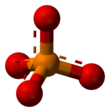
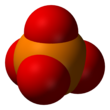
Phosphate

 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name Phosphate[1] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| Beilstein Reference | 3903772 | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| Gmelin Reference | 1997 | ||
| MeSH | Phosphates | ||
PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| PO3− 4 | |||
| Molar mass | 94.9714 g mol−1 | ||
| Conjugate acid | Hydrogen phosphate | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
A phosphate is a salt of phosphoric acid. Phosphates are important in biochemistry. Phosphates have the formula PO43- and a molar mass of 94.973 g/mol. An example of a phosphate is sodium phosphate. Three different types of phosphates are known. They are orthophosphate, PO43-; metaphosphate, PO32-; and pyrophosphate, P2O73-. They have a combining power of 3.

Structure
[change | change source]Phosphates are made of one phosphorus atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms. Many phosphates do not dissolve in water.
Sources
[change | change source]- ↑ "Phosphates – PubChem Public Chemical Database". The PubChem Project. USA: National Center of Biotechnology Information.