Eleftherios Venizelos
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
Eleftheriοs Venizelos | |
|---|---|
| Ελευθέριος Βενιζέλος | |
 Venizelos in 1919 | |
| Prime Minister of Greece | |
| In office 16 January 1933 – 6 March 1933 | |
| President | Alexandros Zaimis |
| Preceded by | Panagis Tsaldaris |
| Succeeded by | Alexandros Othonaios |
| In office 5 June 1932 – 4 November 1932 | |
| President | Alexandros Zaimis |
| Preceded by | Alexandros Papanastasiou |
| Succeeded by | Panagis Tsaldaris |
| In office 4 July 1928 – 26 May 1932 | |
| President | Pavlos Kountouriotis Alexandros Zaimis |
| Preceded by | Alexandros Zaimis |
| Succeeded by | Alexandros Papanastasiou |
| In office 11 January 1924 – 6 February 1924 | |
| Monarch | George II |
| Preceded by | Stylianos Gonatas |
| Succeeded by | Georgios Kafantaris |
| In office 14 June 1917 – 4 November 1920 | |
| Monarch | Alexander |
| Preceded by | Alexandros Zaimis |
| Succeeded by | Dimitrios Rallis |
| In office 10 August 1915 – 24 September 1915 | |
| Monarch | Constantine I |
| Preceded by | Dimitrios Gounaris |
| Succeeded by | Alexandros Zaimis |
| In office 6 October 1910 – 25 February 1915 | |
| Monarchs | George I Constantine I |
| Preceded by | Stefanos Dragoumis |
| Succeeded by | Dimitrios Gounaris |
| Prime Minister of the Cretan State | |
| In office 2 May 1910 – 6 October 1910 | |
| Preceded by | Alexandros Zaimis (as High Commissioner) |
| Minister of Military Affairs | |
| In office 27 June 1917 – 18 November 1920 | |
| Monarch | Alexander |
| Prime Minister | Himself |
| Preceded by | Anastasios Charalambis |
| Succeeded by | Dimitrios Gounaris |
| Minister of Foreign Affairs | |
| In office 23 August – 7 October 1915 | |
| Monarch | Constantine I |
| Prime Minister | Himself |
| Preceded by | Dimitrios Gounaris |
| Succeeded by | Alexandros Zaimis |
| Minister of Justice and Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Cretan State | |
| In office 1908–1910 | |
| Minister of Justice of the Cretan State | |
| In office 17 April 1899 – 18 March 1901 --> | |
| Personal details | |
| Born | 23 August 1864 Mournies, Ottoman Empire (now Greece) |
| Died | 18 March 1936 (aged 71) Paris, France |
| Political party | Liberal Party |
| Spouse(s) | Maria Katelouzou (1891–1894) Helena Schilizzi (1921–1936) |
| Relations | Konstantinos Mitsotakis (nephew) Kyriakos Mitsotakis (great-nephew) |
| Children | Kyriakos Venizelos Sophoklis Venizelos |
| Parent(s) | Kyriakos Venizelos Styliani Ploumidaki |
| Alma mater | University of Athens |
| Profession | Politician Revolutionary Legislator Lawyer Jurist Journalist Translator |
| Awards | |
| Signature | |
| Website | National Foundation Research "Eleftherios K. Venizelos" |
| Military service | |
| Battles/wars | |
| Part of the Politics series |
| Republicanism |
|---|
| |
Eleftherios Kyriakou Venizelos (Greek: Ελευθέριος Κυριάκου Βενιζέλος, romanized: Eleuthérios Kyriákou Venizélos, pronounced [elefˈθeri.os cirˈʝaku veniˈzelos]; 23 August [O.S. 11 August] 1864[1] – 18 March 1936) was a Cretan Greek statesman and prominent leader of the Greek national liberation movement. He is noted for his contribution to the expansion of Greece and promotion of liberal-democratic policies.[2][3] As leader of the Liberal Party, he held office as prime minister of Greece for over 12 years, spanning eight terms between 1910 and 1933. During his governance, Venizelos entered into diplomatic cooperation with the Great Powers and had a profound influence on the internal and external affairs of Greece. He has therefore been labelled as "The Maker of Modern Greece"[4] and is still widely known as the "Ethnarch".[5]
His first entry into the international scene was with his significant role in the autonomy of the Cretan State and later in the union of Crete with Greece. In 1909, he was invited to Athens to resolve the political deadlock and became the country's Prime Minister. He initiated constitutional and economic reforms that set the basis for the modernization of Greek society and reorganized both the Greek Army and the Greek Navy in preparation for future conflicts. Before the Balkan Wars of 1912–1913, Venizelos' catalytic role helped gain Greece's entrance to the Balkan League, an alliance of the Balkan states against the Ottoman Empire. Through his diplomatic acumen with the Great Powers and with the other Balkan countries, Greece doubled its area and population with the liberation of Macedonia, Epirus, and most of the Aegean islands.
In World War I (1914–1918), he brought Greece on the side of the Allies, further expanding the Greek borders. However, his pro-Allied foreign policy brought him into conflict with the nonaligned faction of Constantine I of Greece, causing the National Schism of the 1910s. The Schism became an unofficial civil war, with the struggle for power between the two groups polarizing the population between the royalists and Venizelists for decades.[6] Following the Allied victory, Venizelos secured new territorial concessions in Western Anatolia and Thrace in an attempt to accomplish the Megali Idea, which would have united all Greek-speaking people along the Aegean Sea under the banner of Greece. He was, however, defeated in the 1920 General Election, which contributed to the eventual Greek defeat in the Greco-Turkish War (1919–22). Venizelos, in self-imposed exile, represented Greece in the negotiations that led to the signing of the Treaty of Lausanne and the agreement of a mutual population exchange between Greece and Turkey.
In January 1933 he became prime minister for the last time and in March 1935, after a coup attempt, he fled to Paris where he died. He was buried on a hill at the head of the Akrotiri peninsula beside the eastern outskirts of Chania city in Crete, close to the place where he was born. The Venizelos family graves are today one of the attractions of Chania.
Origins and early years
[edit]Ancestry
[edit]
The ancestors of Venizelos, named Crevvatas, lived in Mystras, in southern Peloponnese. During the Ottoman raids in the peninsula in 1770, a member of the Krevvatas family (Venizelos Krevvatas), the youngest of several brothers, managed to escape to Crete where he established himself. His sons discarded their patronymic and called themselves Venizelos. The family was of Laconic, Maniot, and Cretan origin.[7][additional citation(s) needed] Venizelos' mother, Styliani Ploumidakis, descended from the village of Theriso in Crete.[8]
However, during the National Schism, politician Konstantinos Krevattas denied that his family had any relation to Venizelos. In a letter to a Cretan partner, Venizelos wrote that his father Kyriakos had taken part in the siege of Monemvasia in 1821 with his brother Hatzinikolos Venizelos and 3 more brothers. His grandfather probably was Hatzipetros Venizelos, a merchant from Kythira.[9]
Family and education
[edit]
Eleftherios was born in Mournies, near Chania (formerly known as Canea) in then-Ottoman Crete to Kyriakos Venizelos, a Cretan merchant and revolutionary, and Styliani Ploumidaki.[10] When the Cretan revolution of 1866 broke out, Venizelos' family fled to the island of Syros, due to the participation of his father in the revolution.[7] They were not allowed to return to Crete and stayed in Syros until 1872, when Abdülaziz granted an amnesty.
He spent his final year of secondary education at a school in Ermoupolis in Syros, from which he received his certificate in 1880. In 1881, he enrolled at the University of Athens Law School and got his degree in Law with excellent grades. He returned to Crete in 1886 and worked as a lawyer in Chania. Throughout his life, he maintained a passion for reading and was constantly improving his skills in English, Italian, German, and French.[7]
Entry into politics
[edit]The situation in Crete during Venizelos' early years was fluid. The Ottoman Empire was undermining the reforms, which were made under international pressure, while the Cretans desired to see the Sultan, Abdul Hamid II, abandon "the ungrateful infidels".[11] Under these unstable conditions Venizelos entered into politics in the elections of 2 April 1889 as a member of the island's liberal party.[10] As a deputy, he was distinguished for his eloquence and his radical opinions.[12]
Political career in Crete
[edit]Cretan uprising
[edit]Background
[edit]The numerous revolutions in Crete, during and after the Greek War of Independence (1821, 1833, 1841, 1858, 1866, 1878, 1889, 1895, 1897)[13] were the result of the Cretans' desire for enosis — union with Greece.[14] In the Cretan revolution of 1866, the two sides, under the pressure of the Great Powers, came to an agreement, which was finalized in the Pact of Chalepa.[citation needed] Later the Pact was included in the provisions of the Treaty of Berlin, which was supplementing previous concessions granted to the Cretans — e.g. the Organic Law Constitution (1868) designed by William James Stillman. In summary, the Pact granted a large degree of self-government to Greeks in Crete as a means of limiting their desire to rise up against their Ottoman overlords.[citation needed] However the Muslims of Crete, who identified with Ottoman Empire, were not satisfied with these reforms, as in their view the administration of the island was delivered to the hands of the Christian Greek population. In practice, the Ottoman Empire failed to enforce the provisions of the Pact, thus fueling the existing tensions between the two communities; instead, the Ottoman authorities attempted to maintain order by dispatching substantial military reinforcements during 1880–1896. Throughout that period, the Cretan Question was a major issue of friction in the relations of independent Greece with the Ottoman Empire.[citation needed]
In January 1897, violence and disorder escalated on the island, thus polarizing the population. Massacres against the Christian population took place in Chania[15][16][17][18] and Rethimno.[18][19][20] The Greek government, pressured by public opinion, intransigent political elements, extreme nationalist groups such as Ethniki Etaireia,[21] and the reluctance of the Great Powers to intervene, decided to send warships and army personnel to defend the Cretan Greeks.[22] The Great Powers had no option then but to proceed with the occupation of the island, but they were late. A Greek force of about 2,000 men had landed at Kolymbari on 3 February 1897,[23] and its commanding officer, Colonel Timoleon Vassos declared that he was taking over the island "in the name of the King of the Hellenes" and that he was announcing the union of Crete with Greece.[24] This led to an uprising that spread immediately throughout the island. The Great Powers decided to blockade Crete with their fleets and land their troops, thus stopping the Greek army from approaching Chania.[25]
Events at Akrotiri
[edit]
Venizelos, at that time, was on an electoral tour of the island. Once he "saw Canea in flames",[26] he hurried to Malaxa, near Chania, where a group of about 2,000 rebels had assembled and established himself as their header. He proposed an attack, along with other rebels, on the Turkish forces at Akrotiri in order to displace them from the plains (Malaxa is at a higher altitude). Venizelos' subsequent actions at Akrotiri form a central set-piece in his myth. People composed poems on Akrotiri and his role there; editorials and articles spoke about his bravery, his visions, and his diplomatic genius as the inevitable accompaniment of later greatness.[15] Venizelos spent the night in Akrotiri and a Greek flag was raised. The Ottoman forces requested help from the foreign admirals and attacked the rebels, with the ships of the Great Powers bombarding the rebel positions at Akrotiri. A shell threw down the flag, which was raised up again immediately. The mythologizing became more pronounced when we come to his actions in that February, as the following quotes display:
On 20th of February [he] was ordered by the admirals to lower the flag and disband his rebel force. He refused![27]
Venizelos turned towards the port of Souda, where the warships were anchored, and explained: "You have cannon-balls – fire away! But our flag will not come down" ... [after the flag was hit] Venizelos ran forward; his friends stopped him; why expose a valuable life so uselessly?[28]
There was that famous day in February 1897 when ... he rejected the orders of the Protecting Powers and in the picturesque phrase in the Greek newspapers "defied the navies of Europe"[29]
Under the smooth diplomat of today is the revolutionist who prodded the Turks out of Crete and the bold chieftain who camped with a little band of rebels on a hilltop above Canea and there he defied the consuls and the fleets of all the [Great] Powers![30]
On the same evening of the bombardment, Venizelos wrote a protest to the foreign admirals, which was signed by all the chieftains present at Akrotiri. He wrote that the rebels would keep their positions until everyone was killed by the shells of European warships in order not to let the Turks remain in Crete.[31] The letter was deliberately leaked to international newspapers, evoking emotional reactions in Greece and in Europe, where the idea of Christians, who wanted their freedom, being bombarded by Christian vessels, caused popular indignation. Throughout Western Europe much popular sympathy for the cause of the Christians in Crete was manifested, and much popular applause was bestowed on the Greeks.[25]
War in Thessaly
[edit]

