List of epidemics and pandemics
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
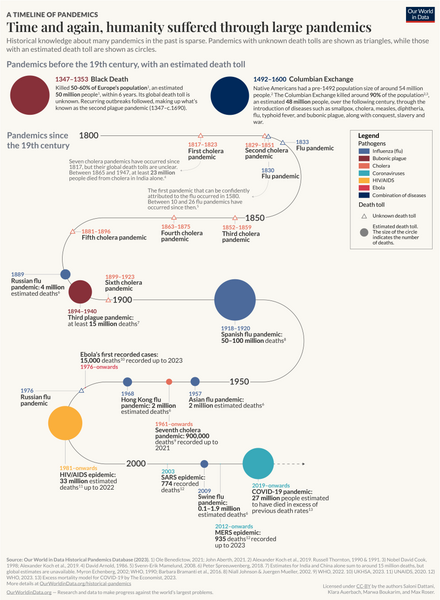
This is a list of the largest known epidemics and pandemics caused by an infectious disease in humans. Widespread non-communicable diseases such as cardiovascular disease and cancer are not included. An epidemic is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of people in a given population within a short period of time; in meningococcal infections, an attack rate in excess of 15 cases per 100,000 people for two consecutive weeks is considered an epidemic.[1] Due to the long time spans, the first plague pandemic (6th century – 8th century) and the second plague pandemic (14th century – early 19th century) are shown by individual outbreaks, such as the Plague of Justinian (first pandemic) and the Black Death (second pandemic).
Infectious diseases with high prevalence are listed separately (sometimes in addition to their epidemics), such as malaria, which may have killed 50–60 billion people throughout history, or about half of all humans that have ever lived.[2]
Major epidemics and pandemics
By death toll
Ongoing epidemics and pandemics are in boldface. For a given epidemic or pandemic, the average of its estimated death toll range is used for ranking. If the death toll averages of two or more epidemics or pandemics are equal, then the smaller the range, the higher the rank. For the historical records of major changes in the world population, see world population.[3]
| Rank | Epidemics/pandemics | Disease | Death toll | Percentage of population lost | Years | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Spanish flu | Influenza A/H1N1 | 17–100 million | 1–5.4% of global population[4] | 1918–1920 | Worldwide |
| 2 | Plague of Justinian | Bubonic plague | 15–100 million | 25–60% of European population[5] | 541–549 | North Africa, Europe, and Western Asia |
| 3 | Black Death | Bubonic plague | 25–50 million | 30–60% of European population[6] | 1346–1353 | Europe, Asia, and North Africa |
| 4 | HIV/AIDS pandemic | HIV/AIDS | 43 million (as of 2024[update]) | [a] | 1981–present[7] | Worldwide |
| 5 | COVID-19 pandemic | COVID-19 | 7–35 million[8][9] (as of 2024[update]) | [a] | 2019[b]–present[10][11][c] | Worldwide |
| 6 | Third plague pandemic | Bubonic plague | 12–15 million | – | 1855–1960 | Worldwide |
| 7 | Cocoliztli epidemic of 1545–1548 | Cocoliztli, caused by an unidentified pathogen | 5–15 million | 27–80% of Mexican population[12] | 1545–1548 | Mexico |
| 8 | Antonine Plague | Smallpox or measles | 5–10 million | 25–33% of Roman population[13] | 165–180 (possibly up to 190) | Roman Empire |
| 9 | 1520 Mexico smallpox epidemic | Smallpox | 5–8 million | 23–37% of Mexican population[12] | 1519–1520 | Mexico |
| 11 | 1957–1958 influenza pandemic | Influenza A/H2N2 | 1–4 million | – | 1957–1958 | Worldwide |
| 12 | Hong Kong flu | Influenza A/H3N2 | 1–4 million | – | 1968–1969 | Worldwide |
| 10 | 1918–1922 Russia typhus epidemic | Typhus | 2–3 million | 1–1.6% of Russian population[14] | 1918–1922 | Russia |
| 13 | Cocoliztli epidemic of 1576 | Cocoliztli | 2–2.5 million | 50% of Mexican population[12] | 1576–1580 | Mexico |
| 14 | 1772–1773 Persian Plague | Bubonic plague | 2 million | – | 1772–1773 | Persia |
| 15 | 735–737 Japanese smallpox epidemic | Smallpox | 2 million | 33% of Japanese population[15] | 735–737 | Japan |
| 16 | Naples Plague | Bubonic plague | 1.25 million | – | 1656–1658 | Southern Italy |
| 17 | 1889–1890 pandemic | Influenza or human coronavirus OC43[16][17] | 1 million | – | 1889–1890 | Worldwide |
| 18 | 1629–1631 Italian plague | Bubonic plague | 1 million | – | 1629–1631 | Italy |
| 19 | 1846–1860 cholera pandemic | Cholera | 1 million | – | 1846–1860 | Worldwide |
Depopulation of the Americas
Not included in the above table are many waves of deadly diseases brought by Europeans to the Americas and Caribbean. Western Hemisphere populations were ravaged mostly by smallpox, but also typhus, measles, influenza, bubonic plague, cholera, malaria, tuberculosis, mumps, yellow fever, and pertussis. The lack of written records in many places and the destruction of many native societies by disease, war, and colonization make estimates uncertain. Deaths probably numbered in the tens or perhaps over a hundred million, with perhaps 90% of the population dead in the worst-hit areas. Lack of scientific knowledge about microorganisms and lack of surviving medical records for many areas makes attribution of specific numbers to specific diseases uncertain.
Infectious diseases with high prevalence
There have been various major infectious diseases with high prevalence worldwide, but they are currently not listed in the above table as epidemics/pandemics due to the lack of definite data, such as time span and death toll.

- Malaria has had multiple documented temporary epidemics in otherwise non-affected or low-prevalence areas, but the vast majority of its deaths are due to its constant prevalence in affected areas.[2]
- Tuberculosis (TB) became epidemic in Europe in the 18th and 19th century, showing a seasonal pattern, and is still taking place globally.[19][20][21] The morbidity and mortality of TB and HIV/AIDS have been closely linked, known as "TB/HIV syndemic".[21][22] According to the World Health Organization, approximately 10 million new TB infections occur every year, and 1.5 million people die from it each year – making it the world's top infectious killer (before COVID-19 pandemic).[21] However, there is a lack of sources which describe major TB epidemics with definite time spans and death tolls.
- Hepatitis B: According to the World Health Organization, as of 2019[update] there are about 296 million people living with chronic hepatitis B, with 1.5 million new infections each year. In 2019, hepatitis B caused about 820,000 deaths, mostly from cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (primary liver cancer).[23] In many places of Asia and Africa, hepatitis B has become endemic.[24] In addition, a person is sometimes infected with both hepatitis B virus (HBV) and HIV, and this population (about 2.7 million) accounts for about 1% of the total HBV infections.[23]
- Hepatitis C: According to the World Health Organization, there are approximately 58 million people with chronic hepatitis C, with about 1.5 million new infections occurring per year. In 2019, approximately 290,000 people died from the disease, mostly from cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (primary liver cancer).[25] There have been many hepatitis C virus (HCV) epidemics in history.[26][27][28]
Chronology
Events in boldface are ongoing.
| Event | Years | Location | Disease | Death toll (estimate) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1350 BC plague of Megiddo | c. 1350 BC | Megiddo, land of Canaan | Amarna letters EA 244, Biridiya, mayor of Megiddo complains to Amenhotep III of his area being "consumed by death, plague and dust" | Unknown | [29] |
| Hittite Plague/"Hand of Nergal" | c. 1330 BC | Near East, Hittite Empire, Alashiya, possibly Egypt | Unknown, possibly Tularemia. Mentioned in Amarna letter EA 35 as the "Hand of Nergal", cause of death of Šuppiluliuma I. | Unknown | |
| Plague of Athens | 430–426 BC | Greece, Libya, Egypt, Ethiopia | Unknown, possibly typhus, typhoid fever or viral hemorrhagic fever | 75,000–100,000 | [30][31][32][33] |
| 412 BC epidemic | 412 BC | Greece (Northern Greece, Roman Republic) | Unknown, possibly influenza | 473,000 (10% of the Roman Population) | [34] |
| Antonine Plague | 165–180 (possibly up to 190) | Roman Empire | Unknown, possibly smallpox | 5–10 million | [35][36] |
| Jian'an Plague | 217 | Han dynasty | Unknown, possibly typhoid fever or viral hemorrhagic fever | 2 Million | [37][38] |
| Plague of Cyprian | 249–262 | Europe | Unknown, possibly smallpox | 310,000 | [39][40] |
| Plague of Justinian (beginning of first plague pandemic) | 541–549 | Europe and West Asia | Bubonic plague | 15–100 million | [5][41][42] |
| 580 Dysentery Epidemic in Gaul | 580 | Gaul | Dysentery or possibly smallpox | 450,000 (10% of the Gaul population) | [43] |
| Roman Plague of 590 (part of first plague pandemic) | 590 | Rome, Byzantine Empire | Bubonic plague | Unknown | [44] |
| Plague of Sheroe (part of first plague pandemic) | 627–628 | Bilad al-Sham | Bubonic plague | 25,000+ | |
| Plague of Amwas (part of first plague pandemic) | 638–639 | Byzantine Empire, West Asia, Africa | Bubonic plague | 25,000+ | [45] |
| Plague of 664 (part of first plague pandemic) | 664–689 | British Isles | Bubonic plague | Unknown | [46] |
| Plague of 698–701 (part of first plague pandemic) | 698–701 | Byzantine Empire, West Asia, Syria, Mesopotamia | Bubonic plague | Unknown | [47] |
| 735–737 Japanese smallpox epidemic | 735–737 | Japan | Smallpox | 2 million (approx. 1⁄3 of Japanese population) | [15][48] |
| Plague of 746–747 (part of first plague pandemic) | 746–747 | Byzantine Empire, West Asia, Africa | Bubonic plague | Unknown | [45] |
| Black Death (start of the second plague pandemic) | 1346–1353 | Eurasia and North Africa | Bubonic plague | 75–200 million (30–60% of European population and 33% percent of the Middle Eastern population) | [49] |
| Sweating sickness (multiple outbreaks) | 1485–1551 | Britain (England) and later continental Europe | Unknown, possibly an unknown species of hantavirus | 10,000+ | [50] |
| 1489 Spain typhus epidemic | 1489 | Spain | Typhus | 17,000 | [51] |
| 1510 influenza pandemic | 1510 | Asia, North Africa, Europe | Influenza | Unknown, around 1% of those infected | [52] |
| 1520 Mexico smallpox epidemic | 1519–1520 | Mexico | Smallpox | 5–8 million (40% of population) | [12] |
