern bushveld trees,
We will fight our countries battles,
in the air, land and sea,
We will fight for right and freedom,
we will keep our honesty,
We are proud to claim the title of the 'Mechanised Infantry'.
Leadership
[edit]Training Battalion
[edit]| From | Honorary Colonel | To |
| From | Officer Commanding | To |
| 1967 | Cmdt H.N.H. Norton | c. 1968 |
| 1969 | Cmdt B.P.U. Strydom | c. 1971 |
| 1975 | Cmdt Len Meyer | c. 1977 |
| 1977 | Cmdt A.J.M. Joebert | c. 1977 |
| 1977 | Cmdt Frank Bestbier | c. 1978 |
| 1981 | Col A. Savides[17] | c. 1983 |
| 1983 | Col G.A. van Zyl | c. 1987 |
| 1990 | Col Cassie Schoeman | c. 1993 |
| 1993 | Col A. Bornman | c. 1995 |
| 1995 | Col C.J. van der Merwe | c. 1996 |
| 1996 | Lt Col Jan Wessels | c. 1999 |
| 2004 | Lt Col T.C. Mokhosi | c. 2008 |
| 2013 | Col T. Mashalaba | c. 2016 |
| 2016 | Lt Col T.S.A. Tseki | c. 2018 |
| 2020 | Lt Col M. Malatji | Nd |
| From | Regimental Sergeants Major | To |
| 1969 | WO1 R.H. Uekermann | 1972 |
| 1973 | WO1 A.A. Calmeyer | 1976 |
| 1976 | WO1 L.B. Calitz | 1980 |
| 1980 | WO1 J.R. Stone | 1986 |
| 1987 | WO1 E.H. Heimann | 1988 |
| 1988 | WO1 W.P. Wiese | 1993 |
| 1993 | WO1 T.J. Visagie | 1996 |
| 1996 | WO1 H.C.A Smit | 1997 |
| 1998 | WO1 J.M Nel | 2004 |
| 2015 | WO1 J. A. Koekemoer | Nd |
Mechanised Leadership Wing
[edit]| From | Officer Commanding | To |
| 1978 | Maj E. van Lill | c. nd |
| 1982 | Cmdt Cassie Schoeman | c. 1985 |
| 1995 | Lt Col. K. Schmidt | c. nd |
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "SADF.info". SADF.info. 26 January 1951. Retrieved 3 June 2012.
- ^ "Fact file: 1 SA Infantry Battalion". DefenceWeb. 1 March 2010. Retrieved 3 June 2012.
- ^ Peled, p.54
- ^ "Tempe killer's steps retraced - IOL News". iol.co.za. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
- ^ IDRC; Cock, Jacklyn; Mckenzie, Penny (1998). From defence to development : redirecting military resources in South Africa. Cape Town, South Africa & Ottawa, Canada: David Philip, International Development Research Centre. hdl:10625/14245. ISBN 0-88936-853-8.
- ^ "Samil 100 Kwevoel Armoured Truck". Tips Transport. Archived from the original on 5 August 2015. Retrieved 19 March 2015.
- ^ "Vehicles:Denel Mechem". Denel.
- ^ a b "Ratel". GlobalSecurity.org.
- ^ Engelbrecht, Leon (17 February 2010). "Fact file: M26 fragmentation hand grenade". defenceWeb. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
- ^ Engelbrecht, Leon (8 November 2010). "Work underway on RPG replacement". defenceWeb.
- ^ Engelbrecht, Leon (5 March 2009). "SA Army horse shod by December?". defenceWeb. Archived from the original on 24 February 2015. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
- ^ Natalie Greve (9 July 2014). "Land Systems SA secures sights contract for Denel's Badger". Engineering News. Retrieved 10 August 2018.
- ^ Venter, Dewald (22 May 2018). "Badger". Tanks Encyclopedia.
- ^ "South Africas Next IFV: Honey Badger Doesn't Care". Defense Industry Daily. 24 June 2014. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
- ^ Helfrich, Kim (29 February 2016). "Badger reaches Product Baseline One milestone - defenceWeb". defenceWeb. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
- ^ Martin, Guy (11 August 2016). "SANDF projects". defenceWeb. Retrieved 10 August 2018.
- ^ Engelbrecht, Leon (23 January 2009). "Tony Savides retires - defenceWeb". defenceWeb.