The Great Powers sent a verbal note on 2 March to the governments of Greece and the Ottoman Empire, presenting a possible solution to the "Cretan Question", under which Crete to become an autonomous state under the suzerainty of the Sultan.[11] The Porte replied on 5 March, accepting the proposals in principle, but on 8 March the Greek government rejected the proposal as a non-satisfactory solution and instead insisted on the union of Crete with Greece as the only solution.[citation needed]
As a representative of the Cretan rebels, Venizelos met the admirals of the Great Powers on a Russian warship on 7 March 1897. Even though no progress was made at the meeting, he persuaded the admirals to send him on a tour of the island, under their protection, in order to explore the people's opinions on the question of autonomy versus union.[33] At the time, the majority of the Cretan population initially supported the union, but the subsequent events in Thessaly turned the public opinion towards autonomy as an intermediate step.[citation needed]
In reaction to the rebellion of Crete and the assistance sent by Greece, the Ottomans had relocated a significant part of their army in the Balkans to the north of Thessaly, close to the borders with Greece.[34] Greece in reply reinforced its borders in Thessaly. However, irregular Greek forces, who were members of the Ethniki Etairia (followers of the Megali Idea) acted without orders and raided Turkish outposts,[35] leading the Ottoman Empire to declare war on Greece on 17 April. The war was a disaster for Greece. The Turkish army was better prepared, in large part due to the recent reforms carried out by a German mission under Baron von der Goltz, and the Greek army was in retreat within weeks. The Great Powers again intervened, and an armistice was signed in May 1897.[36]
Conclusion
[edit]The defeat of Greece in the Greco-Turkish war, costing small territorial losses at the borderline in northern Thessaly and an indemnity of £4,000,000,[36] turned into a diplomatic victory. The Great Powers (Britain, France, Russia, and Italy), following the massacre in Heraklion on 25 August,[18][37][38] imposed a final solution on the "Cretan Question"; Crete was proclaimed an autonomous state under Ottoman suzerainty.[citation needed]
Venizelos played an important role in this solution, not only as the leader of the Cretan rebels but also as a skilled diplomat with his frequent communication with the admirals of the Great Powers.[38] The four Great Powers assumed the administration of Crete; and Prince George of Greece, the second son of King George I of Greece, became High Commissioner, with Venizelos serving as his minister of Justice from 1899 to 1901.[39]
Autonomous Cretan State
[edit]
Prince George of Greece was appointed High Commissioner of the Cretan State for a three-year term.[39] On 13 December 1898, he arrived at Chania, where he received an unprecedented reception. On 27 April 1899, the High Commissioner created an Executive Committee composed of the Cretan leaders. Venizelos became minister of Justice, and with the rest of the Committee, they began to organize the State and create a "Cretan constitution". Venizelos insisted on not making reference to religion so all the residents of Crete would feel represented. For his stance, he was later accused of pro-Turk (pro-Muslim) by his political opponents on the island.
After Venizelos submitted the complete juridical legislation on 18 May 1900, disagreements between him and Prince George began to emerge. [citation needed] Prince George decided to travel to Europe and announced to the Cretan population that "When I am traveling in Europe, I shall ask the Powers for annexation, and I hope to succeed on account of my family connections".[40] The statement reached the public without the knowledge or approval of the Committee. Venizelos said to the Prince that it would not be proper to give hope to the population for something that was not feasible at the given moment. As Venizelos had expected, during the Prince's journey, the Great Powers rejected his request.[39][40]
The disagreements continued on other topics; the Prince wanted to build a palace, but Venizelos strongly opposed it as that would mean the perpetuation of the current arrangement of Governorship; Cretans accepted it only as temporary until a final solution was found.[39] Relations between the two men became increasingly soured, and Venizelos repeatedly submitted his resignation.[41]
In a meeting of the Executive Committee, Venizelos expressed his opinion that the island was not autonomous since the military forces of the Great Powers were still present and that the Great Powers were governing through their representative, the Prince. Venizelos suggested that once the Prince's service expired, then the Great Powers should be invited to the Committee, which, according to article 39 of the constitution (which was suppressed in the conference of Rome) would elect a new sovereign, thereby removing the need for the presence of the Great Powers. Once the Great Powers' troops and their representatives left the island, the union with Greece would be easier to achieve. This proposal was exploited by Venizelos' opponents, who accused him of wanting Crete to be an autonomous hegemony. Venizelos replied to the accusations by submitting his resignation once again, with the reasoning that it would be impossible henceforth to collaborate with the Committee's members; he assured the Commissioner, however, that he did not intend to join the opposition.[39]
On 6 March 1901, in a report, he exposed the reasons that compelled him to resign to the High Commissioner, which was, however, leaked to the press. On 20 March, Venizelos was dismissed because "he, without any authorization, publicly supported opinions opposite of those of the Commissioner".[39][42] Henceforth, Venizelos assumed the leadership of the opposition to the Prince. For the next three years, he carried out a hard political conflict until the administration was virtually paralyzed, and tensions dominated the island. Inevitably, these events led in March 1905 to the Theriso Revolution, whose leader he was.[citation needed]
Revolution of Theriso
[edit]
On 10 March 1905, the rebels gathered in Theriso and declared "the political union of Crete with Greece as a single free constitutional state".[43] The resolution was given to the Great Powers, where it was argued that the illegitimate provisional arrangement was preventing the island's economic growth and that the only logical solution to the "Cretan Question" was the unification with Greece. The High Commissioner, with the approval of the Great Powers, replied to the rebels that military force would be used against them.[39] However, more deputies joined with Venizelos in Theriso. The Great Powers' consuls met with Venizelos in Mournies in an attempt to achieve an agreement, but without any results.[citation needed]


