November 1974 lunar eclipse

| Total eclipse | |||||||||||||||||
| Date | 29 November 1974 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma | 0.30540 | ||||||||||||||||
| Magnitude | 1.28961 | ||||||||||||||||
| Saros cycle | 125 (46 of 72) | ||||||||||||||||
| Totality | 75 minutes, 45 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| Partiality | 208 minutes, 58.7 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| Penumbral | 333 minutes, 11.6 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
A total lunar eclipse took place on Friday, November 29, 1974, the second of two lunar eclipses in 1974. The Moon was plunged into darkness for 1 hour, 15 minutes and 45 seconds, in a deep total eclipse which saw the Moon 28.961% of its diameter inside the Earth's umbral shadow. The visual effect of this depends on the state of the Earth's atmosphere, but the Moon may have been stained a deep red colour. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 28 minutes and 58.7 seconds in total. The penumbral eclipse lasted for 5 hours, 33 minutes and 11.6 seconds. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 28 minutes and 58.7 seconds. The total eclipse lasted for 1 hour, 15 minutes and 45 seconds. Occurring only 3.6 days before perigee (Perigee on Tuesday, December 3, 1974), the Moon's apparent diameter was 1.4% larger than average.
Visibility
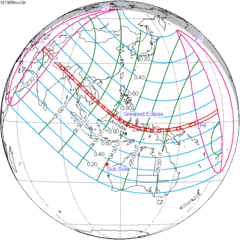
[edit]It was completely visible over Europe, Africa, Asia, Australia, Pacific, western North America, seen rising over Europe and Africa and setting over the central Pacific Ocean and North America.
Related lunar eclipses
[edit]Eclipses in 1974
[edit]- A partial lunar eclipse on Tuesday, 4 June 1974.
- A total solar eclipse on Thursday, 20 June 1974.
- A total lunar eclipse on Friday, 29 November 1974.
- A partial solar eclipse on Friday, 13 December 1974.
Lunar year series
[edit]| Lunar eclipse series sets from 1973–1976 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||||
| Saros | Date Viewing | Type Chart | Gamma | Saros | Date Viewing | Type Chart | Gamma | |
| 110 | 1973 Jun 15 | Penumbral | −1.32166 | 115 | 1973 Dec 10 | Partial | 0.96441 | |
| 120 | 1974 Jun 04 | Partial | −0.54887 | 125 | 1974 Nov 29 | Total | 0.30540 | |
| 130 | 1975 May 25 | Total | 0.23674 | 135 | 1975 Nov 18 | Total | −0.41343 | |
| 140 | 1976 May 13 | Partial | 0.95860 | 145 | 1976 Nov 06 | Penumbral | −1.12760 | |
| Last set | 1973 Jul 15 | Last set | 1973 Jan 18 | |||||
| Next set | 1977 Apr 04 | Next set | 1977 Sep 27 | |||||
Saros series
[edit]Lunar saros series 125, repeating every 18 years and 11 days, has 26 total lunar eclipses. The first was on June 17, 1704 and the last will be on March 19, 2155. The longest totality occurrence of this series (7th) was on August 22, 1812 when totality lasted one hour and 42 minutes.[1]
This is the 16th of 26 total lunar eclipses in series 125. The previous occurrence was on November 18, 1956 and the next will occur on December 9, 1992.
Half-Saros cycle
[edit]A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[2] This lunar eclipse is related to two annular solar eclipses of Solar Saros 132.
| November 23, 1965 | December 4, 1983 |
|---|---|
 |  |
Tritos
[edit]- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of December 30, 1963
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of October 28, 1985
Tzolkinex
[edit]- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of October 18, 1967
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of January 9, 1982
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ Listing of Eclipses of cycle 125
- ^ Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
External links
[edit]- 1974 Nov 29 chart Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC



