MADAM-6

 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
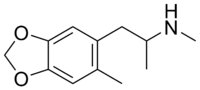
| Preferred IUPAC name N-Methyl-1-(6-methyl-2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)propan-2-amine | |
| Other names 6-Methyl-MDMA | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H17NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 207.273 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
MADAM-6, or 2, N-dimethyl-4,5-methylenedioxyamphetamine, is a lesser-known recreational drug of the methamphetamine class, similar in structure to MDMA (ecstasy).[1] MADAM-6 was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin.[2] In Shulgin's book PiHKAL, the minimum dosage is listed as greater than 280 mg, and the duration is unknown.[2] MADAM-6 produces few to no effects and Shulgin describes it as "not active".[2] Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of MADAM-6.
MADAM-6 has been studied for its potential antiparkinsonian effects.[3] However, no clinical trials suggest the drug is effective against Parkinson's disease.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Patt, M; Gündisch, D; Wüllner, U; Blocher, A; Kovar, K. -A; Machulla, H. -J (1999). "N-[11C]methyl-3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (Ecstasy) and 2-methyl-N-[11C]methyl-4,5-methylenedioxyamphetamine: Synthesis and biodistribution studies". Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry. 240 (2): 535. doi:10.1007/BF02349410. S2CID 96272983.
- ^ a b c MADAM-6 entry in PiHKAL
- ^ US patent US2015025063, Caron; Gainetdinov & Sotnikova, "Antiparkinsonian Action Of Phenylisopropylamines", published 2014-09-30, issued 2015-01-22