Narcobarbital
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
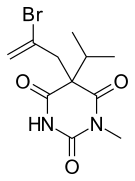
| Formula | C11H15BrN2O3 |
| Molar mass | 303.156 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Narcobarbital (Pronarcon) is a barbiturate derivative developed in 1932 by Carl Heinrich Friedrich Boedecker and Heinrich Gruber Schoneberg, assignors to the firm J. D. Riedel-E. de Haën AG, Berlin, Germany. Later, in 1937, may, was patented in United States.[1] It is an N-methylated derivative of propallylonal and has similar sedative effects. It is still used in veterinary medicine for inducing surgical anaesthesia.[2]
References
[edit]- ^ US 2080071, "Tri-substituted barbituric acid", issued 11 May 1937, assigned to J. D. Riedel-E. de Haën AG.
- ^ Committee for Veterinary Medicinal Products (1999). "Position Paper on availability of Veterinary Medicines agreed on 17 March 1999" (PDF). The European Medicines Agency. pp. 3–8. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 December 2014.