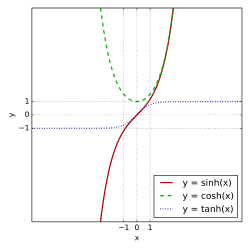
sh , ch та th Гіперболі́чні фу́нкції — сімейство елементарних функцій , які виражаються через експоненту і тісно пов'язані з тригонометричними функціями .
Визначення гіперболічних функцій через гіперболу Гіперболічні функції задаються такими формулами:
s h x = e x − e − x 2 {\displaystyle \mathop {\mathrm {sh} } \,x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{2}}} sinh x {\displaystyle \sinh x} Існує сленгова назва: «шинус».
c h x = e x + e − x 2 {\displaystyle \mathop {\mathrm {ch} } \,x={\frac {e^{x}+e^{-x}}{2}}} cosh x {\displaystyle \cosh x} Існує сленгова назва: «чосинус», «кошинус».
Лінію гіперболічного косинуса називають ланцюговою
t h x = s h x c h x {\displaystyle \mathop {\mathrm {th} } \,x={\frac {\mathop {\mathrm {sh} } \,x}{\mathop {\mathrm {ch} } \,x}}} tanh x {\displaystyle \tanh x} Існують сленгові назви: «щангенс», «цангенс».
Іноді також визначається
c t h x = 1 t h x {\displaystyle \mathop {\mathrm {cth} } \,x={\frac {1}{\mathop {\mathrm {th} } \,x}}} гіперболічні секанс і косеканс : s e c h x = 1 c h x {\displaystyle \mathop {\mathrm {sech} } \,x={\frac {1}{\mathop {\mathrm {ch} } \,x}}} c s c h x = 1 s h x {\displaystyle \mathop {\mathrm {csch} } \,x={\frac {1}{\mathop {\mathrm {sh} } \,x}}} Один зі способів визначення тригонометричних функцій через одиничне коло Гіперболічні функції виражаються через тригонометричні функції від уявного аргументу.
sh x = − i sin ( i x ) , ch x = cos ( i x ) , th x = − i tg ( i x ) {\displaystyle \operatorname {sh} x=-i\sin(ix),\quad \operatorname {ch} x=\cos(ix),\quad \operatorname {th} x=-i\operatorname {tg} (ix)}
sh ( i x ) = i sin x , ch ( i x ) = cos x , th ( i x ) = i tg x {\displaystyle \operatorname {sh} (ix)=i\operatorname {sin} x,\quad \operatorname {ch} (ix)=\cos x,\quad \operatorname {th} (ix)=i\operatorname {tg} x}
Функція Гудермана зв'язує тригонометричні функції та гіперболічні функції без залучення комплексних чисел .
ch 2 x − sh 2 x = 1 {\displaystyle \operatorname {ch} ^{2}x-\operatorname {sh} ^{2}x=1} Парність : sh ( − x ) = − sh x {\displaystyle \operatorname {sh} (-x)=-\operatorname {sh} x} ch ( − x ) = ch x {\displaystyle \operatorname {ch} (-x)=\operatorname {ch} x} th ( − x ) = − th x {\displaystyle \operatorname {th} (-x)=-\operatorname {th} x} Формули додавання: sh ( x ± y ) = sh x ch y ± sh y ch x {\displaystyle \operatorname {sh} (x\pm y)=\operatorname {sh} x\,\operatorname {ch} y\pm \operatorname {sh} y\,\operatorname {ch} x} ch ( x ± y ) = ch x ch y ± sh y sh x {\displaystyle \operatorname {ch} (x\pm y)=\operatorname {ch} x\,\operatorname {ch} y\pm \operatorname {sh} y\,\operatorname {sh} x} th ( x ± y ) = th x ± th y 1 ± th x th y {\displaystyle \operatorname {th} (x\pm y)={\frac {\operatorname {th} x\pm \operatorname {th} y}{1\pm \operatorname {th} x\operatorname {th} y}}} Формули подвоєного кута: sh 2 x = 2 ch x sh x = 2 th x 1 − th 2 x {\displaystyle \operatorname {sh} 2x=2\operatorname {ch} x\,\operatorname {sh} x={\frac {2\,\operatorname {th} x}{1-\operatorname {th} ^{2}x}}} ch 2 x = ch 2 x + sh 2 x = 2 ch 2 x − 1 = 1 + 2 sh 2 x = 1 + th 2 x 1 − th 2 x {\displaystyle \operatorname {ch} 2x=\operatorname {ch} ^{2}x+\operatorname {sh} ^{2}x=2\operatorname {ch} ^{2}x-1=1+2\operatorname {sh} ^{2}x={\frac {1+\operatorname {th} ^{2}x}{1-\operatorname {th} ^{2}x}}} th 2 x = 2 th x 1 + th 2 x {\displaystyle \operatorname {th} 2x={\frac {2\operatorname {th} x}{1+\operatorname {th} ^{2}x}}} cth 2 x = 1 2 ( th x + cth x ) {\displaystyle \operatorname {cth} 2x={\frac {1}{2}}(\operatorname {th} x+\operatorname {cth} x)} th x = ch 2 x − 1 sh 2 x = sh 2 x 1 + ch 2 x {\displaystyle \operatorname {th} x={\frac {\operatorname {ch} 2x-1}{\operatorname {sh} 2x}}={\frac {\operatorname {sh} 2x}{1+\operatorname {ch} 2x}}} ch 2 x ± sh 2 x = ( sh x ± ch x ) 2 {\displaystyle \operatorname {ch} 2x\pm \operatorname {sh} 2x=(\operatorname {sh} x\pm \operatorname {ch} x)^{2}} Формули кратних кутів: sh 3 x = 4 sh 3 x + 3 sh x {\displaystyle \operatorname {sh} 3x=4\operatorname {sh} ^{3}x+3\operatorname {sh} x} ch 3 x = 4 ch 3 x − 3 ch x {\displaystyle \operatorname {ch} 3x=4\operatorname {ch} ^{3}x-3\operatorname {ch} x} th 3 x = th x 3 + th 2 x 1 + 3 th 2 x {\displaystyle \operatorname {th} 3x=\operatorname {th} x{\frac {3+\operatorname {th} ^{2}x}{1+3\operatorname {th} ^{2}x}}} sh 5 x = 16 sh 5 x + 20 sh 3 x + 5 sh x {\displaystyle \operatorname {sh} 5x=16\operatorname {sh} ^{5}x+20\operatorname {sh} ^{3}x+5\operatorname {sh} x} ch 5 x = 16 ch 5 x − 20 ch 3 x + 5 ch x {\displaystyle \operatorname {ch} 5x=16\operatorname {ch} ^{5}x-20\operatorname {ch} ^{3}x+5\operatorname {ch} x} th 5 x = th x th 4 x + 10 th 2 x + 5 5 th 4 x + 10 th 2 x + 1 {\displaystyle \operatorname {th} 5x=\operatorname {th} x{\frac {\operatorname {th} ^{4}x+10\operatorname {th} ^{2}x+5}{5\operatorname {th} ^{4}x+10\operatorname {th} ^{2}x+1}}} Добуток sh x sh y = ch ( x + y ) − ch ( x − y ) 2 {\displaystyle \operatorname {sh} x\operatorname {sh} y={\frac {\operatorname {ch} (x+y)-\operatorname {ch} (x-y)}{2}}} sh x ch y = sh ( x + y ) + sh ( x − y ) 2 {\displaystyle \operatorname {sh} x\operatorname {ch} y={\frac {\operatorname {sh} (x+y)+\operatorname {sh} (x-y)}{2}}} ch x ch y = ch ( x + y ) + ch ( x − y ) 2 {\displaystyle \operatorname {ch} x\operatorname {ch} y={\frac {\operatorname {ch} (x+y)+\operatorname {ch} (x-y)}{2}}} th x th y = ch ( x + y ) − ch ( x − y ) ch ( x + y ) + ch ( x − y ) {\displaystyle \operatorname {th} x\operatorname {th} y={\frac {\operatorname {ch} (x+y)-\operatorname {ch} (x-y)}{\operatorname {ch} (x+y)+\operatorname {ch} (x-y)}}} Суми sh x ± sh y = 2 sh x ± y 2 ch x ∓ y 2 {\displaystyle \operatorname {sh} x\pm \operatorname {sh} y=2\operatorname {sh} {\frac {x\pm y}{2}}\operatorname {ch} {\frac {x\mp y}{2}}} ch x + ch y = 2 ch x + y 2 ch x − y 2 {\displaystyle \operatorname {ch} x+\operatorname {ch} y=2\operatorname {ch} {\frac {x+y}{2}}\operatorname {ch} {\frac {x-y}{2}}} ch x − ch y = 2 sh x + y 2 sh x − y 2 {\displaystyle \operatorname {ch} x-\operatorname {ch} y=2\operatorname {sh} {\frac {x+y}{2}}\operatorname {sh} {\frac {x-y}{2}}} th x ± th y = sh x ± y ch x ch y {\displaystyle \operatorname {th} x\pm \operatorname {th} y={\frac {\operatorname {sh} x\pm y}{\operatorname {ch} x\operatorname {ch} y}}} Формули пониження степеня ch 2 x 2 = ch x + 1 2 {\displaystyle \operatorname {ch} ^{2}{\frac {x}{2}}={\frac {\operatorname {ch} x+1}{2}}} sh 2 x 2 = ch x − 1 2 {\displaystyle \operatorname {sh} ^{2}{\frac {x}{2}}={\frac {\operatorname {ch} x-1}{2}}} Похідні: ( sh x ) ′ = ch x {\displaystyle (\operatorname {sh} x)^{\prime }=\operatorname {ch} x} ( ch x ) ′ = sh x {\displaystyle (\operatorname {ch} x)^{\prime }=\operatorname {sh} x} ( th x ) ′ = 1 ch 2 x {\displaystyle (\operatorname {th} x)^{\prime }={\frac {1}{\operatorname {ch} ^{2}x}}} sh x = ∫ 0 x ch t d t {\displaystyle \operatorname {sh} x=\int \limits _{0}^{x}\operatorname {ch} tdt} ch x = 1 + ∫ 0 x sh t d t {\displaystyle \operatorname {ch} x=1+\int \limits _{0}^{x}\operatorname {sh} tdt} th x = ∫ 0 x d t ch 2 t {\displaystyle \operatorname {th} x=\int \limits _{0}^{x}{\frac {dt}{\operatorname {ch} ^{2}t}}} Інтеграли: ∫ sh x d x = ch x + C {\displaystyle \int \operatorname {sh} x\,dx=\operatorname {ch} x+C} ∫ ch x d x = sh x + C {\displaystyle \int \operatorname {ch} x\,dx=\operatorname {sh} x+C} ∫ th x d x = ln ch x + C {\displaystyle \int \operatorname {th} x\,dx=\ln \operatorname {ch} x+C} ∫ 1 ch 2 x d x = th x + C {\displaystyle \int {\frac {1}{\operatorname {ch} ^{2}x}}\,dx=\operatorname {th} x+C} ∫ 1 sh 2 x d x = − cth x + C {\displaystyle \int {\frac {1}{\operatorname {sh} ^{2}x}}\,dx=-\operatorname {cth} x+C} Дивись також: Таблиця інтегралів гіперболічних функцій Таблиця інтегралів обернених гіперболічних функцій При всіх x ∈ R {\displaystyle x\in \mathbb {R} }
0 ≤ ch x − 1 ≤ | sh x | < ch x {\displaystyle 0\leq \operatorname {ch} x-1\leq |\operatorname {sh} x|<\operatorname {ch} x} | th x | < 1 {\displaystyle |\operatorname {th} x|<1} sh x = x + x 3 3 ! + x 5 5 ! + x 7 7 ! + … = ∑ n = 0 ∞ x 2 n + 1 ( 2 n + 1 ) ! {\displaystyle \operatorname {sh} x=x+{\frac {x^{3}}{3!}}+{\frac {x^{5}}{5!}}+{\frac {x^{7}}{7!}}+\ldots =\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }{\frac {x^{2n+1}}{(2n+1)!}}} ch x = 1 + x 2 2 ! + x 4 4 ! + x 6 6 ! + … = ∑ n = 0 ∞ x 2 n ( 2 n ) ! {\displaystyle \operatorname {ch} x=1+{\frac {x^{2}}{2!}}+{\frac {x^{4}}{4!}}+{\frac {x^{6}}{6!}}+\ldots =\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }{\frac {x^{2n}}{(2n)!}}} th x = x − x 3 3 + 2 x 5 15 − 17 x 7 315 + … = ∑ n = 1 ∞ ( − 1 ) n − 1 2 2 n ( 2 2 n − 1 ) B 2 n x 2 n − 1 ( 2 n ) ! , | x | < π 2 {\displaystyle \operatorname {th} x=x-{\frac {x^{3}}{3}}+{\frac {2x^{5}}{15}}-{\frac {17x^{7}}{315}}+\ldots =\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }{\frac {(-1)^{n-1}2^{2n}(2^{2n}-1)B_{2n}x^{2n-1}}{(2n)!}},\quad |x|<{\frac {\pi }{2}}} cth x = 1 x + x 3 − x 3 45 + 2 x 5 945 + … = 1 x + ∑ n = 1 ∞ ( − 1 ) n − 1 2 2 n B 2 n x 2 n − 1 ( 2 n ) ! , 0 < | x | < π {\displaystyle \operatorname {cth} x={\frac {1}{x}}+{\frac {x}{3}}-{\frac {x^{3}}{45}}+{\frac {2x^{5}}{945}}+\ldots ={\frac {1}{x}}+\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }{\frac {(-1)^{n-1}2^{2n}B_{2n}x^{2n-1}}{(2n)!}},\quad 0<|x|<\pi } Ряд Лорана ).Тут B 2 n {\displaystyle B_{2n}} числа Бернуллі .
sh(x) , ch(x) , th(x) , cth(x) Гіперболічний синус і гіперболічний косинус аналітичний у всій комплексній площині, за винятком істотно особливої точки на нескінченності. Гіперболічний тангенс аналітичний скрізь, окрім полюсів в точках z = i π ( n + 1 2 ) {\displaystyle z=i\pi (n+{\tfrac {1}{2}})} n {\displaystyle n} Лишки у всіх цих полюсах рівні одиниці. Гіперболічний котангенс аналітичний скрізь, окрім точок z = i π n {\displaystyle z=i\pi n}