Potosí Department
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Spanish. (March 2017) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
Potosí | |
|---|---|
 Cerro Lipez, a stratovolcano | |
 Location within Bolivia | |
| Coordinates: 20°40′0″S 66°40′0″W / 20.66667°S 66.66667°W | |
| Country | |
| Capital | Potosí |
| Government | |
| • Body | Departmental Legislative Assembly of Potosí |
| • Governor | Jhonny Mamani (MAS-IPSP) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 118,218 km2 (45,644 sq mi) |
| Population (2024 census) | |
| • Total | 856,419 |
| • Density | 7.2/km2 (19/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC-4 (BOT) |
| HDI (2019) | 0.631[1] medium · 9th of 9 |
| GDP (2023) | in constant values of 2015[2] |
| - Total | US$ 1.8 billion Int$ 4.2 billion (PPP) |
| - Per capita | US$ 1,900 Int$ 4,400 (PPP) |
Potosí (Spanish pronunciation: [potoˈsi]; Quechua: P'utuqsi; Aymara: Putusi) is a department in southwestern Bolivia. Its area is 118,218 km2 and its population is 856,419 (2024 census). The capital is the city of Potosí. It is a mostly barren, mountainous region with one large plateau to the west, where the largest salt flat in the world, Salar de Uyuni, is located.
Cerro Potosí was the richest province in the Spanish empire, providing a great percentage of the silver that was shipped to Europe.
Potosi is also the location of the San Cristóbal silver, zinc and lead mines, developed by the US company Apex Silver Mines Limited of Colorado and sold in November 2008 to the Japanese Sumitomo Corporation.

History
[edit]In March 2023, social organisations in four regions of Potosí, with the support of regional MAS-IPSP lawmakers, called for a strike spanning over 72 hours, to force the government to raise infrastructure investments in the department and to receive an increased amount of the profits generated through lithium mining in the region.[3] Shortly after the strike an agreement with the central government was reached, stipulating the construction of motorways and a cement plant and further discussions about mining conditions.[3]
Government
[edit]Executive offices
[edit]The chief executive office of Bolivia departments (since May 2010) is the governor; until then, the office was called the prefect, and until 2006 the prefect was appointed by the President of Bolivia. The current governor, Jhonny Mamani of the Movement for Socialism – Political Instrument for the Sovereignty of the Peoples was elected on 7 March 2021.[4]
| Took office | Office expired | Prefect/Governor | Party | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23 Jan 2006 | 30 May 2010 | Mario Virreira Iporre | MAS-IPSP | First elected prefect. Elected in Bolivian general election, December 2005 |
| 30 May 2010 | 31 May 2015 | Félix Gonzáles | MAS-IPSP | Elected in regional election on 4 April 2010 with 63.1% of the vote; first governor. |
| 31 May 2015 | 15 Nov 2019 | Juan Carlos Cejas | MAS-IPSP | Elected in regional election on 29 March 2015. |
| 15 Nov 2019 | 3 May 2021 | Omar Veliz Ramos | MAS-IPSP | |
| 3 May 2021 | Jhonny Mamani | MAS-IPSP | Elected in regional election on 7 March 2021.[4] |
Legislative Assembly
[edit]Under the 2009 Constitution, each Bolivian department has an elected Departmental Legislative Assembly. The first elections were held 4 April 2010.
The current executive committee consists of Jacinto Sunagua Dorado as president, Raimunda Cordero Caba as vice-president and Alberto Quispe Mamani as secretary and Blanca Celia Burgos Quispe and Leon Jancko Condori as first and second committee member, respectively.[5]
Demographics
[edit]| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1976 | 657,743 | — | ||
| 1992 | 645,889 | −0.11% | ||
| 2001 | 709,013 | +1.04% | ||
| 2012 | 828,093 | +1.42% | ||
| 2024 | 856,419 | +0.28% | ||
| ||||
| Source: Citypopulation[6] | ||||
Provinces of Potosi Department
[edit]The department is divided into 16 provinces which are further subdivided into 40 municipalities[7] (municipios) and 219 cantons (cantones).