| Cocoliztli epidemic of 1545–1548 | 1545–1548 | Mexico | Possibly Salmonella enterica | 5–15 million (80% of population) | [53][54][55][56] |
| 1557 influenza pandemic | 1557–1559 | Asia, Africa, Europe, and Americas | Influenza | 2.5–5 Million (10% of the infected) | |
| 1561 Chile smallpox epidemic | 1561–1562 | Chile | Smallpox | 120,000–150,000 (20–25% of native population) | [57] |
| 1563 London plague (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1563–1564 | London, England | Bubonic plague | 20,100+ | [58] |
| Cocoliztli epidemic of 1576 | 1576–1580 | Mexico | Possibly Salmonella enterica | 2–2.5 million (50% of population) | [53][54][55][56] |
| 1582 Tenerife plague epidemic (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1582–1583 | Tenerife, Spain | Bubonic plague | 5,000–9,000 | [59] |
| 1592–1596 Seneca nation measles epidemic | 1592–1596 | Seneca nation, North America | Measles | Unknown | [60] |
| 1592–1593 Malta plague epidemic (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1592–1593 | Malta | Bubonic plague | 3,000 | [61] |
| 1592–1593 London plague (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1592–1593 | London, England | Bubonic plague | 19,900+ | [62] |
| 1596–1602 Spain plague epidemic (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1596–1602 | Spain | Bubonic plague | 600,000–700,000 | [63] |
| 1600–1650 South America malaria epidemic | 1600–1650 | South America | Malaria | Unknown | [citation needed] |
| 1603 London plague (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1603 | London, England | Bubonic plague | 40,000 | [64][65][66] |
| 1616 New England infections epidemic | 1616–1620 | Southern New England, British North America, especially the Wampanoag people | Unknown, possibly leptospirosis with Weil syndrome. Classic explanations include yellow fever, bubonic plague, influenza, smallpox, chickenpox, typhus, and syndemic infection of hepatitis B and hepatitis D | 1,143,000–3,429,000 (estimated 30–90% of population) | [67][68] |
| 1629–1631 Italian plague (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1629–1631 | Italy | Bubonic plague | 1 million | [69] |
| 1632–1635 Augsburg plague epidemic (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1632–1635 | Augsburg, Germany | Bubonic plague | 13,712 | [70] |
| Massachusetts smallpox epidemic | 1633–1634 | Massachusetts Bay Colony, Thirteen Colonies | Smallpox | 1,000 | [71] |
| 1634–1640 Wyandot people epidemic | 1634–1640 | Wyandot people, North America | Smallpox and Influenza | 15,000–25,000 | [72] |
| 1637 London plague epidemic (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1636–1637 | London and Westminster, England | Bubonic plague | 10,400 | [73] |
| Great Plague in the late Ming dynasty (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1633–1644 | China | Bubonic plague | 200,000+ | [74][75] |
| Great Plague of Seville (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1647–1652 | Spain | Bubonic plague | 500,000 | [76] |
| 1648 Central America yellow fever epidemic | 1648 | Central America | Yellow fever | Unknown | [77] |
| Naples Plague (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1656–1658 | Italy | Bubonic plague | 1,250,000 | [78] |
| 1663–1664 Amsterdam plague epidemic (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1663–1664 | Amsterdam, Netherlands | Bubonic plague | 24,148 | [79] |
| Great Plague of London (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1665–1666 | England | Bubonic plague | 100,000 | [80][81] |
| 1668 France plague (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1668 | France | Bubonic plague | 40,000 | [82] |
| 1675–1676 Malta plague epidemic (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1675–1676 | Malta | Bubonic plague | 11,300 | [83] |
| 1676–1685 Spain plague (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1676–1685 | Spain | Bubonic plague | Unknown | [84] |
| 1677–1678 Boston smallpox epidemic | 1677–1678 | Massachusetts Bay Colony, British North America | Smallpox | 750–1,000 | [85] |
| Great Plague of Vienna (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1679 | Vienna, Austria | Bubonic plague | 76,000 | [86] |
| 1681 Prague plague epidemic (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1681 | Prague, Czech Kingdom | Bubonic plague | 83,000 | [87] |
| 1687 South Africa influenza outbreak | 1687 | South Africa | Unknown, possibly influenza | Unknown | [88] |
| 1693 Boston yellow fever epidemic | 1693 | Boston, Massachusetts Bay Colony, British North America | Yellow fever | 3,100+ | [89] |
| 1699 Charleston and Philadelphia yellow fever epidemic | 1699 | Charleston and Philadelphia, British North America | Yellow fever | 520 (300 in Charleston, 220 in Philadelphia) | [90] |
| 1702 New York City yellow fever epidemic | 1702 | New York City, British North America | Yellow fever | 500 | [91] |
