Heckler & Koch GMG
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
| GMG | |
|---|---|
 A GMG of the German Army. | |
| Type | Automatic grenade launcher |
| Place of origin | Germany |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1990s–present |
| Used by | See Users |
| Wars | War in Afghanistan (2001–2021) Russian invasion of Ukraine |
| Production history | |
| Designed | 1992–1995 |
| Manufacturer | Heckler & Koch |
| Produced | 1996–present[citation needed] |
| Variants | GMW |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 28.8 kg Gun, 10.7 kg tripod and 8 kg softmount. |
| Length | 1090 mm |
| Barrel length | 415 mm |
| Width | 226 mm (without ammunition box) |
| Height | 208 mm |
| Cartridge | 40x53 mm |
| Action | API Blowback |
| Rate of fire | 340 rounds/min |
| Muzzle velocity | 241 m/s |
| Effective firing range | 1500 m |
| Maximum firing range | 2200 m |
| Feed system | 32-round disintegrating, closed-link belt |
| Sights | Reflex sight and back-up leaf sight |
The GMG (Granatmaschinengewehr or "grenade machine gun") is an automatic grenade launcher developed by Heckler & Koch for the German Army. It is also often referred to as GMW or GraMaWa (Granatmaschinenwaffe).[1]
Design details
[edit]The GMG fires 40 mm grenades at a rate of about 340 rounds per minute.[2] It is belt-fed, and can be loaded from either side, making it easy to mount on most platforms. With a variety of day and night sights available, the GMG can be used for most medium range infantry support situations.
The weapon is 1.09 m long and has a 415 mm rifled barrel; the ammunition box has dimensions of 470 × 160 × 250 mm. The gun cycles on a recoil-operated blow-back basis. It weighs 29 kg; the tripod is an additional 11 kg.
Testing and operation
[edit]The HK GMG was tested in the Yuma desert in Arizona in 1997 in order to compete for future United States contracts.
Users
[edit]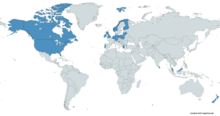
 Belgium: Mounted on the army's Jankel FOX Rapid Reaction Vehicles [3]
Belgium: Mounted on the army's Jankel FOX Rapid Reaction Vehicles [3] Canada: 304 ordered.[4] Designated as the C16 Close Area Suppression Weapon (CASW) and licence-built by Rheinmetall Defence Canada.[5]
Canada: 304 ordered.[4] Designated as the C16 Close Area Suppression Weapon (CASW) and licence-built by Rheinmetall Defence Canada.[5] Finland[6] Locally known as 40 KRKK 2005
Finland[6] Locally known as 40 KRKK 2005 Germany[7]
Germany[7] Greece[7]
Greece[7] Ireland: Irish Army[8]
Ireland: Irish Army[8] Latvia[7][9]
Latvia[7][9] Lithuania: Lithuanian Armed Forces.[10]
Lithuania: Lithuanian Armed Forces.[10] Malaysia: Used by Pasukan Khas Laut (PASKAL) of the Royal Malaysian Navy.[11]
Malaysia: Used by Pasukan Khas Laut (PASKAL) of the Royal Malaysian Navy.[11] Netherlands[12][13]
Netherlands[12][13] New Zealand[14]
New Zealand[14] Norway[15]
Norway[15] Poland: Wojska Specjalne.[citation needed]
Poland: Wojska Specjalne.[citation needed] Portugal: Used by Portuguese Army, Portuguese Marine Corps and National Republican Guard.[7][16]
Portugal: Used by Portuguese Army, Portuguese Marine Corps and National Republican Guard.[7][16] Slovenia[17]
Slovenia[17] Sri Lanka: Used by Sri Lanka Armoured Corps on its Main Battle Tanks & Used by Sri Lanka Navy on its Fast Attack Crafts.
Sri Lanka: Used by Sri Lanka Armoured Corps on its Main Battle Tanks & Used by Sri Lanka Navy on its Fast Attack Crafts. Ukraine: 100 donated by Germany in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine as of July 2024.[18]
Ukraine: 100 donated by Germany in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine as of July 2024.[18] United Kingdom: 44 purchased in 2006 for use in Afghanistan and Iraq.[19] Designated as L134A1.[citation needed]
United Kingdom: 44 purchased in 2006 for use in Afghanistan and Iraq.[19] Designated as L134A1.[citation needed] United States: Used by USSOCOM.[19]
United States: Used by USSOCOM.[19]
- Another GMW/GMG of the German Army.
- HK GMG on display.
- GMG German armed reconnaissance vehicle Fennek
- Manned GMG in Finnish service.
- GMG remotely operated on board a GTK Boxer
- GMW/GMG of the Royal Malaysian Navy on display.
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ "Heckler & Koch :: Home". Archived from the original on 27 November 2011. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "GMG Technical Data". Archived from the original on 8 April 2019. Retrieved 8 February 2022.
- ^ admin (4 July 2018). "First production of Jankel FOX Rapid Reaction Vehicles to Belgian Special Regiment". MilitaryLeak. Retrieved 26 July 2023.
- ^ "Defence". Archived from the original on 8 July 2012. Retrieved 19 December 2010.
- ^ "Too Late? Canada's CASW for 40mm GMGs". Archived from the original on 22 December 2010. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- ^ "Paiste07 - Tekniikkaa - päivän vempele". tietokannat.mil.fi. Archived from the original on 21 August 2009.
- ^ a b c d Jones, Richard D. Jane's Infantry Weapons 2009/2010. Jane's Information Group; 35 edition (27 January 2009). ISBN 978-0-7106-2869-5.
- ^ Thompson, Leroy (1 March 2013). "Ireland's Army Rangers (page 1)". Tactical-Life. Archived from the original on 22 September 2015. Retrieved 19 November 2016.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). www.mod.gov.lv. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 October 2008. Retrieved 22 May 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Lietuvos kariuomenė :: Ginkluotė ir karinė technika » Granatsvaidžiai ir prieštankiniai ginklai » Automatinis granatsvaidis H&K GMG 40 mm". Archived from the original on 9 July 2012. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ Dan, Alex (9 February 2016). "PASKAL Malaysian Special Forces Weapons". Military Factory (Small Arms). Archived from the original on 14 February 2016. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- ^ "Special Forces - Wapens" (in Dutch). Netherlands Legermuseum: Collectie Informatie Centrum. Archived from the original on 27 February 2009. Retrieved 17 October 2009.
- ^ "AGW, automatische granaatwerper 40 mm" (in Dutch). Netherlands Ministry of Defence. Archived from the original on 1 October 2011. Retrieved 24 February 2010.
- ^ "NZ Army" (PDF). NZ Army News (428). February 2012. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 June 2012. Retrieved 10 November 2018.
- ^ "Forsvarsdepartementet får 10 millioner kroner i bot". Aftenposten. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "GNR HK GMG".[permanent dead link]
- ^ "HECKLER & KOCH GMG Automatic Grenade Launcher". Archived from the original on 8 April 2023. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ^ "Military support for Ukraine | Federal Government". Website of the Federal Government | Bundesregierung. 8 July 2024. Retrieved 12 July 2024.
- ^ a b "HEAVY HITTERS" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 July 2011. Retrieved 12 April 2010.
External links
[edit]- Official page Archived 27 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- HKPro The 40 mm GMG