| Province | Capital | Area km2 | Population (2012 census) | Map Number | 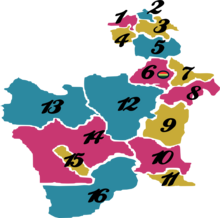 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alonso de Ibáñez | Sacaca | 2.170 | 29.821 | 1 | |
| Antonio Quijarro | Uyuni | 14,890 | 54,947 | 12 | |
| Bernardino Bilbao | Arampampa | 640 | 10,224 | 2 | |
| Charcas | San Pedro de Buena Vista | 2,964 | 41,214 | 3 | |
| Chayanta | Colquechaca | 7,026 | 97,251 | 5 | |
| Cornelio Saavedra | Betanzos | 2,375 | 55,100 | 7 | |
| Daniel Campos | Llica | 12,106 | 5,850 | 13 | |
| Enrique Baldivieso | San Agustín | 2,254 | 1,684 | 15 | |
| José María Linares | Puna | 5,136 | 49,619 | 8 | |
| Modesto Omiste | Villazón | 2,260 | 44,645 | 11 | |
| Nor Chichas | Cotagaita | 8,979 | 42,248 | 9 | |
| Nor Lípez | Colcha K | 20,892 | 14,057 | 14 | |
| Rafael Bustillo | Uncía | 2,235 | 86,947 | 4 | |
| Sud Chichas | Tupiza | 8,516 | 55,879 | 10 | |
| Sud Lípez | San Pablo de Lípez | 22,355 | 6,835 | 16 | |
| Tomás Frías | Potosí | 3,420 | 229,047 | 6 |
Economy
[edit]This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (February 2023) |
Mining
[edit]- Pando mine (Gold)
- Salar de Uyuni mine (Lithium)
- San Vicente mine (Silver)
Languages
[edit]The main languages spoken in the department are Quechua, Spanish and Aymara. The following table shows the number of speakers of recognized languages in Potosí and in all of Bolivia.[8]
| Language | Department | Bolivia |
|---|---|---|
| Quechua | 514,421 | 2,281,198 |
| Aymara | 57,738 | 1,525,321 |
| Guaraní | 374 | 62,575 |
| Other native | 356 | 49,432 |
| Spanish | 438,204 | 6,821,626 |
| Foreign | 3,771 | 250,754 |
| Only native | 226,967 | 960,491 |
| Native and Spanish | 301,280 | 2,739,407 |
| Spanish and foreign | 136,980 | 4,115,751 |
Places of interest
[edit]- Eduardo Avaroa Andean Fauna National Reserve
- Torotoro National Park
- Laguna Colorada
- Laguna Verde
- Laguna Blanca
- Salar de Uyuni
- Potosí
- Uyuni
Notable people
[edit]- Juana Azurduy de Padilla, guerrilla military leader.
- Manuel Ascencio Padilla, namesake of the town of Padilla, Bolivia.
- Modesto Omiste Tinajeros, writer, politician, and namesake of the province Modesto Omiste.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 2018-09-13.
- ^ "TelluBase—BoliviaFact Sheet (Tellusant Public Service Series)" (PDF). Tellusant. Retrieved 2024-01-11.
- ^ a b Kandt, Lia Helguero (20 March 2023). "Konflikt in Bolivien um Lithiumproduktion vorerst beigelegt". amerika21 (in German). Mondial21 e. V. Retrieved 25 March 2023.
- ^ a b "Gobernador de Potosí, Jhonny Mamani". eabolivia.com (in Spanish). Retrieved 26 March 2023.
- ^ "Directiva de la Asamblea Legislativa Departamental de Potosí". asambleadepotosi.gob.bo (in Spanish). Retrieved 26 March 2023.
- ^ "Bolivia: Provinces".
- ^ www.bolivia.com (English)
- ^ obd.descentralizacion.gov.bo Archived 2009-02-18 at the Wayback Machine (Spanish)