The revolutionary government asked that Crete be granted a regime similar to that of Eastern Rumelia. On 18 July, the Great Powers declared martial law, but that did not discourage the rebels. On 15 August, the regular assembly in Chania voted in favor of most of the reforms that Venizelos proposed. The Great Powers' consuls met Venizelos again and accepted the reforms he had proposed. This led to the end of the Theriso revolt and to the resignation of Prince George as the High Commissioner.[citation needed] The Great Powers assigned the authority for selecting the island's new High Commissioner to King George I of Greece, thereby de facto nullifying the Ottoman suzerainty. An ex-Prime Minister of Greece, Alexandros Zaimis, was chosen for the place of High Commissioner, and Greek officers and non-commissioned officers were allowed to undertake the organization of the Cretan Gendarmerie. As soon as the Gendarmerie was organized, the foreign troops began to withdraw from the island. This was also a personal victory for Venizelos, who, as a result, achieved fame not only in Greece but also in Europe.[39]
Following the Young Turk Revolution, which Venizelos welcomed, Bulgaria declared its independence from the Ottoman Empire on 5 October 1908, and one day later Franz Joseph, Emperor of Austria announced the annexation of Bosnia-Herzegovina. Encouraged by these events, on the same day, the Cretans, in turn, rose up. On that day, thousands of citizens in Chania and the surrounding regions formed a rally in which Venizelos declared the union of Crete with Greece. Having communicated with the government of Athens, Zaimis left for Athens before the rally.[citation needed]
An assembly was convened and declared the independence of Crete. The civil servants were sworn in the name of King George I of Greece, while a five-member Executive Committee was established, with the authority to control the island on behalf of the King and according to the laws of the Greek state. Chairman of the committee was Antonios Michelidakis, and Venizelos became Minister of Justice and Foreign Affairs. In April 1910, a new assembly was convened, and Venizelos was elected chairman and then Prime Minister. All foreign troops departed from Crete, and power was transferred entirely to Venizelos' government.[44][clarification needed]
Political career in Greece
[edit]Goudi military revolution of 1909
[edit]After I finished my studies in Athens I returned home and hung out my bandolier. I had not tried many cases in the court of my home island before it became necessary for me to take up arms against the Turkish government. Although my father was born in Greece, I was considered an Ottoman subject—therefore a rebel—because my mother was born under the Turkish flag. At the end of the revolution, I returned again to my hometown and resumed my practice. I did not have time, however, to go far with it, for I had to take up arms again and go to the mountains. I soon reached the point where I had to decide whether I ought to be a lawyer by profession and a revolutionary at intervals or a revolutionary by profession and a lawyer at intervals ... I naturally became a revolutionary by profession.
In May 1909, a number of officers in the Greek army emulating the Young Turk Committee of Union and Progress, sought to reform their country's national government and reorganize the army, thus creating the Military League. The League, in August 1909, camped in the Athenian suburb of Goudi with their supporters, forcing the government of Dimitrios Rallis to resign, and a new one was formed with Kiriakoulis Mavromichalis. An inaugurating period of direct military pressure upon the Chamber followed, but initial public support for the League quickly evaporated when it became apparent that the officers did not know how to implement their demands.[47] The political dead-end remained until the League invited Venizelos from Crete to undertake the leadership.[citation needed]

Venizelos went to Athens, and after consulting with the Military League and with representatives of the political world, he proposed a new government and Parliament's reformation. His proposals were considered by the King and the Greek politicians dangerous for the political establishment. However, King George I, fearing an escalation of the crisis, convened a council with political leaders and recommended they accept Venizelos' proposals. After many postponements, the King agreed to assign Stephanos Dragoumis (Venizelos' indication) to form a new government that would lead the country to elections once the League was disbanded.[48] In the elections of 8 August 1910, almost half the seats in the parliament were won by Independents, who were newcomers to the Greek political scene. Venizelos, despite doubts as to the validity of his Greek citizenship and without having campaigned in person, finished at the top of the electoral list in Attica. He was immediately recognized as the leader of the independents, and thus, he founded the political party, Komma Fileleftheron (Liberal Party). Soon after his election, he decided to call for new elections in the hope of winning an absolute majority. The old parties boycotted the new election in protest[47] and on 11 December 1910, Venizelos' party won 307 seats out of 362, with most of the elected citizens being new in the political scene. Venizelos formed a government and started to reorganize the economic, political, and national affairs of the country.[citation needed]
Reforms in 1910–1914
[edit]Venizelos tried to advance his reform program in the realms of political and social ideologies, education, and literature by adopting practically viable compromises between often conflicting tendencies. In education, for example, the dynamic current in favor of the use of the popular spoken language, dimotiki, provoked conservative reactions, which led to the constitutionally embedded decision (Article 107) in favor of a formal "purified" language, katharevousa, which looked back to classical precedents.[49]
On 20 May 1911, a revision of the Constitution was completed, which focused on strengthening individual freedoms, introducing measures to facilitate the legislative work of the Parliament, establishing obligatory elementary education, the legal right for compulsory expropriation, ensuring permanent appointment for civil servants, the right to invite foreign personnel to undertake the reorganization of the administration and the armed forces, the re-establishment of the State Council and the simplification of the procedures for the reform of the Constitution. The aim of the reform program was to consolidate public security and the rule of law as well as to develop and increase the wealth-producing potential of the country. In this context, the long-planned "eighth" Ministry, the Ministry of National Economy, assumed a leading role. This Ministry, from the time of its creation at the beginning of 1911, was headed by Emmanuel Benakis, a wealthy Greek merchant from Egypt and friend of Venizelos.[49] Between 1911 and 1912 a number of laws aiming to initiate labor legislation in Greece were promulgated. Specific measures were enacted that prohibited child labor and night-shift work for women, regulated the hours of the working week and the Sunday holiday, and allowed for labor organizations.[50] Venizelos also took measures for the improvement of management, justice, and security and for the settlement of the landless peasants of Thessaly.[49]
Balkan Wars
[edit]Background
[edit]
At the time, there were diplomatic contacts with the Ottoman Empire to initiate reforms in Macedonia and in Thrace, which at the time were under the control of the Ottoman Empire, for improving the living conditions of the Christian populations. Failure of such reforms would leave a single option to remove the Ottoman Empire from the Balkans, an idea that most Balkan countries shared. This scenario appeared realistic to Venizelos because the Ottoman Empire was under a constitutional transition, and its administrative mechanism was disorganized and weakened.[51] There was also no fleet capable of transporting forces from Asia Minor to Europe, while in contrast, the Greek fleet was dominating the Aegean Sea. Venizelos did not want to initiate any immediate major movements in the Balkans, until the Greek army and navy were reorganized (an effort that had begun from the last government of Georgios Theotokis) and the Greek economy was revitalized.[52] In light of this, Venizelos proposed to Ottoman Empire to recognize the Cretans the right to send deputies to the Greek Parliament, as a solution for closing the Cretan Question. However, the Young Turks (feeling confident after the Greco-Turkish war in 1897) threatened that they would make a military walk to Athens, if the Greeks insisted on such claims.[citation needed]
Balkan League
[edit]
Venizelos, seeing no improvements after his approach with the Turks on the Cretan Question and at the same time not wanting to see Greece remain inactive as in the Russo-Turkish War in 1877 (where Greece's neutrality left the country out of the peace talks), he decided that the only way to settle the disputes with Ottoman Empire, was to join the other Balkan countries, Serbia, Bulgaria and Montenegro, in an alliance known as the Balkan League. Crown Prince Constantine was sent to represent Greece to a royal feast in Sofia, and in 1911 Bulgarian students were invited to Athens.[53] These events had a positive impact and on 30 May 1912 Greece and the Kingdom of Bulgaria signed a treaty that ensured mutual support in case of a Turkish attack on either country. Negotiations with Serbia, which Venizelos had initiated to achieve a similar agreement, were concluded in early 1913,[54] before that there were only oral agreements.[55]
Montenegro opened hostilities by declaring war on the Ottoman Empire on 8 October 1912. On 17 October 1912, Greece along with her Balkan allies, declared war on the Ottoman Empire, thus joining the First Balkan War.[54] On 1 October, in a regular session of the Parliament Venizelos announced the declaration of war to the Ottomans and accepting the Cretan deputies, thus closing the Cretan Question, with the declaration of the union of Crete with Greece. The Greek population received these developments very enthusiastically.[citation needed]
First Balkan War – The first conflict with Prince Constantine
[edit]
The outbreak of the First Balkan War caused Venizelos a great deal of trouble in his relations with Crown Prince Constantine. Part of the problems can be attributed to the complexity of the official relations between the two men. Although Constantine was a Prince and the future King, he also held the title of army commander, thus remaining under the direct order of the Ministry of Military Affairs, and subsequently under Venizelos. But his father, King George, in accordance with the constitutional conditions of the time, had been the undisputed leader of the country. Thus in practical terms, Venizelos' authority over his commander of the army was diminished due to the obvious relation between the Crown Prince and the King.[citation needed]
In these conditions, the army started a victorious march to Macedonia under the command of Constantine. Soon, the first disagreement between Venizelos and Constantine emerged, and it concerned the aims of the army's operations. The Crown Prince insisted on the clear military aims of the war: to defeat the opposed Ottoman army as a necessary condition for any occupation, wherever the opponent army was or was going, and the main part of the Ottoman army soon started retreating to the north towards Monastir. Venizelos was more realistic and insisted on the political aims of the war: to liberate as many geographical areas and cities as fast as possible, particularly Macedonia and Thessaloniki; thus heading east. The debate became evident after the victory of the Greek army at Sarantaporo, when the future direction of the armies' march was to be decided. Venizelos intervened and insisted that Thessaloniki, as a major city and strategic port in the surrounding area, should be taken at all costs and thus a turn to the east was necessary.[citation needed] In accordance to his views, Venizelos sent the following telegraph to the General Staff:
Salonique à tout prix![56]

