Rutinose
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
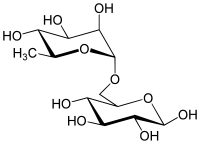
| IUPAC name α-L-Rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranose | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (2R,3S,4S,5S)-6-[ [(2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-oxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxane-2,3,4,5-tetrol | |
| Other names 6-O-(α-L-Rhamnosyl)-D-glucose, 6-O-(α-L-Rhamnopyranosyl)-D-glucopyranose, 6-O-(6-Deoxy-alpha-L-mannopyranosyl)-D-glucose | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.832 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H22O10 | |
| Molar mass | 326.297 g/mol |
| Density | 1.662 g/mL |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Rutinose is the disaccharide also known as 6-O-α-L-rhamnosyl-D-glucose (C12H22O10) that is present in some flavonoid glycosides. It is prepared from rutin by hydrolysis with the enzyme rhamnodiastase.
References
[edit]- Kamiya, Shintaro; Sachiko Esaki; Reiko Tanaka (1985). "Synthesis of Some Disaccharides Containing an L-Rhamnopyranosyl or L-Mannopyranosyl Residue, and the Substrate-specificity of α-L-Rhamnosidase from Aspergillus niger". Agricultural and Biological Chemistry. 49 (1): 55–62. doi:10.1271/bbb1961.49.55. Retrieved 26 May 2009.