Clapham Junction railway station
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
| Clapham Junction | |
|---|---|
 South West (Brighton Yard) entrance | |
| Location | Battersea |
| Local authority | London Borough of Wandsworth |
| Managed by | Network Rail |
| Station code | CLJ |
| DfT category | B |
| Number of platforms | 17 |
| Accessible | Yes[1] |
| Fare zone | 2 |
| Cycle parking | Yes – external |
| Toilet facilities | Yes – behind gateline |
| National Rail annual entry and exit | |
| 2018–19 | |
| – interchange | |
| 2019–20 | |
| – interchange | |
| 2020–21 | |
| – interchange | |
| 2021–22 | |
| – interchange | |
| 2022–23 | |
| – interchange | |
| Key dates | |
| 2 March 1863 | Opened |
| Other information | |
| External links | |
| Coordinates | 51°27′53″N 0°10′14″W / 51.4646°N 0.1705°W |
Clapham Junction railway station (/ˈklæpəm ˈdʒʌŋkʃən/[3]) is a major railway station and transport hub near St John's Hill in southwest Battersea in the London Borough of Wandsworth. It is 2 miles 57 chains (2.71 mi; 4.37 km) from London Victoria and 3 miles 74 chains (3.93 mi; 6.32 km) from London Waterloo;[4] it is on both the South West Main Line and Brighton Main Line as well as numerous other routes and branch lines passing through or diverging from the main lines at this station. Despite its name, Clapham Junction is not located in Clapham, a district situated approximately 1 mile (1.6 km) to the southeast and is instead sited in Battersea.
Routes from London's south and southwest termini, Victoria and Waterloo, funnel through the station, making it the busiest in Europe[5][better source needed] by number of trains using it: between 100 and 180 per hour except for the five hours after midnight. The station is also the busiest UK station for interchanges between services,[6] as well as the only railway station in Great Britain with more interchanges than entries or exits.[7]
History[edit]
On 21 May 1838 the London and Southampton Railway became the London and South Western Railway (L&SWR), and opened its line from Nine Elms as far as Woking. The second line, initially from Nine Elms to Richmond, opened on 27 July 1846. Nine Elms was replaced in 1848 as the terminus by Waterloo Bridge station, now Waterloo. The line to Victoria opened by 1860.

Clapham Junction opened on 2 March 1863, a joint venture of the L&SWR, the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR) and the West London Extension Railway (WLER) as an interchange station for their lines.[9]
The railway companies, to attract a middle- and upper-class clientele, seized the nonindustrial parish calculating that being upon the slopes of Clapham's plateau would only reinforce this distinction, leading to a long-lasting misunderstanding that the station is in Clapham.[10][11]
London Overground | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Legend | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Discontinued proposals[edit]
A £39.5 million planning application from Metro Shopping Fund was withdrawn before governmental planning committee consideration on 20 May 2009.[n 1]
A 'Heathrow Airtrack' to reduce the 95-minute journey by tube and Gatwick Express to Gatwick and unite the Great Western Main Line with Heathrow, Gatwick and the South West Main Line was cancelled in 2011 following improvements to the 2005-built Heathrow Connect track from Hayes and Harlington and practical impediments, such as pressure for continued high-frequency services on the three deemed-'entrenched' semi-fast and slow services between Clapham Junction and Staines. Overground, the change would have been at Clapham Junction.[12]
Incidents and accidents[edit]
Clapham rail disaster[edit]
On the morning of 12 December 1988, two collisions involving three commuter trains occurred slightly south-west of the station due to a defective signal. 35 people died and 484 were injured.[13][14]
Track bombing[edit]
On the morning of 16 December 1991, a bomb ripped through tracks on one of the station's platforms, causing major disruption to the rail network. The Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA) claimed responsibility.[15]
The Junction[edit]
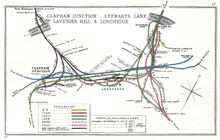