| 1702–1703 St. Lawrence Valley smallpox epidemic | 1702–1703 | New France, Canada | Smallpox | 1,300 | [92] |
| 1707–1708 Iceland smallpox epidemic | 1707–1709 | Iceland | Smallpox | 18,000+ (36% of population) | [93] |
| Great Northern War plague outbreak (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1710–1712 | Denmark, Sweden, Lithuania | Bubonic plague | 164,000 | [94][95] |
| 1713–1715 North America measles epidemic | 1713–1715 | Thirteen Colonies and New France, Canada | Measles | Unknown | [96][97] |
| Great Plague of Marseille (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1720–1722 | France | Bubonic plague | 100,000+ | [98] |
| 1721 Boston smallpox outbreak | 1721–1722 | Massachusetts Bay Colony | Smallpox | 844 | [99] |
| 1730 Cádiz yellow fever epidemic | 1730 | Cádiz, Spain | Yellow fever | 2,200 | [100] |
| 1732–1733 Thirteen Colonies influenza epidemic | 1732–1733 | Thirteen Colonies | Influenza | Unknown | [101] |
| 1733 New France smallpox epidemic | 1733 | New France, Canada | Smallpox | Unknown | [102] |
| 1735–1741 diphtheria epidemic | 1735–1741 | New England, Province of New York, Province of New Jersey, British North America | Diphtheria | 20,000 | [103] |
| Great Plague of 1738 (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1738 | Balkans | Bubonic plague | 50,000 | [104] |
| 1738–1739 North Carolina smallpox epidemic | 1738–1739 | Province of Carolina, Thirteen Colonies | Smallpox | 7,700–11,700 | [105] |
| 1741 Cartagena yellow fever epidemic | 1741 | Cartagena, Colombia | Yellow fever | 20,000 | [106] |
| 1743 Sicily plague epidemic (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1743 | Messina, Sicily, Italy | Bubonic plague | 40,000–50,000 | [107][108] |
| 1759 North America measles outbreak | 1759 | North America | Measles | Unknown | [109] |
| 1760 Charleston smallpox epidemic | 1760 | Charleston, British North America | Smallpox | 730–940 | [110][111] |
| 1762 Havana yellow fever epidemic | 1762 | Havana, Cuba | Yellow fever | 8,000 | [106] |
| 1763 Pittsburgh area smallpox outbreak | 1763 | North America, present-day Pittsburgh area | Smallpox | Unknown | [112] |
| 1770–1772 Russian plague (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1770–1772 | Russia | Bubonic plague | 50,000 | [113] |
| 1772 North America measles epidemic | 1772 | North America | Measles | 1,080 | [114] |
| 1772–1773 Persian Plague (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1772–1773 | Persia | Bubonic plague | 2 million | [115] |
| 1775–1776 England influenza outbreak | 1775–1776 | England | Influenza | Unknown | [116] |
| 1775–1782 North American smallpox epidemic | 1775–1782 | Native populations in what is now the Pacific Northwest of the United States | Smallpox | 11,000+ | [117][118] |
| 1778 Spain dengue fever outbreak | 1778 | Spain | Dengue fever | Unknown | [119] |
| 1782 Influenza pandemic | 1782 | Worldwide | Influenza | Unknown | |
| 1788 Pueblo Indians smallpox epidemic | 1788 | Pueblo Indians in northern New Spain (what is now the Southwestern United States) | Smallpox | Unknown | [120] |
| 1789–1790 New South Wales smallpox epidemic | 1789–1790 | New South Wales, Australia | Smallpox | 125,251–175,351 (50–70% of native population) | [121][122] |
| 1793 Philadelphia yellow fever epidemic | 1793 | Philadelphia, United States | Yellow fever | 5,000+ | [123] |
| 1800–1803 Spain yellow fever epidemic | 1800–1803 | Spain | Yellow fever | 60,000+ | [124] |
| 1801 Ottoman Empire and Egypt bubonic plague epidemic | 1801 | Ottoman Empire, Egypt | Bubonic plague | Unknown | [125] |
| 1802–1803 Saint-Domingue yellow fever epidemic | 1802–1803 | Saint-Domingue | Yellow fever | 29,000–55,000 | [126] |
| 1812 Russia typhus epidemic | 1812 | Russia | Typhus | 300,000 | [51] |
| 1812–1819 Ottoman plague epidemic (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1812–1819 | Ottoman Empire | Bubonic plague | 300,000+ | [127] |
| 1813–1814 Malta plague epidemic (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1813–1814 | Malta | Bubonic plague | 4,500 | [128] |
| Caragea's plague (part of the second plague pandemic) | 1813 | Romania | Bubonic plague | 60,000 | [129] |
| 1817–1819 Ireland typhus epidemic | 1817–1819 | Ireland | Typhus | 65,000 | [130] |
| First cholera pandemic | 1817–1824 | Asia, Europe | Cholera | 100,000+ | [131] |
| 1820 Savannah yellow fever epidemic | 1820 | Savannah, Georgia, United States | Yellow fever | 700 | [132] |
| 1821 Barcelona yellow fever epidemic | 1821 | Barcelona, Spain | Yellow fever | 5,000–20,000 | [133][134] |
| Second cholera pandemic | 1826–1837 | Asia, Europe, North America | Cholera | 100,000+ | [135] |
| 1828–1829 New South Wales smallpox epidemic | 1828–1829 | New South Wales, Australia | Smallpox | 19,000 | [136][137] |
