Leptonetidae
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
| Leptonetids Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Tayshaneta anopica | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Chelicerata |
| Class: | Arachnida |
| Order: | Araneae |
| Infraorder: | Araneomorphae |
| Family: | Leptonetidae Simon, 1890 |
| Diversity | |
| 21 genera, 365 species | |
 | |
Leptonetidae is a family of small spiders adapted to live in dark and moist places such as caves.[1] The family is relatively primitive having diverged around the Middle Jurassic period.[2] They were first described by Eugène Simon in 1890.[3]
Distinguishing characteristics
[edit]Leptonetids are small, with most falling between 2 and 5mm in total length.[2] They are generally pale in color and feature a greenish or bluish shine due to microscopic texture on the cuticle of their exoskeleton.[1] Those species which have retained their eyes, have 6 eyes set in a distinctive pattern, with posterior pair set back from the others. If a spider from this family looses a leg, it usually separates between the patella and tibia rather than at the coxa/trochanter joint. [4]
Habitat
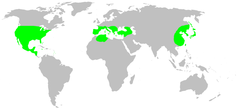
[edit]Many live in caves or in leaf litter around the Mediterranean, and in Eurasia, Japan and southern North America.[5]
Genera
[edit]As of April 2022[update], the World Spider Catalog accepted the following genera:[5]
- Appaleptoneta Platnick, 1986 — United States
- Barusia Kratochvíl, 1978 — Montenegro, Croatia, Greece
- Calileptoneta Platnick, 1986 — United States
- Cataleptoneta Denis, 1955 — Asia, Europe
- Chisoneta Ledford & Griswold, 2011 — United States, Mexico
- Falcileptoneta Komatsu, 1970 — Japan, Korea
- Jingneta Wang & Li, 2020
- Leptoneta Simon, 1872 — Europe, Asia, Algeria
- Leptonetela Kratochvíl, 1978 — Greece, Asia
- Longileptoneta Seo, 2015 — Korea
- Masirana Kishida, 1942 — Japan, Korea
- Montanineta Ledford & Griswold, 2011 — United States
- Neoleptoneta Brignoli, 1972 — Mexico
- Ozarkia Ledford & Griswold, 2011 — United States
- Paraleptoneta Fage, 1913 — Algeria, Italy
- Protoleptoneta Deltshev, 1972 — Europe
- Rhyssoleptoneta Tong & Li, 2007 — China
- Sulcia Kratochvíl, 1938 — Europe
- Tayshaneta Ledford & Griswold, 2011 — United States
- Teloleptoneta Ribera, 1988 — Portugal
- Yueleptoneta Tong, 2022
Two genera have been moved to the family Archoleptonetidae:[6]
- Archoleptoneta Gertsch, 1974 — United States
- Darkoneta Ledford & Griswold, 2010 — North America, Central America
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Spiders of the world : a natural history. Norman I. Platnick, Gustavo Hormiga, Peter, Jäger, R. Jocqué, Martín J. Ramírez, Robert J. Raven. Princeton, NJ. 2020. ISBN 978-0-691-20498-7. OCLC 1223249471.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ a b Ledford, Joel; Derkarabetian, Shahan; Ribera, Carles; Starrett, James; Bond, Jason E.; Griswold, Charles; Hedin, Marshal (2021-03-24). "Phylogenomics and biogeography of leptonetid spiders (Araneae : Leptonetidae)". Invertebrate Systematics. 35 (3): 332–349. doi:10.1071/IS20065. ISSN 1447-2600.
- ^ Simon, E. (1890). Etudes arachnologiques.
- ^ Bradley, Richard A. (2012). "FAMILY LEPTONETIDAE • Midget Cave Spiders". Common Spiders of North America. p. 137. doi:10.1525/california/9780520274884.003.0032. ISBN 978-0-520-27488-4.
- ^ a b "Family: Leptonetidae Simon, 1890". World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern. Retrieved 2022-04-05.
- ^ "Family: Archoleptonetidae Gertsch, 1974". World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern. Retrieved 2022-04-05.
Further reading
[edit]- Gertsch, W.J. (1978). The spider family Leptonetidae in North America. Journal of Arachnology 1:145-203. PDF
- Platnick, N.I. (1986). On the tibial and patellar glands, relationships, and American genera of the spider family Leptonetidae (Arachnida, Araneae). American Museum Novitates 2855. PDF