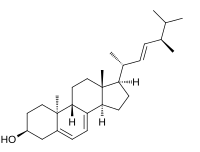
Lumisterol

 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name (22E)-9β,10α-Ergosta-5,7,22-trien-3β-ol | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (1R,3aR,7S,9aS,9bR,11aR)-1-[(2R,3E,5R)-5,6-Dimethylhept-3-en-2-yl]-9a,11a-dimethyl-2,3,3a,6,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-7-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.808 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H44O | |
| Molar mass | 396.659 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Lumisterol is a compound that is part of the vitamin D family of steroid compounds. It is the (9β,10α) stereoisomer of ergosterol and was produced as a photochemical by-product in the preparation of vitamin D1, which was a mixture of vitamin D2 and lumisterol.[1][2] Vitamin D2 can be formed from lumisterol by an electrocyclic ring opening and subsequent sigmatropic [1,7] hydride shift.
Lumisterol has an analog based on 7-dehydrocholesterol, known as lumisterol 3.[3]
References
[edit]- ^ Dewick, Paul M. (2002). Medicinal Natural Products. A Biosynthetic Approach (PDF) (Second ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons. p. 259. ISBN 0-471-49640-5.
- ^ Friedmann, Ernst (1989). Neurath, Hans (ed.). Vitamin D. Perspectives in Biochemistry. Vol. 1. Washington, DC: American Chemical Society. ISBN 978-0-8412-1621-1.
- ^ National Center for Biotechnology Information. "Lumisterol 3 (CID=111049)". PubChem Compound Database. Retrieved 10 April 2018.