| Groningen epidemic | 1829 | Netherlands | Malaria | 2,800 | [138] |
| 1829–1833 Pacific Northwest malaria epidemic | 1829–1833 | Pacific Northwest, United States | Malaria, possibly other diseases too | 150,000 | [139][140] |
| 1829–1835 Iran plague outbreak | 1829–1835 | Iran | Bubonic plague | Unknown | [141] |
| 1834–1836 Egypt plague epidemic | 1834–1836 | Egypt | Bubonic plague | Unknown | [142] |
| 1837 Great Plains smallpox epidemic | 1837–1838 | Great Plains, United States and Canada | Smallpox | 17,000+ | [143] |
| 1841 Southern United States yellow fever epidemic | 1841 | Southern United States (especially Louisiana and Florida) | Yellow fever | 3,498 | [144] |
| 1847 North American typhus epidemic | 1847–1848 | Canada | Typhus | 20,000+ | [145] |
| 1847 Southern United States yellow fever epidemic | 1847 | Southern United States (especially New Orleans) | Yellow fever | 3,400 | [146] |
| 1847–1848 influenza epidemic | 1847–1848 | Worldwide | Influenza | Unknown | [147] |
| 1848–1849 Hawaii epidemic of infections | 1848–1849 | Hawaiian Kingdom | Measles, whooping cough, dysentery and influenza | 10,000 | [148] |
| 1853 New Orleans yellow fever epidemic | 1853 | New Orleans, United States | Yellow fever | 7,970 | [133] |
| Third cholera pandemic | 1846–1860 | Worldwide | Cholera | 1 million+ | [149] |
| 1853 Ottoman Empire plague epidemic | 1853 | Ottoman Empire | Bubonic plague | Unknown | [150] |
| 1853 Copenhagen cholera outbreak | 1853 | Copenhagen, Denmark | Cholera | 4,737 | [151] |
| 1854 Broad Street cholera outbreak | 1854 | London, England | Cholera | 616 | [152] |
| 1855 Norfolk yellow fever epidemic | 1855 | Norfolk and Portsmouth, England | Yellow fever | 3,000 (2,000 in Norfolk, 1,000 in Portsmouth) | [153] |
| Third plague pandemic | 1855–1960 | Worldwide | Bubonic plague | 12–15 million (India and China) | [154][155] |
| 1855–1857 Montevideo yellow fever epidemic | 1855–1857 | Montevideo, Uruguay | Yellow fever | 3,400 (first wave; 900, second wave; 2,500) | [156] |
| 1857 Lisbon yellow fever epidemic | 1857 | Lisbon, Portugal | Yellow fever | 6,000 | [133] |
| 1857 Victoria smallpox epidemic | 1857 | Victoria, Australia | Smallpox | Unknown | [157] |
| 1857–1859 Europe and the Americas influenza epidemic | 1857–1859 | Europe, North America, South America | Influenza | Unknown | [158] |
| 1862 Pacific Northwest smallpox epidemic | 1862–1863 | Pacific Northwest, Canada and United States | Smallpox | 20,000+ | [159][160][161] |
| 1861–1865 United States typhoid fever epidemic | 1861–1865 | United States | Typhoid fever | 80,000 | [162] |
| Fourth cholera pandemic | 1863–1875 | Middle East | Cholera | 600,000 | [163] |
| 1867 Sydney measles epidemic | 1867 | Sydney, Australia | Measles | 748 | [164] |
| 1871 Buenos Aires yellow fever epidemic | 1871 | Buenos Aires, Argentina | Yellow fever | 13,500–26,200 | [165] |
| 1870–1875 Europe smallpox epidemic | 1870–1875 | Europe | Smallpox | 500,000 | [166][167] |
| 1875 Fiji measles outbreak | 1875 | Fiji | Measles | 40,000 | [168] |
| 1875–1876 Australia scarlet fever epidemic | 1875–1876 | Australia | Scarlet fever | 8,000 | [164] |
| 1876 Ottoman Empire plague epidemic | 1876 | Ottoman Empire | Bubonic plague | 20,000 | [169] |
| 1878 New Orleans yellow fever epidemic | 1878 | New Orleans, United States | Yellow fever | 4,046 | [126] |
| 1878 Mississippi Valley yellow fever epidemic | 1878 | Mississippi Valley, United States | Yellow fever | 13,000 | [126] |
| Fifth cholera pandemic | 1881–1896 | Asia, Africa, Europe, South America | Cholera | 298,600 | [170] |
| 1885 Montreal smallpox epidemic | 1885 | Montreal, Canada | Smallpox | 3,164 | [171] |
| 1889–1890 pandemic | 1889–1890 | Worldwide | Influenza or Human coronavirus OC43 / HCoV-OC43[17][172] (disputed) | 1 million | [173] |
| 1894 Hong Kong plague (part of the third plague pandemic) | 1894–1929 | Hong Kong | Bubonic plague | 20,000+ | [174] |
| Bombay plague epidemic (part of the third plague pandemic) | 1896–1905 | Bombay, India | Bubonic plague | 20,788 | [175] |
| 1896–1906 Congo Basin African trypanosomiasis epidemic | 1896–1906 | Congo Basin | African trypanosomiasis | 500,000 | [176] |
| 1899 Porto plague outbreak (part of the third plague pandemic) | 1899 | Porto, Portugal | Bubonic plague | 132 | [177] |
| Sixth cholera pandemic | 1899–1923 | Europe, Asia, Africa | Cholera | 800,000+ | [178] |
| San Francisco plague of 1900–1904 (part of the third plague pandemic) | 1900–1904 | San Francisco, United States | Bubonic plague | 119 | [179] |
| 1900 Sydney bubonic plague epidemic (part of the third plague pandemic) | 1900 | Australia | Bubonic plague | 103 | [180] |
| 1900–1920 Uganda African trypanosomiasis epidemic | 1900–1920 | Uganda | African trypanosomiasis | 200,000–300,000 | [176] |
| Papua New Guinea kuru epidemic | 1901–2009 | Papua New Guinea | Kuru | 2,700–3,000+ | [181][182] |
| 1903 Fremantle plague epidemic (part of the third plague pandemic) | 1903 | Fremantle, Western Australia | Bubonic plague | 4 | [183] |
| 1906 malaria outbreak in Ceylon | 1906–1936 | Ceylon | Malaria | 80,000 | [184] |
| Manchurian plague (part of the third plague pandemic) | 1910–1911 | China | Pneumonic plague | 60,000 | [185] |
| 1916 United States polio epidemic | 1916 | United States | Poliomyelitis | 7,130 | [186] |
| 1918 influenza pandemic ('Spanish flu') | 1918–1920 | Worldwide | Influenza A virus subtype H1N1 | 17–100 million | [187][188][189] |
| 1918–1922 Russia typhus epidemic | 1918–1922 | Russia | Typhus | 2–3 million | [190] |
| 1919–1930 encephalitis lethargica epidemic | 1919–1930 | Worldwide | Encephalitis lethargica | 500,000 | [191][192][193] |
| 1924 Los Angeles pneumonic plague outbreak | 1924 | Los Angeles, United States | Pneumonic plague | 30 | [194] |
| 1924–1925 Minnesota smallpox epidemic | 1924–1925 | Minnesota, United States | Smallpox | 500 | [195] |
| 1927 Montreal typhoid fever epidemic | 1927 | Montreal, Canada | Typhoid fever | 538 | [196] |
| 1929–1930 psittacosis pandemic | 1929–1930 | Worldwide | Psittacosis | 100+ | [197] |
| Croydon typhoid outbreak of 1937 | 1937 | Croydon, United Kingdom | Typhoid fever | 43 | [198] |
| 1937 Australia polio epidemic | 1937 | Australia | Poliomyelitis | Unknown | [199] |
| 1940 Sudan yellow fever epidemic | 1940 | Sudan | Yellow fever | 1,627 | [200] |
| 1942–1944 Egypt malaria epidemic | 1942–1944 | Egypt | Malaria | Unknown | [142][201] |
| 1946 Egypt relapsing fever epidemic | 1946 | Egypt | Relapsing fever | Unknown | [142][201] |
| 1947 Egypt cholera epidemic | 1947 | Egypt | Cholera | 10,277 | [142][201][202] |
| 1948–1952 United States polio epidemic | 1948–1952 | United States | Poliomyelitis | 9,000 | [186] |
| 1957–1958 influenza pandemic ('Asian flu') | 1957–1958 | Worldwide | Influenza A virus subtype H2N2 | 1–4 million | [187][203][204] |
| 1960–1962 Ethiopia yellow fever epidemic | 1960–1962 | Ethiopia | Yellow fever | 30,000 | [205] |
| Seventh cholera pandemic | 1961–present | Worldwide | Cholera (El Tor strain) | 36,000 [citation needed] | [206] |
| Hong Kong flu | 1968–1970 | Worldwide | Influenza A virus subtype H3N2 | 1–4 million | [187][203][204] |
| 1971 Staphorst polio epidemic | 1971 | Staphorst, Netherlands | Poliomyelitis | 5 | [207] |
| 1972 Yugoslav smallpox outbreak | 1972 | Yugoslavia | Smallpox | 35 | [208] |
| London flu | 1972–1973 | United States | Influenza A virus subtype H3N2 | 1,027 | [209] |
| 1973 Italy cholera epidemic | 1973 | Italy | Cholera (El Tor strain) | 24 | [210] |
| 1974 smallpox epidemic in India | 1974 | India | Smallpox | 15,000 | [211] |
| 1977 Russian flu | 1977–1979 | Worldwide | Influenza A virus subtype H1N1 | 700,000 | [212][213] |
| Sverdlovsk anthrax leak | 1979 | Russia | Anthrax | 105 | [214] |
| HIV/AIDS epidemic | 1981–present | Worldwide | HIV/AIDS | 42 million (as of 2023[update]) | [215] |
| 1984 Western Sahara plague | 1984 | Western Sahara | Bubonic plague | 64 | [citation needed] |
| 1986 Oju yellow fever epidemic | 1986 | Oju, Nigeria | Yellow fever | 5,600+ | [216] |
| 1987 Mali yellow fever epidemic | 1987 | Mali | Yellow fever | 145 | [217] |
| 1988 Shanghai hepatitis A epidemic | 1988 | Shanghai, China | Hepatitis A | 31–47 | [218][219][220] |
| 1991 Bangladesh cholera epidemic | 1991 | Bangladesh | Cholera | 8,410–9,432 | [221] |
| 1991 Latin America cholera epidemic | 1991–1993 | Peru, Chile, Bolivia, Ecuador, Colombia, Mexico, El Salvador, Guatemala | Cholera | 8,000 | [222][223] |
| 1994 plague in India | 1994 | India | Bubonic plague and Pneumonic plague | 56 | [224] |
| United Kingdom BSE outbreak | 1996–2001 | United Kingdom | Variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease / vCJD | 178 | [225][226] |
| 1996 West Africa meningitis epidemic | 1996 | West Africa | Meningitis | 10,000 | [227] |
| 1998–1999 Malaysia Nipah virus outbreak | 1998–1999 | Malaysia | Nipah virus infection | 105 | [228] |
| 1998–2000 Democratic Republic of the Congo Marburg virus outbreak | 1998–2000 | Democratic Republic of the Congo | Marburg virus | 128 | [229] |
| 2000 Central America dengue epidemic | 2000 | Central America | Dengue fever | 40+ | [230] |
| 2001 Nigeria cholera epidemic | 2001 | Nigeria | Cholera | 400+ | [231] |
| 2001 South Africa cholera epidemic | 2001 | South Africa | Cholera | 139 | [232][233] |
| 2002–2004 SARS outbreak | 2002–2004 | Worldwide | Severe acute respiratory syndrome / SARS | 774 | [234] |
| 2003–2019 Asia and Egypt avian influenza epidemic | 2003–2019 | China, Southeast Asia and Egypt | Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 | 455 | [235] |
| 2004 Indonesia dengue epidemic | 2004 | Indonesia | Dengue fever | 658 | [236] |
| 2004 Sudan Ebola outbreak | 2004 | Sudan | Ebola | 7 | [237] |
| 2004–2005 Angola Marburg virus outbreak | 2004–2005 | Angola | Marburg virus | 227 | [229] |
| 2005 dengue outbreak in Singapore | 2005 | Singapore | Dengue fever | 27 | [238] |
| 2006 Luanda cholera epidemic | 2006 | Luanda, Angola | Cholera | 1,200+ | [239] |
| 2006 Ituri Province plague epidemic | 2006 | Ituri Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo | Bubonic plague | 61 | [240][241] |
| 2006 India malaria outbreak | 2006 | India | Malaria | 17 | [242] |
| 2006 dengue outbreak in India | 2006 | India | Dengue fever | 50+ | [243] |
| 2006 dengue outbreak in Pakistan | 2006 | Pakistan | Dengue fever | 50+ | [244] |
| 2006 Philippines dengue epidemic | 2006 | Philippines | Dengue fever | 1,000 | [245] |
| 2006–2007 East Africa Rift Valley fever outbreak | 2006–2007 | East Africa | Rift Valley fever | 394 | [246] |
| Mweka Ebola epidemic | 2007 | Democratic Republic of the Congo | Ebola | 187 | [247] |
| 2007 Ethiopia cholera epidemic | 2007 | Ethiopia | Cholera | 684 | [248] |
| 2007 Iraq cholera outbreak | 2007 | Iraq | Cholera | 10 | [249] |
| 2007 Puerto Rico, Dominican Republic, and Mexico dengue fever epidemic | 2007 | Puerto Rico, Dominican Republic, Mexico | Dengue fever | 183 | [250] |
| 2007 Uganda Ebola outbreak | 2007 | Uganda | Ebola | 37 | [237] |
| 2007 Netherlands Q-fever epidemic | 2007–2018 | Netherlands | Q-fever | 95 | [251] |
| 2008 Brazil dengue epidemic | 2008 | Brazil | Dengue fever | 67 | [252] |
| 2008 Cambodia dengue epidemic | 2008 | Cambodia | Dengue fever | 407 | [253] |
| 2008 Chad cholera epidemic | 2008 | Chad | Cholera | 123 | [254] |
| 2008–2017 China hand, foot, and mouth disease epidemic | 2008–2017 | China | Hand, foot, and mouth disease | 3,322+ | [255] |
| 2008 India cholera epidemic | 2008 | India | Cholera | 115 | [256] |
| 2008 Madagascar plague outbreak | 2008 | Madagascar | Bubonic plague | 18+ | [257] |
| 2008 Philippines dengue epidemic | 2008 | Philippines | Dengue fever | 172 | [258] |
| 2008 Zimbabwean cholera outbreak | 2008–2009 | Zimbabwe | Cholera | 4,293 | [259] |
| 2009 Bolivian dengue fever epidemic | 2009 | Bolivia | Dengue fever | 18 | [260] |
| 2009 Gujarat hepatitis outbreak | 2009 | India | Hepatitis B | 49 | [261] |
| Queensland 2009 dengue outbreak | 2009 | Queensland, Australia | Dengue fever | 1+ (503 cases) | [262] |
| 2009–2010 West African meningitis outbreak | 2009–2010 | West Africa | Meningitis | 1,100 | [263] |
| 2009 swine flu pandemic | 2009–2010 | Worldwide | Influenza A virus subtype H1N1 | Lab confirmed deaths: 18,449 (reported to the WHO) | [264] |
| Estimated death toll: 284,000 (possible range 151,700–575,400) | [265] | ||||
| 2010s Haiti cholera outbreak | 2010–2019 | Haiti | Cholera (strain serogroup O1, serotype Ogawa) | 10,075 | [266] |
| 2010–2014 Democratic Republic of the Congo measles outbreak | 2010–2014 | Democratic Republic of the Congo | Measles | 4,500+ | [267][268] |
| 2011 Vietnam hand, foot, and mouth disease epidemic | 2011 | Vietnam | Hand, foot, and mouth disease | 170 | [269][270] |
| 2011 dengue outbreak in Pakistan | 2011 | Pakistan | Dengue fever | 350+ | [271] |
| 2012 yellow fever outbreak in Darfur, Sudan | 2012 | Darfur, Sudan | Yellow fever | 171 | [272] |
| MERS outbreak | 2012–present | Worldwide | Middle East respiratory syndrome / MERS-CoV | 941 (as of 8 May 2021[update]) | [273][274] |
| 2013 dengue outbreak in Singapore | 2013 | Singapore | Dengue fever | 8 | |
| 2013 Vietnam measles outbreak | 2013–2014 | Vietnam | Measles | 142 | [275] |
| Western African Ebola virus epidemic | 2013–2016 | Worldwide, primarily concentrated in Guinea, Liberia, Sierra Leone | Ebola | 11,323+ | [276][277][278] |
| 2013–2014 chikungunya outbreak | 2013–2015 | Americas | Chikungunya | 183 | [279] |
| 2013–19 avian influenza epidemic | 2013–2019 | China | Influenza A virus subtype H7N9 | 616 | [280] |
| 21st century Madagascar plague outbreaks | 2014–2017 | Madagascar | Bubonic plague | 292 | [281] |
| Flint water crisis | 2014–2015 | Flint, Michigan, United States | Legionnaires' disease | 12 | [282] |
| 2014 Odisha hepatitis outbreak | 2014–2015 | India | Primarily Hepatitis E, but also Hepatitis A | 36 | [283] |
| 2015 Indian swine flu outbreak | 2015 | India | Influenza A virus subtype H1N1 | 2,035 | [284][285][286] |
| 2015–16 Zika virus epidemic | 2015–2016 | Worldwide | Zika virus | 53 | [287] |
| 2016 Angola and Democratic Republic of the Congo yellow fever outbreak | 2016 | Angola and Democratic Republic of the Congo | Yellow fever | 498 (377 in Angola, 121 in Congo) | [288] |
| 2016–2022 Yemen cholera outbreak | 2016–2023 | Yemen | Cholera | 4,004 (as of June 11, 2023[update]) | [289] |
| 2017 Nigeria Lassa fever epidemic | 2017–2023 | Nigeria | Lassa fever | 1103 (as of April 2023) | [290] |
| 2017 dengue outbreak in Peshawar | 2017 | Peshawar, Pakistan | Dengue fever | 69 | [291] |
