Aclidinium bromide

 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Bretaris Genuair, Eklira Genuair, Tudorza Pressair |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | Inhalation |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | <5% (in system) 30% (in lung) |
| Metabolism | Ester hydrolysis |
| Elimination half-life | 2–3 hrs |
| Duration of action | >24 hrs |
| Excretion | 65% urine, 33% feces |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.260.213 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
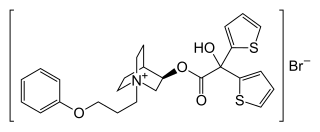
| Formula | C26H30BrNO4S2 |
| Molar mass | 564.55 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Aclidinium bromide (INN) is a long-acting, inhaled muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) approved in the United States in July 2012[3] as a maintenance treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).[4]
Evidence shows that it can improve quality of life and prevent hospitalization in those with COPD.[5] However, it does not appear to affect the risk of death or the frequency steroids are needed.[5] It is unclear if it differs from the similar medication tiotropium or other commonly used medications from the class of LAMAs.[5]
Aclidinium is delivered via a multidose dry powder inhaler, the Genuair inhaler. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[6]
Adverse effects
[edit]The substance is generally well tolerated. Common side effects (in more than 1% of patients) are sinusitis, nasopharyngitis, headache, cough, diarrhoea and nausea. The latter is less common under the drug than under placebo. Skin reactions such as rash, as well as side effects that are typical of muscarinic antagonists (fast heart rate, palpitations, and urinary retention), occur in less than 1% of patients.[7][8]
A small increase of cardiovascular risk cannot be excluded from available data. Patients with relevant cardiovascular diseases were excluded from studies.[9]
Interactions
[edit]No systematic interaction studies have been performed. It is expected that adverse effects of aclidinium increase if it is combined with other muscarinic antagonists. In clinical practice, no interactions with other COPD medications such as glucocorticoids, β2-adrenergic agonists and theophylline have been described. As aclidinium does not relevantly interact with cytochrome P450 liver enzymes or P-glycoprotein, and is quickly metabolized as soon as it reaches the bloodstream, it is considered to have a very low potential for interactions.[7][9]
Pharmacology
[edit]Mechanism of action
[edit]Aclidinium is a long-acting, reversible antagonist at muscarinic receptors, with similar affinity to all five subtypes, but with a dissociation half-life from subtype M3 of 29.2 hours, or six times longer than that from M2. For comparison, M3 dissociation half-lives of the related drugs ipratropium and tiotropium are 0.47 hours and 62.2 hours, respectively.[9]
Its action at subtype M3 at the smooth muscle of the bronchioles is responsible for its desired effect: it reduces contraction of these muscles and improves the airflow.[7][8] M2 affinity is the main reason for adverse effects at the heart.[9]
Pharmacokinetics
[edit]About 30% of inhaled aclidinium are deposited in the lung.[9] Its action there lasts for more than 24 hours.[8] From the lung, it is absorbed into the bloodstream, reaching highest blood plasma concentrations after five minutes in healthy persons and after 10 to 15 minutes in COPD patients. The substance is quickly hydrolysed to the carboxylic acid and the alcohol, so that less than 5% of the inhaled dose are found unchanged in the plasma. Hydrolysis is both non-enzymatic and enzymatic, the latter mainly by butyrylcholinesterase.[7][9]
The acid metabolite has a plasma protein binding of 87%, and the alcohol of 15%. These metabolites are found to 65% in the urine and to 33% in the faeces. Elimination half-life is two to three hours. Unchanged aclidinium accounts for only 0.1% of the excreted dose.[7]
Chemistry
[edit]Aclidinium is a quaternary ammonium cation with an asymmetric carbon atom. It is used as the pure R-enantiomer. The salt, aclidinium bromide, is a crystalline powder that is hardly soluble in water or ethanol.
Society and culture
[edit]Brand names
[edit]It is marketed under the brand name Tudorza Pressair in the US, Eklira Genuair in the UK, and Tudorza Genuair in Canada; licensed to Menarini under the brand name Bretaris Genuair for majority of EU member states.[10]
An inhalable combination with formoterol is marketed as Brimica Genuair[11] and Duaklir Genuair[12] in the European Union.
References
[edit]- ^ "Prescription medicines: registration of new chemical entities in Australia, 2014". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 21 June 2022. Retrieved 10 April 2023.
- ^ "Bretaris Genuair EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 20 July 2012. Retrieved 21 June 2024.
- ^ "Forest Laboratories and Almirall Announce FDA Approval of Tudorza Pressair for the Long-Term Maintenance Treatment of COPD" (Press release). Forest Laboratories. Retrieved 24 July 2012.
- ^ Gavaldà A, Miralpeix M, Ramos I, et al. (2009). "Characterization of aclidinium bromide, a novel inhaled muscarinic antagonist, with long duration of action and a favorable pharmacological profile". J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 331 (2): 740–51. doi:10.1124/jpet.109.151639. PMID 19710368. S2CID 10533142.
- ^ a b c Ni H, Soe Z, Moe S (September 2014). "Aclidinium bromide for stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2014 (9): CD010509. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010509.pub2. PMC 8922974. PMID 25234126.
- ^ World Health Organization (2021). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 22nd list (2021). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/345533. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.02.
- ^ a b c d e Haberfeld H, ed. (2015). Austria-Codex (in German). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag.
- ^ a b c FDA Professional Drug Information on Tudorza Pressair.
- ^ a b c d e f Dinnendahl V, Fricke U, eds. (2014). Arzneistoff-Profile (in German). Vol. 1 (27 ed.). Eschborn, Germany: Govi Pharmazeutischer Verlag. ISBN 978-3-7741-9846-3.
- ^ "Almirall and Menarini sign a licence agreement and commercial alliance for Aclidinium in the majority of European member states and a number of non-EU countries" (Press release). Menarini. Retrieved 26 March 2012.
- ^ "Brimica Genuair: Uses, Side Effects, Benefits/Risks". Drugs.com. 19 November 2014. Retrieved 26 July 2020.
- ^ "Duaklir Genuair: Uses, Side Effects, Benefits/Risks". Drugs.com. 19 November 2014. Retrieved 26 July 2020.