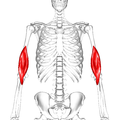
肱肌

| 肱肌 | |
|---|---|
 胸部及上臂部深層肌肉,圖中可見腋窩的邊界,肱肌位於圖右下方 | |
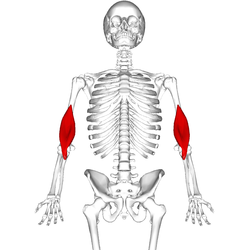 肱肌的位置(紅色部分) | |
| 基本信息 | |
| 起點 | 肱骨腹側,位於肱骨一半長度處 |
| 終點 | 尺骨冠突及尺骨粗隆 |
| 动脉 | 橈側返動脈, brachial artery |
| 神经 | 肌皮神經(C5-C7) and radial nerve (C5, C6) |
| 相關動作 | 肘關節的屈曲 |
| 标识字符 | |
| 拉丁文 | musculus brachialis |
| TA98 | A04.6.02.018 |
| TA2 | 2469 |
| FMA | FMA:37667 |
| 格雷氏 | p.444 |
| 《肌肉解剖学术语》 [在维基数据上编辑] | |
解剖學
[编辑]起點及終點
[编辑]肱肌有兩個起點,分別為較粗的淺端及較細的深端。淺端的起點始於肱骨前外側面,毗鄰於深端。淺端含有綜走纖維,匯聚為圓柱狀的肌腱,最終附著於尺骨粗隆。深端則為帆狀腱膜,最終附著於冠突[1]。
變異
[编辑]在某些人身上可能會出現兩條肱肌。
神經支配
[编辑]肱肌受到肌皮神經所支配,肌皮神經會由肱二頭肌及肱肌之間下行[2]。橈神經則負責傳遞肱肌的本體感覺,以及支配深端下外側的肌纖維[1]。
功能
[编辑]有學者認為肱肌較為粗壯的淺端可與與肱二頭肌協同作出肘關節屈曲的動作[1][2]。而較細小的深端則因附著於橈骨的冠突上,因此可負責肘動脈屈曲的起始動作[1]。
歷史
[编辑]語源
[编辑]肱肌的現行標準解剖學術語「musculus bracchialis」源自於拉丁文[3][4][5],意指「肱部的肌肉」[6]。在古典拉丁語中「bracchialis」為後綴形容詞,表示「肱部的」[7],源自於「上臂」(bracchium)這個詞[7]
附加圖像
[编辑]- 肱肌位置全像動畫
- 肱肌位置
- 上臂水平切面,肱肌位於圖中左方。
- 下臂肌肉,圖左下方可見到肱肌的終末肌腱
- 左側肱骨腹面觀
- 左側前臂骨骼腹面觀
- 左側上肢神經
- 肱肌
參見
[编辑]本條目使用了部分解剖術語。
參考文獻
[编辑]本條目包含來自屬於公共領域版本的《格雷氏解剖學》之內容,而其中有些資訊可能已經過時。
- ^ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Leonello, Domenic T.; Galley, Ian J.; Bain, Gregory I.; Carter, Christopher D. Brachialis muscle anatomy. A study in cadavers. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 2007-06-01, 89 (6): 1293–1297 [2016-07-30]. ISSN 0021-9355. PMID 17545433. doi:10.2106/JBJS.F.00343. (原始内容存档于2013-08-25).
- ^ 2.0 2.1 Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul. Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. 2005: 662,672. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0.
- ^ Federative Committee on Anatomical Terminology (FCAT) (1998). Terminologia Anatomica. Stuttgart: Thieme
- ^ Dirckx, J.H. (Ed.) (1997).Stedman’s concise medical dictionary for the health professions. (3rd edition). Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins.
- ^ Anderson, D.M. (2000). Dorland’s illustrated medical dictionary (29th edition). Philadelphia/London/Toronto/Montreal/Sydney/Tokyo: W.B. Saunders Company.
- ^ Triepel, H. (1910). Die anatomischen Namen. Ihre Ableitung und Aussprache. Mit einem Anhang: Biographische Notizen.(Dritte Auflage). Wiesbaden: Verlag J.F. Bergmann.
- ^ 7.0 7.1 Lewis, C.T. & Short, C. (1879). A Latin dictionary founded on Andrews' edition of Freund's Latin dictionary. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
外部連結
[编辑]- Illustration: brachialis from The Department of Radiology at the University of Washington
- -1777991623 於 GPnotebook
- Muscles/Brachialis at exrx.net