The station is named Clapham Junction because it is at the junction of several rail lines. The name is not given to any rail junction near the station which, without end-on intercompany junctions, are:
- Falcon Junction at the south end of the station, where the West London Line (WLL) joins the Brighton Slow Lines[16]
- Ludgate Junction at the eastern end of the Windsor Line platforms to the WLL[17]
- Latchmere SW Junction connecting the WLL to the Windsor lines at Ludgate Junction.[16]
- Latchmere Main Junction connecting the WLL to the Brighton Line at Falcon Junction.[16]
- West London Extension Junction and Junction for Waterloo, relaid for Eurostar empty-stock moves from the Windsor Lines to the WLL.[16]
- Pouparts Junction where the low-level and high-level approaches to Victoria split.[18]
The station today[edit]
This section needs additional citations for verification. (February 2015) |
Railways around Clapham Junction | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Each day more than 2,000 trains, over half of them stopping, pass through the station, more than through any other station in Europe.[19] At peak times up to 200 trains per hour pass through of which 122 stop. It is not the busiest station by number of passengers, most of whom (about 430,000 on a weekday, of which 135,000 are at rush hours) pass through. Interchanges make some 40% of the activity and on that basis too it is the busiest station in the UK.[20]
In 2011 the station had three entrances, all with staffed ticket offices, though only the south-east entrance is open 24 hours a day. The most heavily used of the three, this leads from St John's Hill via a small indoor shopping centre into a subway some 15 feet (4.6 m) wide, that connects to the eastern ends of all platforms.
The north entrance, which has restricted opening hours, leads from the Winstanley Estate on Grant Road to the same subway.[21][22] The subway is crowded during rush hours, with the ticket barriers at the ends being pinch points.
The south-west entrance, also known as the Brighton Yard entrance, as the buildings still bear signage for the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway, has a more traditional appearance, with a Victorian station building set at the back of a large forecourt. This entrance leads to a very wide covered footbridge, which joins the western ends of all platforms. This entrance includes cycle parking and a taxi rank. It was re-opened in May 2011 as part of a wider programme of access improvements that included installing lifts to the platforms.[23]
There are public and disabled toilets at the south-west entrance. There are refreshment kiosks in the subway, on the footbridge and on some platforms; and a small shopping centre, including a small branch of Sainsbury's supermarket, in the south-east entrance.
British Transport Police maintain a neighbourhood policing presence,[24] whereas the Metropolitan Police Service and the part-Transport for London funded Safer Transport Command provides a police presence in the area outside the station.
On 9 December 2012 a new platform for the East London Line opened, creating an orbital railway around inner London.[25]
Overcrowding is most frequent in the often convenient but narrow cross-platform subway. Using this rather than the wide, elegant flying concourse for interchange, a visitors' eyes assessment of fabric and environment listed Clapham Junction in the most needy 10% of Department for Transport category B stations.
In an attempt to reduce overcrowding, a staircase to platforms 13 and 14 was replaced with a new wider staircase in April 2023.[26]
Platforms[edit]

The station has seventeen platforms, numbered 1 to 17.[27] In general, platforms 1 and 2 are used by London Overground trains, platforms 3–11 by South Western Railway trains, and platforms 12–17 by Southern trains. Non-stop Gatwick Express trains pass through platforms 12 and 13.
- Platforms 1 and 2 are northeast-facing bay platforms connected to West London and South London Lines, respectively used by London Overground services to and from Stratford via Willesden Junction and Dalston Junction via Peckham. Usually, platform 1 is served by trains on the West London line, while platform 2 is used by services on the South London line, although this usage can be reversed.
- Platforms 3 and 4 are through platforms on the Waterloo–Reading line towards London Waterloo.
- Platforms 5 and 6 are through platforms on the Waterloo–Reading line towards Reading.
- Platform 7 is a through platform located at a siding off the South West Main Line fast line towards London Waterloo, used by stopping trains.
- Platform 8 is a through platform on the South West Main Line fast line towards London Waterloo, used by non-stop trains passing through this station.
- Platform 9 is a through platform on the South West Main Line fast line towards Woking.
- Platform 10 is a through platform on the South West Main Line slow line towards London Waterloo.
- Platform 11 is a through platform on the South West Main Line slow line towards Woking.
- Platform 12 is a through platform on the Brighton Main Line fast line towards London Victoria.
- Platform 13 is a through platform on the Brighton Main Line fast line towards East Croydon.
- Platform 14 is a through platform on the Brighton Main Line slow line towards London Victoria.
- Platform 15 is a through platform on the Brighton Main Line slow line towards East Croydon.
- Platforms 16 and 17 are platforms connecting the Brighton Main Line slow line and the West London Line, used by Southern services. Platform 16 is the northbound platform (towards Watford Junction) and platform 17 is the southbound platform (towards East Croydon). Platform 17 can also be used by some terminating London Overground services as well.
Sidings leading into railway sheds at the west of the station are located between platforms 6 and 7.
Because the platform gap is too wide at platform 8, it must not be used for stopping trains unless in an emergency.[28]
Services[edit]


