Tosk Albanian

| Tosk | |
|---|---|
| toskërishtja | |
| Region | Albania, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Italy, Greece, Turkey |
Native speakers | 1.8 million (2011 census)[1] |
Early form | |
| Dialects |
|
| Albanian alphabet, formerly Elbasan | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | als |
| Glottolog | alba1268tosk1239 |
| Linguasphere | to 55-AAA-ace 55-AAA-aca to 55-AAA-ace |
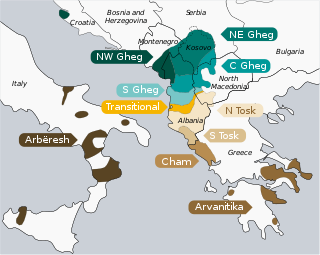 A map showing Tosk speakers in the two palest shades of brown. | |
Tosk (Albanian definite form: toskërishtja) is the southern group of dialects of the Albanian language, spoken by the ethnographic group known as Tosks. The line of demarcation between Tosk and Gheg (the northern variety) is the Shkumbin River. Tosk is the basis of the standard Albanian language.
Major Tosk-speaking groups include the Myzeqars of Myzeqe, Labs of Labëria, Chams of Çamëria, Arvanites of Greece and the Arbëreshë of Italy, as well as the original inhabitants of Mandritsa in Bulgaria. In North Macedonia, there were approximately 3000 speakers in the early 1980s.[2]
Tosk features
[edit]This section should specify the language of its non-English content, using {{lang}}, {{transliteration}} for transliterated languages, and {{IPA}} for phonetic transcriptions, with an appropriate ISO 639 code. Wikipedia's multilingual support templates may also be used. (August 2020) |
- Rhotacism: Proto-Albanian *-n- becomes -r- (e.g. rëra "sand")
- Tosk dialects preserve the consonant sequences mb, ngj and nd which are assimilated to m, nj and n in Gheg.[3]
- Proto-Albanian *ō becomes va.
- Nasal vowels: There is a lack of nasal vowels in Tosk (e.g. sy "eye") and Late Proto-Albanian *â plus a nasal becomes ë (e.g. nëntë "nine").
- e-vowel: The e becomes ë in some varieties in some words qën for qen in Vjosë.
- ë-vowel: The ë may have several pronunciations depending on dialect: the ë is more backed in Labërisht dialects like that of Vuno, where mëz "foal" is [mʌz]). Final -ë drops in many Tosk dialects and lengthens the preceding vowel.
- y-vowel: The y vowel often derounds to i in Labërisht, Çam, Arvanitika and Arbëresh (e.g. dy "two" becomes di).
- Dh and Ll: These sounds may interchange in some words in some varieties.
- H: This may drop in any position in some dialects.
- Gl/Kl: Some varieties of Çam, Arberësh, and Arvanitika retain kl and gl in place of q and gj (e.g. gjuhë "tongue" is gluhë in Çam, gluhë in Siculo-Arberësh, and gljuhë in Arvanitika; "klumësh" for "qumësht" "milk" in Arbëresh).
- Rr: Rr becomes r in some varieties.
Northern Tosk
[edit]Vowels
[edit]| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i y | u | |
| Close-mid | e | ||
| Open-mid | ɜ | ɔ | |
| Open | a |
| IPA | Description | Written as |
|---|---|---|
| i | Close front unrounded vowel | i |
| y | Close front rounded vowel | y |
| e | Close-mid front unrounded vowel | e |
| a | Open central unrounded vowel | a |
| ɜ | Open-mid central unrounded vowel | ë |
| ɔ | Open-mid back rounded vowel | o |
| u | Close back rounded vowel | u |
- Mid sounds e, o can also be heard as [ɛ, o], in free variation.[4]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Tosk at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Fraenkel, Eran; Kramer, Christina Elizabeth (1993). Language Contact - Language Conflict. P. Lang. p. 36. ISBN 9780820416526.
Thus, for example, even the small numbers of Tosk Albanians of southern North Macedonia (only approximately 3,000 in the early 1980s)
- ^ Orel, Vladimir E. (1998). Albanian etymological dictionary. Leiden: Brill. ISBN 9789004110243.
- ^ Coretta, Stefano; Riverin-Coutlée, Josiane; Kapia, Enkeleida; Nichols, Stephen (16 August 2022). "Northern Tosk Albanian". Journal of the International Phonetic Association: 1–23. doi:10.1017/S0025100322000044. hdl:20.500.11820/ebce2ea3-f955-4fa5-9178-e1626fbae15f.