Insubres
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
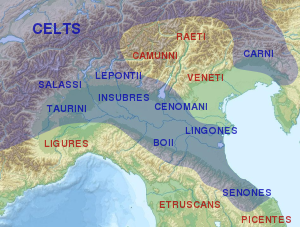
The Insubres or Insubri were an ancient Celtic[1] population settled in Insubria, in what is now the Italian region of Lombardy. They were the founders of Mediolanum (Milan). Though completely Gaulish at the time of Roman conquest, they were the result of the fusion of pre-existing Ligurian and Celtic population (Golasecca culture) with Gaulish tribes.
Classical sources
[edit]The Insubres are mentioned by Caecilius Statius, Cicero, Polybius, Livy, Pliny the Elder, and Strabo.
Ethnicity of the Insubres
[edit]
Polybius called the Insubres the most important Celtic tribe of the Italian peninsula, while according to Livy they were the first to inhabit Cisalpine Gaul, from the 7th century BC.
The Insubres were part of the Golasecca culture, which takes its name from a town near Varese, where Abbot Giovanni Battista Giani made the first findings of about fifty Celtic graves with pottery and metal objects. It is a culture that developed at the end of the Late Bronze Age, between the rivers Po, Serio and Sesia, and which has its counterpart in the Central European Hallstatt culture.
Culture and society
[edit]The Insubres culture followed then what was a slow end of its own evolution. Thanks to the cultural and commercial exchanges with neighboring areas, such as Etruria, Venetia and Transalpine Gaul, the Insubres made some advances and created a distinct society of their own. In the light of archaeological findings it can be also assumed that it was an oligarchic society, where power was in the hands of a few Lords.
History
[edit]The History of the Insubres, like that of other Gauls and of Italic peoples, was written by ancient Roman and Greek writers. Apart from Livy's section on the Gallic Invasion of northern Italy, their writings came in the context of their covering Roman history and concentrated on battles between the Romans and the Insubres and other Gallic tribes in northern Italy.
In 225 BC, the Insubres and the Boii, their Gallic neighbours to the south of the River Po, rebelled against Rome. This was prompted by developments that started in 283 BC, when unspecified Celts besieged Arretium (Arezzo in Tuscany) and defeated a Roman force that came to the aid of the city. The Romans sent envoys to negotiate the release of Roman prisoners, but the envoys were killed.[2]
A Roman army was sent to the ager Gallicus, the name the Romans gave to an area on the Adriatic coast that had been conquered by the Senone Gauls. This army routed a Senone force, occupied their territory, killed most of the Senones and drove the rest out of their land. Afraid that the same fate might occur to them, the neighbouring Boii joined the Etruscans in a rebellion. Their combined force was defeated at the Battle of Lake Vadimo in the same year.[3]
What prompted the Insubres to join the Boii in another rebellion was a law passed in Rome that provided for the subdivision of the ager gallicus into Roman administrative units. This created fears among the Boii and Insubres that the Romans were now fighting wars to exterminate and expel the enemy and annex their territory.[4]
In 225 BC, the Boii and Insubres paid large sums of money to Gaesatae mercenaries led by Aneroëstes and Concolitanus. The Gaesatae were Gauls from Gallia Transalpina, the Roman name for what is now southern France. A force of up to 70,000 men ravaged Etruria. The Gauls encountered Roman forces near Clusium (Chiusi); instead of engaging, they withdrew to Feasulae (Fiesole) at night. They then defeated the Romans at the Battle of Faesulae (225 BC). They were routed by the combined forces of the two Roman consuls, Lucius Aemilius Papus and Gaius Atilius Regulus, at the Battle of Telamon.[5]
After the Battle of Telamon, the Romans attacked and defeated the Boii and forced them to submit to Rome.[6] In 224 BC, the Romans attacked Insubre territory. In 223 BC, the Insubres sued for peace, but the Romans turned this down and attacked them. The Romans were now determined to be in control of Gallia Cisalpina, the Roman name for the area where the Gallic tribes of northern Italy lived.[7]
In 222 BC, the Romans besieged Acerrae, an Insubre fortification on the right bank of the River Adda between Cremona and Laus Pompeia (Lodi Vecchio). The Insubres could not relieve Acerrae because the Romans controlled all the strategic points around it. Therefore, they hired 30,000 Gaesatae mercenaries and, led by Viridomarus (or Britomartus), they besieged Clastidium, an important and strategically well placed town of the Marici, a Ligurian people who were Roman allies, hoping that this would force the Romans to lift their siege.[8]
Instead, the Romans split their forces. The consul Marcus Claudius Marcellus headed for Clastidium and his colleague Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Calvus continued the siege of Acerrae. At the Battle of Clastidium, Marcus Claudius defeated the Gallic forces and killed Viridomarus in single combat. Meanwhile, Gnaeus Cornelius took Acerrae. With the fortress taken and the Insubre king dead, the Romans then easily took the capital of the Insubres, which they named Mediolanum (Milan).[9]
The Insubres surrendered and were forced to become Roman allies. The Romans founded garrisoned colonies at Cremona and Placentia (Piacenza). The former was on the north bank of the River Po and the latter was close to its south bank (in Insubre and Boii territory respectively). This was done to secure the crossing of the river and the gateway to Liguria. They also established a garrison at Mutina (Modena), which was to become a colony in 182 BC.[10]
In 218 BC, the Insubres and the Boii rebelled in anticipation of Hannibal's invasion of Italy in the Second Punic War (218-201 BC). They attacked Cremona and Placentia, forcing the settlers to flee to Mutina, which was besieged. The praetor Lucius Manlius Vulso set off from Ariminum with 20,000 infantry and 1,600 cavalry. He was ambushed twice on the way. He relieved the siege of Mutina, but was in turn besieged nearby. The consul Publius Cornelius Scipio was sent to support him with fresh troops. Meanwhile, Hannibal reached Italy. He defeated Publius Scipio at the Battle of Ticinus, in Insubre territory[11][12] and the other consul, Tiberius Sempronius Longus, at the Battle of the Trebia, near Placentia.[13][14]
Hannibal wintered near Placentia and then moved on to central and southern Italy. Some Insubres joined him, among them Ducarius who killed Consul Gaius Flaminius at the Battle of Trasimene (217 BC). We next hear of the Gauls during the Second Punic War in relation to the Battle of the Metaurus (207 BC). Hannibal's brother, Hasdrubal Barca, was bringing reinforcements from Spain for his brother who was in southern Italy. He passed through northern Italy and recruited Gallic soldiers. Hasdrubal's forces, including his Gauls were routed at this battle in central Italy.[15][16] At this point, Hannibal's campaign in Italy came to a dead end.
