分枝鎖アミノ酸
 ウィキペディアから無料の百科事典
ウィキペディアから無料の百科事典
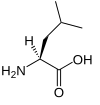
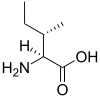
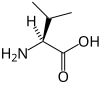
分枝鎖アミノ酸または分岐鎖アミノ酸(branched-chain amino acids、BCAA)とは、分枝(任意の炭素原子に2以上の別の炭素原子が結合)のある脂肪族側鎖を有するアミノ酸である。タンパク質を構成するアミノ酸では、ロイシン、イソロイシンおよびバリンの3種の分枝鎖アミノ酸がある[1]。
概要[編集]
先述の3種の分枝鎖アミノ酸はヒトでは必須アミノ酸であり、筋タンパク質中の必須アミノ酸の35%を占め、哺乳類にとって必要とされるアミノ酸の40%を占める[2]。分枝鎖アミノ酸は臨床では、火傷の治療や[3]、肝性脳症の治療に用いられている[4]。
サプリメント[編集]
運動後の筋損傷を抑制し、筋疲労や筋肉痛を軽減する効果があるとされており[5]、サプリメントとして販売されている。
代謝[編集]
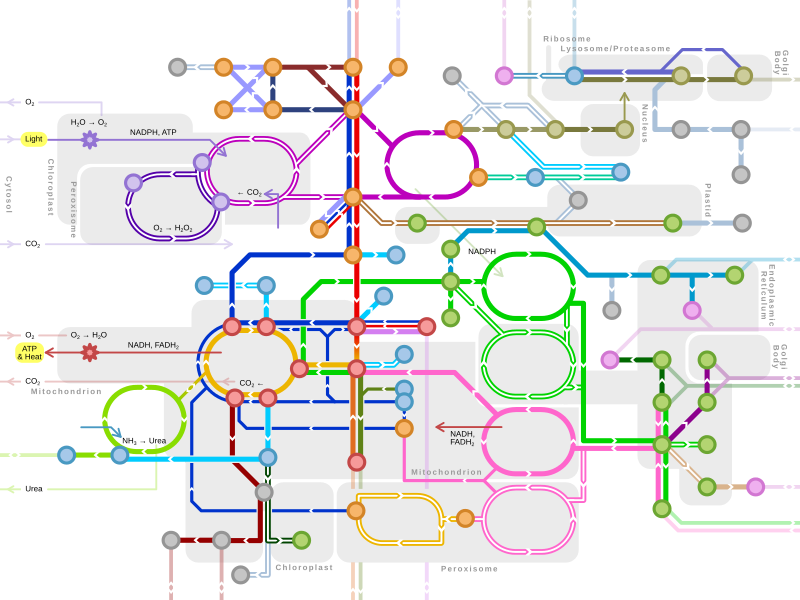
分枝鎖アミノ酸の分解には分枝鎖α-ケト酸デヒドロゲナーゼ複合体(BCKDH)が関与している。この複合体が欠損すると、分枝鎖アミノ酸およびその毒性副産物が血液や尿に蓄積し、メープルシロップ尿症が発症する。関与する酵素は分枝鎖アミノトランスフェラーゼと3-メチル-2-オキソブタン酸デヒドロゲナーゼ (2-メチルプロパノイル基転移)である。BCKDH複合体によって分枝鎖アミノ酸はアシルCoA誘導体に変換され、これは続いてアセチルCoAもしくはスクシニルCoAとなり、最終的にクエン酸回路に組み込まれる[6]。
出典[編集]
- ^ Sowers, Strakie. “A Primer On Branched Chain Amino Acids”. Huntington College of Health Sciences. 2011年3月22日閲覧。
- ^ “Exercise Promotes BCAA Catabolism: Effects of BCAA Supplementation on Skeletal Muscle during Exercise”. J. Nutr. 134 (6): 1583S-1587S. (2004) 2011年3月22日閲覧。.
- ^ “Therapeutic use of branched-chain amino acids in burn, trauma, and sepsis”. J. Nutr.. 1 Suppl 136 (30): 8S-13S. (2006) 2011年3月22日閲覧。.
- ^ “Nutrition in hepatic encephalopathy”. Nutr Clin Pract. 25 (3): 257-64. (2010). doi:10.1177/0884533610368712.
- ^ Koba, T.; Hamada, K.; Sakurai, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Hayase, H.; Imaizumi, K.; Tsujimoto, H.; Mitsuzono, R. (2007-09). “Branched-chain amino acids supplementation attenuates the accumulation of blood lactate dehydrogenase during distance running”. The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness 47 (3): 316–322. ISSN 0022-4707. PMID 17641599.
- ^ “Mechanisms of human insulin resistance and thiazolidinedione-mediated insulin sensitization”. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 106 (44): 18745-18750. (2009). doi:10.1073/pnas.0903032106 2011年3月22日閲覧。.
参考文献[編集]
- Karlsson HK, Nilsson PA, Nilsson J, Chibalin AV, Zierath JR, Blomstrand E (2004). “Branched-chain amino acids increase p70S6k phosphorylation in human skeletal muscle after resistance exercise”. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 287 (1): E1–7. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00430.2003. PMID 14998784.
- Blomstrand E, Eliasson J, Karlsson HK, Köhnke R (2006). “Branched-chain amino acids activate key enzymes in protein synthesis after physical exercise”. J. Nutr. 136 (1 Suppl): 269S–73S. PMID 16365096.
- Norton LE, Layman DK (2006). “Leucine regulates translation initiation of protein synthesis in skeletal muscle after exercise”. J. Nutr. 136 (2): 533S–537S. PMID 16424142.
関連項目[編集]
外部リンク[編集]
- Branched-chain amino acids - MeSH・アメリカ国立医学図書館・生命科学用語シソーラス(英語)