and tried to keep frequent communication with the key figure, the King, in order to prevent the Crown Prince from marching north.[56] Subsequently, although the Greek army won the Battle of Giannitsa situated 40 km west of Salonika, Constantine's hesitation in capturing the city after a week had passed, led into an open confrontation with Venizelos. Venizelos, having accurate information from the Greek embassy in Sofia about the movement of the Bulgarian army towards the city, sent a telegram to Constantine in a strict tone, holding him responsible for the possible loss of Thessaloniki. The tone in Venizelos' telegram and that in the answer from Constantine that followed to announce the final agreement with the Turks, is widely considered as the start of the conflict between the two men that would lead Greece into the National Schism during World War I. Finally, on 26 October 1912, the Greek army entered Thessaloniki, shortly ahead of the Bulgarians.[57] But soon a new reason of friction emerged due to Venizelos' concern about Constantine's acceptance of the Bulgarian request to enter the city. A small Bulgarian unit, which soon became a full division, moved into the city and immediately started an attempt to establish a condominium in spite of initial assurances to the contrary, showing no intentions to leave. After Venizelos' protest Constantine asked him to take the responsibility (as a prime minister) by ordering him to force them out, but that was hardly an option since that would certainly lead to confrontation with the Bulgarians. To Venizelos' view, since Constantine allowed the Bulgarians to enter the city, he now passed the responsibility of a possible conflict with them to him, in an attempt to deny his initial fault. To Constantine, it was an attempt by Venizelos to get involved in clearly military issues. Most historians agree that Constantine failed to see the political dimensions of his decisions. As a consequence both incidents increased mutual misunderstanding shortly before Constantine's accession to the throne.[citation needed]
Once the campaign in Macedonia was completed, a large part of the Greek army under the Crown Prince was redeployed to Epirus, and in the Battle of Bizani, the Ottoman positions were overcome and Ioannina taken on 22 February 1913. Meanwhile, the Greek navy rapidly occupied the Aegean islands, which were still under Ottoman rule. After two victories, the Greek fleet established naval supremacy over the Aegean, preventing the Turks from bringing reinforcements to the Balkans.[58][59]
On 20 November, Serbia, Montenegro, and Bulgaria signed a truce treaty with Turkey. It followed a conference in London, in which Greece took part, although the Greek army still continued its operations in the Epirus front. The conference led to the Treaty of London between the Balkan countries and Turkey. These two conferences gave the first indications of Venizelos' diplomatic efficiency and realism. During the negotiations and facing the dangers of Bulgarian maximalism, Venizelos succeeded in establishing close relations with the Serbs. A Serbian-Greek military protocol was signed on 1 June 1913, ensuring mutual protection in case of a Bulgarian attack.[citation needed]
Second Balkan War
[edit]

Despite all this, the Bulgarians still wanted to become a hegemonic power in the Balkans and made excessive claims to this end, while Serbia asked for more territory than what was initially agreed with the Bulgarians. Serbia was asking for a revision of the original treaty since it had already lost north Albania due to the Great Powers' decision to establish the state of Albania in an area that had been recognized as a Serbian territory of expansion under the prewar Serbo-Bulgarian treaty. Bulgarians also laid claims on Thessaloniki and most of Macedonia. In the conference of London, Venizelos rebuffed these claims, citing the fact that it had been occupied by the Greek army,[60] and that Bulgaria had denied any definite settlement of territorial claims during the pre-war discussions, as it had done with Serbia.[citation needed]
The rupture between the allies, due to the Bulgarian claims, was inevitable, and Bulgaria found herself standing against Greece and Serbia. On 19 May 1913, a pact of alliance was signed in Thessaloniki between Greece and Serbia. On 19 June, the Second Balkan War began with a surprise Bulgarian assault against Serbian and Greek positions.[citation needed] Constantine, now King after his father's assassination in March, neutralized the Bulgarian forces in Thessaloniki and pushed the Bulgarian army further back with a series of hard-fought victories. Bulgaria was overwhelmed by the Greek and Serbian armies,[citation needed] while in the north Romania interfered against Bulgaria and the Romanian army was marching towards Sofia; Ottomans also took advantage of the situation and retook most of the territory taken by Bulgaria. The Bulgarians asked for a truce. Venizelos went to Hadji-Beylik, where the Greek headquarters were, to confer with Constantine on the Greek territorial claims in the peace conference. Then he went to Bucharest, where a peace conference was assembled. On 28 June 1913 a peace treaty was signed with Greece, Montenegro, Serbia and Romania on one side and Bulgaria on the other. Thus, after two successful wars, Greece had doubled its territory by gaining most of Macedonia, Epirus, Crete and the rest of the Aegean Islands,[61] although the status of the latter remained as yet undetermined and a cause of tension with the Ottomans.[citation needed]
World War I and Greece
[edit]Dispute over Greece's role in World War I
[edit]
With the outbreak of World War I and the Austro-Hungarian invasion of Serbia, a major issue started regarding the participation of Greece and Bulgaria in the war. Greece had an active treaty with Serbia, which was the treaty activated in the 1913 Bulgarian attack that caused the Second Balkan War. That treaty was envisaged in a purely Balkan context and was thus invalid against Austria-Hungary, as was supported by Constantine and his advisors.[citation needed]
The situation changed when the Allies, in an attempt to help Serbia, offered Bulgaria the Monastir–Ochrid area of Serbia and the Greek Eastern Macedonia (the Kavala and Drama areas) if she joined the Entente. Venizelos, having received assurances over Asia Minor if the Greeks participated in the alliance, agreed to cede the area to Bulgaria.[62]
But Constantine's anti-Bulgarism made such a transaction impossible. Constantine refused to go to war under such conditions, and the men parted. As a consequence, Bulgaria joined the Central Powers and invaded Serbia, an event that led to Serbia's final collapse. Greece remained neutral. Venizelos supported an alliance with the Entente, not only believing that Britain and France would win but also that it was the only choice for Greece because the combination of the strong Anglo-French naval control over the Mediterranean and the geographical distribution of the Greek population to the coast, could have ill effects in the case of a naval blockade, as he characteristically remarked:
One cannot kick against geography![63]
On the other hand, Constantine favored the Central Powers and wanted Greece to remain neutral.[citation needed] He was influenced both by his belief in the military superiority of Germany and also by his German wife, Queen Sophia, and his pro-German court. He therefore strove to secure a neutrality, which would be favorable to Germany and Austria.[64]
In 1915, Winston Churchill (then First Lord of the Admiralty) suggested that Greece take action in Dardanelles on behalf of the allies.[65] Venizelos saw this as an opportunity to bring the country on the side of the Entente in the conflict. However, the King and the Hellenic Army General Staff disagreed and Venizelos submitted his resignation on 21 February 1915.[64] Venizelos' party won the elections and formed a new government.[citation needed]
National Schism
[edit]
Even though Venizelos promised to remain neutral, after the elections of 1915, he said that Bulgaria's attack on Serbia, with which Greece had a treaty of alliance, obliged him to abandon that policy. A small-scale mobilization of the Greek army took place.
The dispute between Venizelos and the King reached its height shortly after that, and the King invoked a Greek constitutional provision that gave the monarch the right to dismiss a government unilaterally. Meanwhile, using the excuse of saving Serbia, in October 1915, the Entente disembarked an army in Thessaloniki,[citation needed] after invitation by Venizelos. Prime Minister Venizelos's action enraged Constantine.
The dispute continued between the two men, and in December 1915, King Constantine forced Venizelos to resign for a second time and dissolved the Liberal-dominated parliament, calling for new elections. Venizelos left Athens and moved back to Crete. Venizelos did not take part in the elections, as he considered the dissolution of Parliament unconstitutional.[66][67]

