Distal hereditary motor neuropathy type V
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
| Distal hereditary motor neuropathy type V | |
|---|---|
| Other names | dHMN V |
Distal hereditary motor neuropathy type V is a particular type of neuropathic disorder. In general, distal hereditary motor neuropathies affect the axons of distal motor neurons and are characterized by progressive weakness and atrophy of muscles of the extremities.[1] It is common for them to be called "spinal forms of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT)", because the diseases are closely related in symptoms and genetic cause. The diagnostic difference in these diseases is the presence of sensory loss in the extremities.[2] There are seven classifications of dHMNs, each defined by patterns of inheritance, age of onset, severity, and muscle groups involved. Type V (sometimes notated as Type 5) is a disorder characterized by autosomal dominance, weakness of the upper limbs that is progressive and symmetrical, and atrophy of the small muscles of the hands.[3]
Signs and symptoms
[edit]Onset usually occurs within the first two decades of life, commonly in the teenage years or the twenties. Life expectancy is normal.
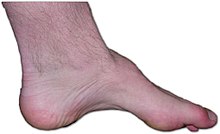
High arch of the foot (pes cavus) is common. Patients also have trouble controlling their hands, due to muscle loss on the thumb side of the index finger and palm below the thumb.[4] It is rare for a person with this disorder to lose the ability to walk, though changes in gait may occur later in life.[5]
Frequency of this disorder is unknown.[6]
Genetics
[edit]dHMN V has a pattern of autosomal dominance, meaning that only one copy of the gene is needed for the development of the disease. However, there is incomplete penetrance of this disorder, meaning that some individuals with the disease-causing mutations will not display any symptoms.[3] Mutations on chromosome 7 have been linked to this disease. It is allelic (i.e., caused by mutations on the same gene) with Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease and with Silver’s Syndrome, a disorder also characterized by small muscle atrophy in the hands.[1][7] Another rare form of dHMN V is associated with a splicing mutation in REEP-1, a gene often associated with hereditary spastic neuroplegia.[8]
Diagnosis
[edit]In an individual with dHMN V, electromyography will show pure motor neuropathy, patterns of weakness without upper motor neuron damage, in the hands. Tendon reflexes will also appear normal.[9] Clinical, electrophysiological, and pathological testing will show a lack of damage to sensory neurons, differentiating this disease from CMT.[10]
Treatment
[edit]Physical therapy is the predominant treatment of symptoms. Orthopedic shoes and foot surgery can be used to manage foot problems.[5]
References
[edit]- ^ a b Seo, Ah Jung; Park, Byung Sun; Jeong, Na Young; Kim, Doyen; Kim, Sunghoon; Park, Chan; Jung, Junyang; Huh, Youngbuhm (2014). "Adenoviral-mediated mouse model of motor impairment in distal spinal muscular atrophy type V". Animal Cells and Systems. 18 (5): 311–317. doi:10.1080/19768354.2014.950330. ISSN 1976-8354. S2CID 73528377.
- ^ Middleton, L. T.; Christodoulou, K.; Mubaidin, A.; Zamba, E.; Tsingis, M.; Kyriacou, K.; Abu-Sheikh, S.; Kyriakides, T.; Neocleous, V.; Georgiou, D. M.; El-Khateeb, M.; Al-Qudah, A.; Horany, K. (1999). "Distal Hereditary Motor Neuronopathy of the Jerash Type". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 883 (1 CHARCOT–MARIE): 439–442. Bibcode:1999NYASA.883..439M. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb08604.x. ISSN 0077-8923. PMID 29086938. S2CID 27780275.
- ^ a b Rakočević-Stojanović, V.; Milić-Rašić, V.; Perić, S.; Baets, J.; Timmerman, V.; Dierick, I.; Pavlović, S.; De Jonghe, P. (2010). "N88S mutation in the BSCL2 gene in a Serbian family with distal hereditary motor neuropathy type V or Silver syndrome". Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 296 (1–2): 107–109. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2010.06.015. ISSN 0022-510X. PMID 20598714. S2CID 21874798.
- ^ "Distal hereditary motor neuropathy, type V". Think Genetic. 10 June 2016. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017. Retrieved 5 November 2016.
- ^ a b Ito, Daisuke; Suzuki, Norihiro (2007). "Molecular pathogenesis of seipin/BSCL2-related motor neuron diseases". Annals of Neurology. 61 (3): 237–250. doi:10.1002/ana.21070. ISSN 0364-5134. PMID 17387721. S2CID 43661842.
- ^ Reference, Genetics Home. "distal hereditary motor neuropathy, type V". Genetics Home Reference.
- ^ Dubourg, O.; Azzedine, H.; Yaou, R. B.; Pouget, J.; Barois, A.; Meininger, V.; Bouteiller, D.; Ruberg, M.; Brice, A.; LeGuern, E. (12 June 2006). "The G526R glycyl-tRNA synthetase gene mutation in distal hereditary motor neuropathy type V". Neurology. 66 (11): 1721–1726. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000218304.02715.04. PMID 16769947. S2CID 22868888.
- ^ Beetz, Christian; Pieber, Thomas R.; Hertel, Nicole; Schabhüttl, Maria; Fischer, Carina; Trajanoski, Slave; Graf, Elisabeth; Keiner, Silke; Kurth, Ingo; Wieland, Thomas; Varga, Rita-Eva; Timmerman, Vincent; Reilly, Mary M.; Strom, Tim M.; Auer-Grumbach, Michaela (2012). "Exome Sequencing Identifies a REEP1 Mutation Involved in Distal Hereditary Motor Neuropathy Type V". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 91 (1): 139–145. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.05.007. ISSN 0002-9297. PMC 3397265. PMID 22703882.
- ^ Antonellis, Anthony; Ellsworth, Rachel E.; Sambuughin, Nyamkhishig; Puls, Imke; Abel, Annette; Lee-Lin, Shih-Queen; Jordanova, Albena; Kremensky, Ivo; Christodoulou, Kyproula; Middleton, Lefkos T.; Sivakumar, Kumaraswamy; Ionasescu, Victor; Funalot, Benoit; Vance, Jeffery M.; Goldfarb, Lev G.; Fischbeck, Kenneth H.; Green, Eric D. (2003). "Glycyl tRNA Synthetase Mutations in Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type 2D and Distal Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type V". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 72 (5): 1293–1299. doi:10.1086/375039. ISSN 0002-9297. PMC 1180282. PMID 12690580.
- ^ Pareyson, Davide; Marchesi, Chiara (2009). "Diagnosis, natural history, and management of Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease". The Lancet Neurology. 8 (7): 654–667. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70110-3. ISSN 1474-4422. PMID 19539237. S2CID 665324.