Ginger

| Ginger | |
|---|---|
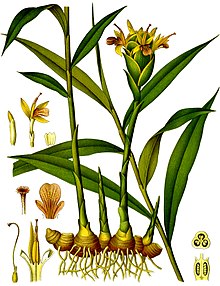 | |
| 1896 color plate from Köhler's Medicinal Plants | |
 | |
| Inflorescence | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Clade: | Commelinids |
| Order: | Zingiberales |
| Family: | Zingiberaceae |
| Genus: | Zingiber |
| Species: | Z. officinale |
| Binomial name | |
| Zingiber officinale | |
Ginger is a flowering plant whose rhizome, ginger root or ginger, is used as a spice and a folk medicine.[2]
It is a herbaceous perennial which grows annual pseudostems. These are false stems made of rolled leaves: about one meter tall with narrow leaf blades. The inflorescences come directly from the rhizome on separate shoots.[3]
Ginger is used as a cooking spice throughout the world. The ginger plant has long been cultivated. It came from China and spread to India, Southeast Asia, West Africa, and the Caribbean.
Ginger is also a term used to describe a red-brown colour, as in ginger hair.
References
[change | change source]- ↑ "Zingiber officinale". Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN). Agricultural Research Service (ARS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Retrieved 10 December 2017.
- ↑ "Ginger". US National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. 1 September 2016. Retrieved 2 February 2019.
- ↑ Sutarno H, Hadad EA, Brink M (1999). "Zingiber officinale Roscoe". In De Guzman CC, Siemonsma JS (eds.). Plant resources of South-East Asia: no.13: Spices. Leiden (Netherlands): Backhuys. pp. 238–244.