On 26 May 1916 the Fort Rupel (a significant military fort in Macedonia) was unconditionally surrendered by the royalist government to Germano-Bulgarian forces.[68] This produced a deplorable impression. The Allies feared a possible secret alliance between the royalist government and the Central Powers, placing their armies in grave danger in Macedonia. On the other hand, the surrender of Fort Rupel for Venizelos and his supporters meant the beginning of the destruction of Greek Macedonia. Despite German assurances that the integrity of the Kingdom of Greece would be respected, they were unable to restrain the Bulgarian forces, which had started dislocating the Greek population, and by 4 September Kavala was occupied.[69]
On 16 August 1916, during a rally in Athens, and with the support of the allied army that had landed in Thessaloniki under the command of General Maurice Sarrail, Venizelos publicly announced his total disagreement with the Crown's policies. The effect of this was to further polarize the population between the royalists (also known as anti-Venezelists), who supported the crown, and Venizelists, who supported Venizelos. On 30 August 1916, Venizelist army officers organized a military coup in Thessaloniki, and proclaimed the "Provisional Government of National Defence". Venizelos, along with Admiral Pavlos Kountouriotis and General Panagiotis Danglis agreed to form a provisional government, and on 9 October, they moved to Thessaloniki and assumed command of the National Defence to oversee the Greek participation in the allied war effort. The triumvirate, as the three men became known, had formed this government in direct conflict with the Athens political establishment.[70] There they founded a separate "provisional state" including Northern Greece, Crete, and the Aegean Islands, with the support of the Entente.[71] Primarily, these areas comprised the "New Lands" won during the Balkan Wars, in which Venizelos enjoyed broad support, while "Old Greece" was mostly pro-royalist. However, Venizelos declared, "we are not against the King, but against the Bulgarians". He didn't want to abolish the monarchy and continued his efforts to persuade the King to join the Allies, blaming his "bad advisors" for his stance.
The National Defence government started assembling an army for the Macedonian front and soon participated in operations against the Central Powers forces.[citation needed]
"Noemvriana" – Greece enters World War I
[edit]
In the months following the creation of the provisional government in Thessaloniki in late August, negotiations between the Allies and the king intensified. The Allies wanted further demobilization of the Greek army as a counterbalance to the royalist government's unconditional surrender of Fort Rupel and the military evacuation of Thessaly to ensure the safety of their troops in Macedonia. On the other hand, the king wanted assurances that the Allies would not officially recognize Venizelos' provisional government or further support it, guarantees that Greece's integrity and neutrality would be respected, and a promise that any war material surrendered to the Allies would be returned after the war.[72]
The Franco-British use of Greece's territory in co-operation with the Venizelos government[i] throughout 1916 was opposed in royalist circles and therefore increased Constantine's popularity, and caused much excitement and several anti-Allied demonstrations took place in Athens.[70] Moreover, a growing movement had been developed in the army among lower officers, led by military officers Ioannis Metaxas and Sofoklis Dousmanis, determined to oppose disarmament and the surrender of any war materials to the Allies.[73]

The Allies' pressure on the government of Athens continued. On the next day, 24 November, du Fournet presented a new ultimatum ending on 1 December to the government of Athens, demanding the immediate surrender of at least ten mountain batteries.[74] The admiral made a last effort to persuade the king to accept France's demands. He advised the king that according to his orders, he would land an Allied contingent with the aim to occupy certain positions in Athens until his demands were satisfied.[74] In reply, the King claimed that he was pressed by the army and the people not to submit to disarmament and refused to make any commitment. However, he promised that the Greek forces would receive orders not to fire against the Allied contingent.[75] Despite the gravity of the situation, both the royalist government and the Allies let the events take their own course. The royalist government decided to reject the admirals' demands on 29 November, and armed resistance was organized. By 30 November, military units and royalist militia (the epistratoi, "reservists") from surrounding areas had been recalled and gathered in and around Athens (in total over 20,000 men[76][77][78]) and occupied strategic positions, with orders not to fire unless fired upon.[75] On the other hand, the Allied authorities failed in their assessment of the prevailing temper. A diplomat characteristically insisted that the Greeks were bluffing, and in the face of force, they would "bring the cannons on a plater"; a viewpoint that Du Fournet also shared.[75]

The Allies landed a small contingent in Athens on 1 December [O.S. 18 November] 1916. However, it met organized resistance, and an armed confrontation took place for a day till a compromise was reached. After the evacuation of the Allied contingent from Athens the following day, a royalist mob raged through the city for three days, targeting supporters of Venizelos. The incident became known as the Noemvriana in Greece, which was using the Old Style calendar at the time, and drove a deep wedge between the Venizelists and their political opponents, deepening what would become known as the National Schism.[citation needed]
After the armed confrontation in Athens, on 2 December [O.S. 19 November] 1916, Britain and France officially recognized the government under Venizelos as the lawful government, effectively splitting Greece into two separate entities.[79] On 7 December [O.S. 24 November] 1916, Venizelos' provisional government officially declared war on the Central Powers.[80][81] In reply, a royal warrant for the arrest of Venizelos was issued and the Archbishop of Athens, under pressure by the royal house,[82] anathematised him.[83] The Allies unwilling to risk a new fiasco, but determined to solve the problem, established a naval blockade around southern Greece, which was still loyal to the king, and that caused extreme hardship to people in those areas.[84] In June, France and Great Britain decided to invoke their obligation as "protecting powers", who had promised to guarantee a constitutional form for Greece at the time the Kingdom was created, to demand the king's resignation.[85] Constantine accepted and on 15 June 1917 went to exile, leaving his son Alexander on the throne as demanded (whom the Allies considered as pro-Entente), instead of his elder son and crown prince, George.[86][87] His departure was followed by the deportation of many prominent royalists, especially army officers such as Ioannis Metaxas, to exile in France and Italy.
The course of events paved the way for Venizelos to return to Athens on 29 May 1917, and Greece, now unified, officially entered the war on the side of the Allies. Subsequently, the entire Greek army was mobilized (though tensions remained inside the army between supporters of the monarchy and supporters of Venizelos) and began to participate in military operations against the Central Powers army on the Macedonian front.[88]
Conclusion of World War I
[edit]

By the fall of 1918, the Greek army had 300,000 soldiers, and it was the largest single national component of the Allied army on the Macedonian front.[88] The presence of the entire Greek army gave the critical mass that altered the balance between the opponents in the Macedonian front. Under the command of French General Franchet d'Espèrey, a combined Greek, Serbian, French, and British force launched a major offensive against the Bulgarian and German army, starting on 14 September 1918. After the first heavy fighting (see Battle of Skra), the Bulgarians gave up their defensive positions and began retreating towards their country. On 24 September, the Bulgarian government asked for an armistice, which was signed five days later.[citation needed] The Allied army then pushed north and defeated the remaining German and Austrian forces that tried to halt the Allied offensive. By October 1918, the Allied armies had recaptured all of Serbia and prepared to invade Hungary. The offensive was halted because the Hungarian leadership offered to surrender in November 1918, marking the Austro-Hungarian empire's dissolution. The breaking of the Macedonian front was one of the important breakthroughs of the military stalemate and helped to bring an end to the War. Greece was granted a seat under Venizelos at the Paris Peace Conference.[89]
Treaty of Sèvres and assassination attempt
[edit]
Following the conclusion of World War I, Venizelos took part in the Paris Peace Conference of 1919 as Greece's chief representative. During his absence from Greece for almost two years, he acquired a reputation as an international statesman of considerable stature.[3] President Woodrow Wilson was said to have placed Venizelos first in point of personal ability among all delegates gathered in Paris to settle the terms of Peace.[90]
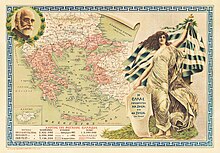
In July 1919, Venizelos reached an agreement with the Italians on the cession of the Dodecanese, and secured an extension of the Greek area in the periphery of Smyrna. The Treaty of Neuilly with Bulgaria on 27 November 1919, and the Treaty of Sèvres with the Ottoman Empire on 10 August 1920, were triumphs both for Venizelos and for Greece.[3][91][92] As the result of these treaties, Greece acquired Western Thrace, Eastern Thrace, Smyrna, the Aegean islands Imvros, Tenedos and the Dodecanese except Rhodes.[91][ii]