After several other clashes, the Insubres made an alliance with Rome in 194 BC, maintaining some autonomy. In 89 BC, they obtained Latin citizenship and, in 49 BC, Roman citizenship. The Romanisation of the Insubres was probably quick owing to the presence of Roman colonies and to Julius Caesar using Mediolanum as a staging post for his conquest of Gaul (58–50 BC). Caecilius Statius (c. 220 BC – c. 166 BC), a Roman comic poet, was born in Insubria, possibly in Mediolanum. He was originally a slave and was probably a war captive who was taken to Rome. Caecilius was the name of his patron, probably a member of the powerful Metelli clan. His work was greatly acclaimed.
References
[edit]- ^ Lafond, Yves (Bochum); Radke, Gerhard (2006). "Insubres". Brill's New Pauly. doi:10.1163/1574-9347_bnp_e525110.
- ^ Polybius, The Histories, 2.19-20
- ^ Polybius, The Histories, 2.19-20
- ^ Polybius, The Histories, 2.21.-9
- ^ Polybius, The Histories, 2.22-27
- ^ Polybius, The Histories, 2.31.7
- ^ Polybius, The Histories, 2.19-20
- ^ Polybius, The Histories, 2.19-20
- ^ Polybius, The Histories, 2.19-20
- ^ Polybius, The Histories, 2.19-20
- ^ Livy, The History of Rome, 21.46
- ^ Polybius, The Histories, 3.65
- ^ Livy, The History of Rome, 21.53-55
- ^ Polybius, The Histories, 3.71-74
- ^ Livy, The History of Rome, 27.48-49
- ^ Polybius, The Histories, 11.1-3
Bibliography
[edit]- Ardovino, A.G., (2001)Archeologi e storici sulla Lombardia preromana, tra equivoci e prospettive, dall'etnogenesi alla Wölkerwanderung al diffusionismo, in La protostoria in Lombardia, (Atti del 3° Convegno Archeologico Regionale Como 1999), Como, pp. 77–96.
- Arslan, E. A., (2004) Dai Golasecchiani agli Insubri, in Celti dal cuore dell'Europa all'Insubria, Celti d'Insubria. Guerrieri del territorio di Varese, Catalogo della mostra (Varese, 28.11.2004-25.4.2005), pp. 18–25.
- Berresford Ellis, Peter,(1998) Celt and Roman, The Celts in Italy, New York, St Martin's Press, ISBN 978-0094758209
- De Marinis, Raffaele, (1991). "I Celti Golasecchiani". In Multiple Authors, I Celti, Bompiani.
- De Marinis, Raffaele, (1990) Liguri e Celto-Liguri, Officine grafiche Garzanti Milano, Garzanti-Scheiwiller
- Giangiulio, M., (1999)Storiografie, ideologie, metodologie. Ancora sul transitus Gallorum in Italiam in Livio (V,34-35) e nella tradizione letteraria, in Rassegna Studi del Civico Museo Archeologico di Milano 63–64, pp. 21–34.
- Grassi, M. T., (1995) La romanizzazione degli Insubri. Celti e Romani in Transpadana attraverso la documentazione storica e archeologica, Milano.
- Grassi, M. T., (1999) I Celti della Cisalpina Centrale: dall'ager Insubrium alla XI Regio Transpadana, in Insubri e Cenomani tra Sesia e Adige, Seminario di Studi (Milano 27–28.2.1998), "Rassegna di Studi del Civico Museo Archeologico e del Civico Gabinetto Numismatico di Milano", LXIII-LXIV, pp. 101–108.
- Livy, (2004) The War with Hannibal: The History of Rome from its Foundation Books 21-30, London, Penguin Classics, ISBN 978-0140441451
- Polybius, (2010) The Histories(Oxford World's Classics), Oxford, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0199534708
- Tibiletti Bruno, M. G., (1978) "Ligure, leponzio e gallico". In Popoli e civiltà dell'Italia antica vi, Lingue e dialetti, ed. Prosdocimi, A. L., 129–208. Rome: Biblioteca di Storia Patria.
- Tibiletti Bruno, M. G., (1981) "Le iscrizioni celtiche d'Italia". In I Celti d'Italia, ed. E. Campanile, 157–207. Pisa: Giardini.
- Whatmough, J., (1933) The Prae-Italic Dialects of Italy, vol. 2, "The Raetic, Lepontic, Gallic, East-Italic, Messapic and Sicel Inscriptions", Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press