All South Western Railway services from Waterloo pass through the station, as do Southern and Gatwick Express trains from Victoria. The West London line and South London line services of London Overground have Clapham Junction as one of the termini.
The typical off-peak service of 118 trains an hour comprises:
South Western Railway:
- 35 tph to London Waterloo
- 1 tph to Alton
- 1 tph to Basingstoke (slow)
- 1 tph to Exeter St Davids via Salisbury
- 1 tph to Haslemere
- 1 tph to Portsmouth and Southsea via Haslemere
- 1 tph to Salisbury (roughly 1tp2h extended to Yeovil Pen Mill)
- 1 tph to Weymouth
- 2 tph to Chessington South
- 2 tph to Dorking via Wimbledon
- 2 tph to Guildford via Cobham & Stoke d'Abernon
- 2 tph to Guildford via Epsom
- 2 tph to Hampton Court via Surbiton
- 2 tph to Shepperton via Wimbledon
- 2 tph to Woking (slow)
- 2 tph to London Waterloo by the Kingston Loop via Wimbledon, Kingston and Richmond
- 2 tph to London Waterloo by the Hounslow Loop via Brentford, Hounslow and Richmond
- 2 tph to London Waterloo by the Hounslow Loop via Richmond, Hounslow and Brentford
- 2 tph to London Waterloo by the Kingston Loop via Richmond, Kingston and Wimbledon
- 2 tph to Reading via Wokingham
- 2 tph to Weybridge via Brentford, Hounslow and Staines
- 2 tph to Windsor & Eton Riverside
Southern:
- 18 tph to London Victoria
- 1 tph to Bognor Regis and Portsmouth & Southsea dividing at Horsham
- 1 tph to Bognor Regis and Southampton Central, dividing at Horsham
- 2 tph to Littlehampton
- 2 tph to East Grinstead via Oxted
- 2 tph to Eastbourne, with 1 continuing to Ore
- 2 tph to Reigate
- 2 tph to Dorking via Sutton and Epsom, of which one continues to Horsham
- 2 tph to Epsom Downs
- 2 tph to London Bridge via Crystal Palace
- 2 tph to West Croydon
- 1 tph to East Croydon via Norbury
- 1 tph to Watford Junction via Kensington Olympia
London Overground:
- 4 tph to Dalston Junction via Canada Water
- 4 tph to Stratford via Highbury & Islington
During peak hours on weekdays express services on the South West Main Line and outer suburban services to Alton and Basingstoke typically do not stop at the station.


| Preceding station | Following station | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| London Waterloo | South Western Railway | Wimbledon, Woking or Basingstoke. | ||
| South Western Railway | Wimbledon or Surbiton | |||
| Vauxhall | South Western Railway | Earlsfield. | ||
| London Waterloo or Vauxhall | South Western Railway | Richmond | ||
| Vauxhall | South Western Railway | Putney | ||
| Queenstown Road | South Western Railway | Wandsworth Town. | ||
| London Victoria | Southern | East Croydon | ||
| Battersea Park or London Victoria | Southern
| Wandsworth Common or Balham | ||
| Southern |
| |||