In spite of all this, fanaticism continued to create a deep rift between the opposing political parties and to impel them towards unacceptable actions. On his journey home on 12 August 1920, Venizelos survived an assassination attack by two royalist soldiers at the Gare de Lyon railway station in Paris.[93] This event provoked unrest in Greece, with Venizelist supporters engaging in acts of violence against known anti-Venizelists, and provided further fuel for the national division. The persecution of Venizelos' opponents reached a climax with the assassination of the idiosyncratic anti-Venizelist Ion Dragoumis[64] by paramilitary Venizelists on 13 August.[94] After his recovery Venizelos returned to Greece, where he was welcomed as a hero because he had liberated areas with Greek populations and had created a state stretching over "five seas and two continents".[64]
1920 electoral defeat, self-exile, and the Great Disaster
[edit]
King Alexander of Greece died of blood poisoning caused by a monkey bite two months after the signing of the treaty on 25 October 1920. His death revived the constitutional question of whether Greece should be a monarchy or a republic and transformed the November elections into a contest between Venizelos and the return of the exiled King Constantine I of Greece, Alexander's father. In the elections anti-Venizelists, most of them supporters of Constantine, secured 246 out of 370 seats.[95] The defeat came as a surprise to most people, and Venizelos failed even to get elected as an MP.[64] Venizelos himself attributed this to the war-weariness of the Greek people that had been under arms with almost no intermission since 1912. Venizelists believed that the promise of demobilization and withdrawal from Asia Minor was the most potent weapon of opposition. Abuse of power by Venizelists in the period of 1917–1920 and prosecution of their adversaries were also a further cause for people to vote in favor of the opposition.[96] Thus, on 6 December 1920, King Constantine was recalled by a plebiscite.[64] This caused great dissatisfaction not only to the newly liberated populations in Asia Minor but also to the Great Powers who opposed the return of Constantine.[95] As a result of his defeat Venizelos left for Paris and withdrew from politics.[97]

Once the anti-Venizelists came to power, it became apparent that they intended to continue the campaign in Asia Minor. However, the dismissal of the war experienced pro-Venizelist military officers for political reasons[95] and underestimating the capabilities of the Turkish army,[97] influenced the subsequent course of the war. Italy and France also found a useful pretext in the royal restoration for making peace with Mustafa Kemal (leader of the Turks). By April 1921, all Great Powers had declared their neutrality; Greece was alone in continuing the war.[98] Mustafa Kemal launched a massive attack on 26 August 1922, and the Greek forces were routed to Smyrna, which soon fell to the Turks on 8 September 1922 (see Great Fire of Smyrna).[98]

Following the defeat of the Greek army by the Turks in 1922 and the subsequent armed insurrection led by Colonels Nikolaos Plastiras and Stylianos Gonatas, King Constantine was dethroned (and succeeded by his eldest son, George), and six royalist leaders were executed.[citation needed] Venizelos assumed the leadership of the Greek delegation that negotiated peace terms with the Turks. He signed the Treaty of Lausanne with Turkey on 24 July 1923. The effect of this was that more than a million Greeks (Christians) were expelled from Turkey in exchange for the more than 500,000 Turks (Muslims) expelled from Greece, and Greece was forced to give up claims to eastern Thrace, Imbros, and Tenedos to Turkey. Following a failed pro-royalist insurrection led by General Ioannis Metaxas, King George II of Greece was forced into exile. Venizelos returned to Greece and served as prime minister until 1924, when quarrels with anti-monarchists forced him back into exile.[citation needed]
During these absences from power, he translated Thucydides into modern Greek, although the translation and incomplete commentary were only published in 1940, after his death.[citation needed]

Return to power (1928–32): Greco-Turkish alliance, assassination attempt and subsequent exile
[edit]In the elections held on 5 July 1928, Venizelos' party regained power and forced the government to hold new elections on 19 August of the same year; this time, his party won 228 out of 250 places in Parliament. During this period, Venizelos attempted to end Greece's diplomatic isolation by restoring normal relations with the country's neighbors. His efforts proved to be successful in the cases of the newly founded Kingdom of Yugoslavia and Italy. Firstly Venizelos signed an agreement on 23 September 1928 with Benito Mussolini in Rome, and then he started negotiations with Yugoslavia which resulted in a Treaty of Friendship signed on 27 March 1929. An additional protocol settled the status of the Yugoslav free trade zone of Thessaloniki in a way favorable to Greek interests.[99] Nevertheless, despite the co-ordinated British efforts under Arthur Henderson in 1930–1931, full reconciliation with Bulgaria was never achieved during his premiership.[100] Venizelos was also cautious towards Albania, and although bilateral relations remained at a good level, no initiative was taken by either side aiming at the final settlement of the unresolved issues (mainly related with the status of the Greek minority of South Albania).[101]

Venizelos' greatest achievement in foreign policy during this period was the reconciliation with Turkey. Venizelos had expressed his will to improve the bilateral Greek–Turkish relations even before his electoral victory in a speech in Thessaloniki (23 July 1928). Eleven days after the formation of his government, he sent letters to both the prime minister and the minister of foreign affairs of Turkey (İsmet İnönü and Tevfik Rüştü Aras respectively), declaring that Greece had no territorial aspirations to the detriment of their country. İnönü's response was positive and Italy was eager to help the two countries reach an agreement. Negotiations, however, stalled because of the complicated issue of the properties of the exchanged populations. Finally, the two sides reached an agreement on 30 April 1930; on 25 October, Venizelos visited Turkey and signed a treaty of friendship. Venizelos even forwarded Atatürk's name for the 1934 Nobel Peace Prize,[102] highlighting the mutual respect between the two leaders.[103] The German Chancellor Hermann Müller described the Greek-Turkish rapprochement as the "greatest achievement seen in Europe since the end of the Great War". Nevertheless, Venizelos' initiative was criticized domestically not only by the opposition but also by members of his own party that represented the Greek refugees from Turkey. Venizelos was accused of making too many concessions on the issues of naval armaments and of the properties of the Greeks who were expelled from Turkey according to the Treaty of Lausanne.[104]

In 1929, the Venizelos government, in an effort to avoid reactions from the lower classes whose conditions had worsened due to the wave of immigration, introduced the so-called Idionymon (#4229), a law that restricted civil liberties and initiated the repression against unionism, left-wing supporters and communists.[citation needed]
His domestic position was weakened, however, by the effects of the Great Depression in the early 1930s;[105] and in the elections of 1932 he was defeated by the People's Party under Panagis Tsaldaris. The political climate became more tense, and in 1933 Venizelos was the target of a second assassination attempt.[106] The pro-royalist tendencies of the new government led to two Venizelist coup attempts by General Nikolaos Plastiras: one in 1933 and the other in 1935. The failure of the latter proved decisive for the future of the Second Hellenic Republic. After the coup's failure, Venizelos left Greece once more, while in Greece, trials and executions of prominent Venizelists were carried out, and he himself was sentenced to death in absentia. The severely weakened Republic was abolished in another coup in October 1935 by General Georgios Kondylis, and George II returned to the throne following a rigged referendum in November.[107]
Death
[edit]Venizelos left for Paris and on 12 March 1936 wrote his last letter to Alexandros Zannas. He suffered a stroke on the morning of the 13th and died five days later in his flat at 22 rue Beaujon.[108] The absolution was performed on 21 March at St. Stephen's Greek Orthodox Church; his body was deposed in the crypt before its transportation on the 23rd at the beginning of the afternoon to the Gare de Lyon. His body was then taken by the destroyer Pavlos Kountouriotis to Chania, avoiding Athens in order not to cause unrest. A great ceremony with wide public attendance accompanied his burial at Akrotiri, Crete.[citation needed]
Legacy
[edit]

One of the main contributions of Venizelos to Greek political life was the creation, in 1910, of the Liberal Party, which contrasted with the Greek parties of that period. Until the early twentieth century, the Greek parties were inspired by the protecting powers (French or English Party for example) or clustered around a political personality, such as Charilaos Trikoupis. The Liberal Party was based on the ideas of Venizelos (and the military coup of Goudi), but it survived its creator. In addition, the birth of a leading party would coincide with the birth of an opposing party. The opposing party was reflected around the personality of the king, but that survived the various abolitions of the monarchy.[109] Venizelism, from its inception, is essentially a liberal Republican movement which opposes anti-Venizelist monarchist and conservative ideologies. These two competed for power throughout the inter-war period.[110]
Its main ideas, adapted from its creator, were: opposition to the monarchy; the defense of the Megali Idea; formation of alliances with Western democratic countries, in particular, the United Kingdom and France against Germany during the First and Second World Wars, and later with the United States against the Soviet Union during the Cold War; and finally a protectionist economic policy.[111]
Themistoklis Sofoulis was, from the 1920s, the successor of Venizelos as leader of the Liberal Party, which survived policy failures, exile, and ultimately, the death of the historical founder. In 1950, the son of Venizelos, Sophoklis Venizelos, succeeded as head of the Liberal Party at a time when an agreement was formed with the populists (name of the Royalist party) against the communists during the civil war. The Center Union (Enosis Kendrou), founded in 1961 by Georgios Papandreou, became the ideological descendant of the Liberal Party. The Center Union eventually faded in the late 1970s and was replaced by a party further to the left, Panhellenic Socialist Movement of Andreas Papandreou.[112]
Venizelos was one Greek politician who achieved worldwide fame during his lifetime, and in the six years between 1915 and 1921, five biographies of him were published in English together with numerous profiles in the newspapers.[113] The character of Constantine Karolides, the able and charismatic prime minister of Greece in John Buchan's 1915 adventure spy novel The Thirty-Nine Steps, is a thinly disguised version of Venizelos.[113] Venizelos's advocacy throughout his career in varying ways of a bloc of Balkan states led the press, especially in Britain, to portray him as a far-sighted statesman who was bringing peace and stability to the unstable Balkans.[114]

