Isopropyl nitrite

 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Isopropyl alcohol nitrite; nitrous acid, isopropyl ester; 1-methylethyl nitrite; 2-propyl nitrite |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.982 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
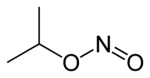
| Formula | C3H7NO2 |
| Molar mass | 89.094 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 0.8684 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 40 °C (104 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
The chemical compound isopropyl nitrite (or 2-propyl nitrite) is an alkyl nitrite made from isopropanol. It is a clear pale yellow oil that is insoluble in water.[2]

Applications
[edit]Isopropyl nitrite is one of the compounds used as poppers, an inhalant drug that induces a brief euphoria.
Safety
[edit]Isopropyl nitrite has been associated with eye maculopathy, visual impairment with central scotomata, bilateral foveal yellow spots, and inner segment/outer segment (IS/OS) junction disruption,[3] which may be reversible.[4]
References
[edit]- ^ Anvisa (2024-05-28). "RDC Nº 877 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 877 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União. Archived from the original on 2024-09-25. Retrieved 2024-09-25.
- ^ Lide DR, ed. (2004). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (85th ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8493-0485-9.
- ^ Davies AJ, Kelly SP, Naylor SG, Bhatt PR, Mathews JP, Sahni J, et al. (November 2012). "Adverse ophthalmic reaction in poppers users: case series of 'poppers maculopathy'". Eye. 26 (11): 1479–1486. doi:10.1038/eye.2012.191. PMC 3496104. PMID 23079752.
- ^ Vignal-Clermont C, Audo I, Sahel JA, Paques M (October 2010). "Poppers-associated retinal toxicity". The New England Journal of Medicine. 363 (16): 1583–5. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1005118. PMID 20942681.