Athens International Airport is named after Venizelos.
Personal life and family
[edit]In December 1891, Venizelos married Maria Katelouzou, daughter of Eleftherios Katelouzos. The newlyweds lived on the upper floor of the Chalepa house, while Venizelos' mother and his brother and sisters lived on the ground floor. There, they enjoyed the happy moments of their marriage and also had the birth of their two children, Kyriakos in 1892 and Sofoklis in 1894. Their married life was short and marked by misfortune. Maria died of post-puerperal fever in November 1894 after the birth of their second child. Her death deeply affected Venizelos and as a sign of mourning, he grew his characteristic beard and mustache, which he retained for the rest of his life.[10]
After his defeat in the November elections of 1920, he left for Nice and Paris in self-imposed exile. In September 1921, twenty-seven years after the death of his first wife Maria, he married Helena Schilizzi (sometimes referred to as Elena Skylitsi or Stephanovich) in London. Advised by police to be wary of assassination attempts, they held the religious ceremony in private at Witanhurst, the mansion of a family friend and socialite Lady Domini Crosfield. The Crosfields were well connected and Venizelos met Arthur Balfour, David Lloyd George and the arms dealer Basil Zaharoff in subsequent visits to the house.[citation needed]
The married couple settled down in Paris in a flat at 22 rue Beaujon.[clarification needed] He lived there until 1927 when he returned to Chania.[10]
Gallery
[edit]- Venizelos father's shop in Chania.
- Venizelos in 1935
- Building 22 rue Beaujon in Paris where Venizelos died.
- A bust by Athanasios Apartis
See also
[edit]- History of Modern Greece
- Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922)
- List of massacres during the Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922)
- History of Northern Epirus from 1913 to 1921
Notes
[edit]^ i: The most pronounced violation was when the Allies occupied the island of Corfu and used it as a base to gather the remains of the Serbian army. The Allies informed Athens of their intention a few hours before the first ships reached the island.[115]
^ ii: Rhodes became a part of Greece in 1949.
Citations
[edit]- ^ Note: Greece officially adopted the Gregorian calendar on 16 February 1923 (which became 1 March). All dates prior to that, unless specifically denoted, are Old Style.
- ^ Kitromilides, 2006, p. 178
- ^ a b c "Liberty Still Rules", Time, 18 February 1924.
- ^ Duffield, J. W. (30 October 1921). "Venizelos, Maker of Modern Greece". The New York Times.
- ^ Yilmaz, 2012, p. 82.
- ^ "Intrigue in Greece". The Argus. Melbourne. 4 July 1916. p. 7. Retrieved 29 November 2012 – via National Library of Australia.
- ^ a b c Chester, 1921, p. 4
- ^ "Τα γεγονότα που σημάδεψαν τη ζωή του Ελευθέριου Βενιζέλου". Εφημερίδα ΠΑΤΡΙΣ. 18 March 2010. Retrieved 23 August 2024.
- ^ "Ποιος ήταν ο παππούς του Ελευθερίου Βενιζέλου". 11 May 2020.
- ^ a b c d Mitsotaki, Zoi (2008). "Venizelos the Cretan. His roots and his family". National Foundation Research. Archived from the original on 18 May 2007.
- ^ a b Ion, 1910, p. 277
- ^ Kitromilides, 2006, pp. 45, 47
- ^ Kitromilides, 2006, p. 16
- ^ Clogg, 2002, p. 65
- ^ a b Kitromilides, 2006, p. 58
- ^ Lowell Sun (newspaper), 6 February 1897, p. 1
- ^ Holland, 2006, p. 87
- ^ a b c Papadakis, Nikolaos E. (2008). "Eleftherios Venizelos His path between two revolutions 1889–1897". National Foundation Research. Archived from the original on 18 May 2007.
- ^ Holland, 2006, p. 91
- ^ Chester, 1921, p. 35
- ^ Chester, 1921, p. 34
- ^ Kitromilides, 2006, p. 30
- ^ Kitromilides, 2006, p. 62
- ^ Kerofilias, 1915, p. 14
- ^ a b Dunning, Jun. 1987, p. 367
- ^ Chester, 1921, pp. 35–36
- ^ Gibbons, p. 24
- ^ Kerofilias, 1915, pp. 13–14
- ^ Leeper, 1916, pp. 183–184
- ^ Anne O'Hare, McCormark, "Venizelos the new Ulysses of Hellas", The New York Times Magazine, 2 September, p. 14
- ^ Kitromilides, 2006, pp. 63–64
- ^ Understanding life in the borderlands: boundaries in depth and in motion, I. William Zartman, 2010, p. 169
- ^ Kitromilides, 2006, p. 65
- ^ Rose, 1897, pp. 2–3
- ^ Dunning, June 1897, p. 368
- ^ a b Dunning Dec. 1897, p. 744
- ^ Ion, 1910, p. 278
- ^ a b Kitromilides, 2006, p. 68
- ^ a b c d e f g h Manousakis, George (2008). "Eleftherios Venizelos during the years of the High Commissionership of Prince George (1898–1906)". National Foundation Research. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007.
- ^ a b Kerofilias, 1915, pp. 30–31
- ^ Kerofilias, 1915, p. 33
- ^ Chester, 1921, p. 82
- ^ Chester, 1921, p. 95
- ^ Archontaki, Stefania (2008). "1906–1910, The Preparation and Emergence of Venizelos on the Greek Political Stage – Venizelos as Prime Minister". National Foundation Research. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007.
- ^ Gibbons pp. 35–37
- ^ Alastos p. 38
- ^ a b Mazower, 1992, p. 886
- ^ Chester, 1921, pp. 129–133
- ^ a b c Gardika-Katsiadaki, Eleni (2008). "Period 1910–1914". National Foundation Research. Archived from the original on 18 May 2007.
- ^ Kyriakou, 2002, pp. 491–492
- ^ Hall, 2000, pp. 1–9
- ^ Kitromilides, 2006, p. 141
- ^ Chester, 1921, p. 150
- ^ a b Kitromilides, 2006, p. 145
- ^ Hall, 2000, p. 13
- ^ a b Chester, 1921, pp. 159–160
- ^ Hall, 2000, pp. 61–62
- ^ Chester, 1921, pp. 161–164
- ^ Hall, 2000, p. 17
- ^ Chester, 1921, p. 169
- ^ Tucker, 1999, p. 107
- ^ Kitromilides, 2006, p. 154
- ^ Seligman, 1920, p. 31
- ^ a b c d e f Theodorakis, Emanouil; Manousakis George (2008). "First World War 1914–1918". National Foundation Research. Archived from the original on 18 May 2007.
- ^ Firstworldwar.com The Minor Powers During World War One – Greece
- ^ Chester, 1921, p. 271
- ^ Kitromilides, 2006, p. 122
- ^ Leon, 1974, pp. 356–357
- ^ Leon, 1974, p. 381
- ^ a b Kitromilides, 2008, p. 124
- ^ Clogg, 2002, p. 87
- ^ Leon, 1974, p. 422
- ^ Leon, 1974, p. 428
- ^ a b Leon, 1974, p. 434
- ^ a b c Leon, 1974, p. 435
- ^ Chester, 1921, p. 293
- ^ Seligman, 1920, p. 139
- ^ Ion, 1918, pp. 796–812
- ^ Burg, 1998, pp. 145–146
- ^ Vatikotes, 1998 p. 98
- ^ Burg, 1998, p.145
- ^ Kitromilides, 2006, p. 367
- ^ Hickey, 2004, p. 87
- ^ Clogg, 2002, p. 89
- ^ Gibbons, 1920, p. 299
- ^ Chester, 1921, pp. 295–304
- ^ "Land of Invasion", Time, 4 November 1940.
- ^ a b Chester, 1921, p. 311
- ^ Chester, 1921, pp. 312–313
- ^ Chester, 1921, p. 6
- ^ a b Kitromilides, 2006, p. 165
- ^ Chester, 1921, p. 320
- ^ "Venizelos shot, twice wounded by Greeks in Paris". The New York Times. 13 August 1920. p. 1.
- ^ Kitromilides, 2006, p. 129
- ^ a b c Clogg, 2002, p. 95
- ^ Kitromilides, 2006, p. 131
- ^ a b Theodorakis, Emanouil; Manousakis George (2008). "Period 1920–1922". National Foundation Research. Archived from the original on 18 May 2007.
- ^ a b Clogg, 2002, p. 96
- ^ Karamanlis, 1995, p. 55, 70
- ^ Karamanlis, 1995, pp. 144–146
- ^ Karamanlis, 1995, pp. 158–160
- ^ Nobel Foundation. The Nomination Database for the Nobel Prize in Peace, 1901–1955.nobelprize.org
- ^ Clogg, 2002, p. 107
- ^ Karamanlis, 1995, pp. 95–97
- ^ Black, 1948, p. 94
- ^ Clogg, 2002, p. 103
- ^ Black, 1948, pp. 93–96
- ^ Manolikakis, 1985, pp. 18–22; Hélène Veniselos, A l'ombre de Veniselos (Paris, 1955)
- ^ Koliopoulos, 2002, pp. 53–54
- ^ Legg, pp. 188–189
- ^ Contogeorgis, 1996, pp. 379–404
- ^ Koliopoulos, 2002, p. 104
- ^ a b Michail, 2011 p. 111
- ^ Michail, 2011 pp. 111–112
- ^ Leon, 1974, pp. 315–316
General references
[edit]Books
[edit]- Abbott, G. F. (2008). Greece and the Allies 1914–1922. London: Methuen & co. ltd. ISBN 978-0554394626.
- Alastos, D. (1942). Venizelos, Patriot, Statesman, Revolutionary. London: P. Lund, Humphries & co.
- Bagger, E. S. (1922). Eminent Europeans; studies in continental reality (PDF). G.P. Putnam's Sons.
- Beaton, Roderick (2019). Greece: Biography of a Modern Nation. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0226673745.
- Βερέμης, Θάνος; Koliopoulos, Giannēs (2006). "Ελλάς. Η σύγχρονη συνέχεια: από το 1821 μέχρι σήμερα" (in Greek). Καστανιώτης. ISBN 978-960-03-4246-8.
- Burg, D. F. (1998). Almanac of World War I. Lexington: University Press of Kentucky. ISBN 0813120721.
- Chester, S. M. (1921). Life of Venizelos, with a letter from His Excellency M. Venizelos (PDF). London: Constable.
- Clogg, R. (2002). A Concise History of Greece. London: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521004799.
- Dalby, Andrew (2011). Eleftherios Venizelos: Greece. Haus Publishing. ISBN 978-1907822339.
- Dutton, D. (1998). The Politics of Diplomacy: Britain and France in the Balkans in the First World War. I. B. Tauris. ISBN 978-1860640797.
- Fotakis, Z. (2005). Greek naval strategy and policy, 1910–1919. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0415350143.
- Gibbons, H. A. (1920). Venizelos. Houghton Mifflin Company.
- Hall, Richard C. (2000). The Balkan Wars, 1912–1913: Prelude to the First World War. Routledge. ISBN 0415229464.
- Hibben, Paxton (1920). Constantine I and the Greek People. New York: The Century Co. ISBN 978-1110760329.
- Hickey, M. (2007). First World War: Volume 4 The Mediterranean Front 1914–1923. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1841763736.[permanent dead link]
- Holland, R. F.; Makrides D. (2006). The British and the Hellenes: Struggles for mastery in the Eastern Mediterranean 1850–1960. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0199249962.
- Kerofilias, C. (1915). Eleftherios Venizelos, his life and work (PDF). John Murray.
- Kitromilides, P. (2006). Eleftherios Venizelos: The Trials of Statesmanship. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 0748624783.
- Koliopoulos, G.; Veremis, T. (2002). Greece : the modern sequel : from 1831 to the present. New York: NYU Press. ISBN 0814747671.
- Legg, K. R. (1969). Politics in modern Greece. Stanford University Press. ISBN 0804707057.
- Leon, G. B. (1974). Greece and the Great Powers 1914–17. Thessaloniki: Institute of Balkan Studies.
- Manolikakis, Giannis (1985). Eleftherios Venizelos: his unknown life. Athens.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Michalopoulos, Dimitris (2012). Eleutherios Venizelos: An Outline of His life and Time. Saarbrücken: Lambert Academic Publishing. ISBN 978-3659267826..
- Michail, Eugene (2011). The British and the Balkans: Forming Images of Foreign Lands, 1900–1950. London: Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-1441170613.
- Pentzopoulos, D.; Smith M. L. (2002). The Balkan exchange of minorities and its impact on Greece. C. Hurst & Co Publishers. ISBN 1850656746.
- Price, Crawfurd (1917). Venizelos and the war, a sketch of personalities and politics (PDF). London: Simpkin.
- Rose, W. K. (2003) [1987 (1st ed.)]. With the Greeks in Thessaly (2nd ed.). Adamant Media Corporation. ISBN 1402106289.
- Seligman, V. J. (1920). Victory of Venizelos (PDF).
- Tucker, Spencer C.; Wood, L. M.; Murphy, J. D. (1999). The European Powers in the First World War: An Encyclopedia. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 081533351X.
- Vatikotes, P. (1998). Popular autocracy in Greece, 1936–41: a political biography of general Ioannis Metaxas. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0714648699.
- Venizelos, E.; Anthony S.; Xanthaky, Sakellarios N. G. (1916). Greece in Her True Light: Her Position in the World-wide War as Expounded by E. Venizelos (PDF). New York.
- Yilmaz, Hakan (2012). Perceptions of Islam in Europe: Culture, Identity and the Muslim 'Other'. Bloomsbury Academic. ISBN 978-1848851641.
Journals
[edit]- Black, Cyril E. (January 1948). "The Greek Crisis: Its Constitutional Background". The Review of Politics. 10 (1): 84–99. doi:10.1017/S0034670500044521. JSTOR 1404369. S2CID 144919492.
- Christopoulos, Marianna. "Anti-Venizelist criticism of Venizelos' policy during the Balkan Wars (1912–13)". Byzantine and Modern Greek Studies 39.2 (2015): 249–265. doi:10.1017/S0307013100015378.
- Dunning, Wm. A. (June 1897). "Record of Political Events". Political Science Quarterly. 12 (3): 352–380. doi:10.2307/2140141. JSTOR 2140141.
- Dunning, Wm. A. (December 1897). "Record of Political Events". Political Science Quarterly. 12 (4): 734–756. doi:10.2307/2139703. JSTOR 2139703.
- Gerolymatos, Andre. "Lloyd George and Eleftherios Venizelos, 1912–1917". Journal of the Hellenic Diaspora (1988) Vol. 15 Issue 3/4, pp. 37–50.
- Ion, Theodore P. (April 1910). "The Cretan Question". The American Journal of International Law. 4 (2): 276–284. doi:10.2307/2186614. JSTOR 2186614. S2CID 147554500.
- Kyriakidou, Maria (2002). "Legislation in Inter-war Greece Labour Law and Women Workers: A Case Study of Protective" (PDF). European History Quarterly. 32 (4): 489. doi:10.1177/0269142002032004147. S2CID 143711700. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 March 2009. Retrieved 12 June 2008.
- Leeper, A. W. A. (1916). "Allied Portraits: Eleftherios Venizelos". The New Europe I.
- Mazower, M. (December 1992). "The Messiah and the Bourgeoisie: Venizelos and Politics in Greece, 1909–1912". The Historical Journal. 35 (4): 885–904. doi:10.1017/S0018246X00026200. JSTOR 2639443. S2CID 154495315.
- Papacosma, S. Victor. "The Republicanism of Eleftherios Venizelos: Ideology or Tactics?" Byzantine and Modern Greek Studies 7 (1981): 169–202.
- Prevelakis, Eleutherios. "Eleutherios Venizelos and the Balkan Wars". Balkan Studies 7.2 (1966): 363–378.