| 2017 Gorakhpur hospital deaths | 2017 | India | Japanese encephalitis | 1,317 | [292] |
| 2017 dengue outbreak in Sri Lanka | 2017 | Sri Lanka | Dengue fever | 440 | [293] |
| 2018 Nipah virus outbreak in Kerala | 2018 | India | Nipah virus infection | 17 | [294] |
| Kivu Ebola epidemic | 2018–2020 | Democratic Republic of the Congo and Uganda | Ebola | 2,280 | [295][296][297] |
| 2018 NDM-CRE outbreak in Italy | 2018–2019 | Italy | New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae | 31 (as of September 2019) | [298] |
| 2019–2020 measles outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo | 2019–2020 | Democratic Republic of the Congo | Measles | 7,018+ | [299] |
| 2019–2020 New Zealand measles outbreak | 2019–2020 | New Zealand | Measles | 2 | [300] |
| 2019 measles outbreak in the Philippines | 2019 | Philippines | Measles | 415 | [301] |
| 2019 Kuala Koh measles outbreak | 2019 | Kuala Koh, Malaysia | Measles | 15 | [302] |
| 2019 Samoa measles outbreak | 2019 | Samoa | Measles | 83 | [303] |
| 2019–2020 dengue fever epidemic | 2019–2020 | Asia-Pacific, Latin America | Dengue fever | 3,931 | [304] |
| COVID-19 pandemic | 2019[b]–present | Worldwide | COVID-19 | 7–35 million | [306] |
| 2020 Democratic Republic of the Congo Ebola outbreak | 2020 | Democratic Republic of the Congo | Ebola | 55 | [307] |
| 2020 dengue outbreak in Singapore | 2020 | Singapore | Dengue fever | 32 | [308] |
| 2020 Nigeria yellow fever epidemic | 2020 | Nigeria | Yellow fever | 296 (as of 31 December 2020) | [309] |
| 2021 South Sudan disease outbreak | 2021 | South Sudan | Unkown | 97 (as of December 2021) | [310] |
| 2021 India black fungus epidemic | 2021–2022 | India | Black fungus (COVID-19 condition) | 4,332 | [311] |
| 2022 hepatitis of unknown origin in children | 2021–2022 | Worldwide | Hepatitis by Adenovirus variant AF41 (Unconfirmed) | 18 | [312][313][314] |
| 2022–2023 mpox outbreak | 2022–2023 | Worldwide | Mpox | 280 | [315][316][317][318] |
| 2022 Uganda Ebola outbreak | 2022–2023 | Uganda | Sudan ebolavirus | 77 | [319] |
| 2023 South Poland Legionellosis outbreak | 2023 | Poland | Legionnaires' disease | 41 | [320][321] |
| African mpox epidemic | 2023–present | Worldwide, primarly Africa | Mpox | 812 | [322] |
| 2023–2024 Bangsamoro measles outbreak | 2023–present | Bangsamoro, Philippines | Measles | 14 | |
| 2023–2024 Oropouche virus disease outbreak | 2023–present | Brazil | Oropouche fever | 2 | [323][324][325] |
| 2024 American dengue epidemic | 2024–present | Latin America and the Caribbean | Dengue virus | 4,500 | [326] |
See also
- Globalization and disease – Overview of globalization and disease transmission
- History of smallpox
- List of Ebola outbreaks – Cases and outbreaks of Ebola virus disease
- List of infectious diseases
- List of natural disasters by death toll#Deadliest epidemics
- Timeline of plague – Human and animal disease
Explanatory notes
- ^ a b Global population increase outpaced the death rate significantly during the period of this pandemic.
- ^ a b The COVID-19 pandemic started as a regional outbreak/epidemic of COVID-19 in China in late 2019. The World Health Organization referred to it as a "pandemic" on 11 March 2020.[305] The starting time of this epidemic is thus 2019, regardless of the time when it became a pandemic.
- ^ The disease was a public health emergency of international concern from January 30, 2020 – May 5, 2023.
References
- ^ Green MS; Swartz T; Mayshar E; Lev B; Leventhal A; Slater PE; Shemer Js (January 2002). "When is an epidemic an epidemic?". Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 4 (1): 3–6. PMID 11802306.
- ^ a b Whitfield, J. (2002). "Portrait of a serial killer". Nature. doi:10.1038/news021001-6. Archived from the original on 2023-10-17. Retrieved 2023-03-30.
- ^ "World Population History". World Population. Archived from the original on 2021-02-26. Retrieved 2021-03-01.
- ^ "The Spanish flu (1918–20): The global impact of the largest influenza pandemic in history". Our World in Data. Archived from the original on 2021-09-07. Retrieved 2021-02-06.
- ^ a b Mordechai, Lee; Eisenberg, Merle; Newfield, Timothy P.; Izdebski, Adam; Kay, Janet E.; Poinar, Hendrik (2019-12-17). "The Justinianic Plague: An inconsequential pandemic?". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 116 (51): 25546–25554. Bibcode:2019PNAS..11625546M. doi:10.1073/pnas.1903797116. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 6926030. PMID 31792176.
- ^ Wade, Lizzie (2020-05-14). "From Black Death to fatal flu, past pandemics show why people on the margins suffer most". Science. Archived from the original on 2021-10-01. Retrieved 2021-02-06.
- ^ Beyrer C (June 2021). "A pandemic anniversary: 40 years of HIV/AIDS". Lancet (Review). 397 (10290): 2142–2143. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01167-3. PMID 34087110. S2CID 235273243.
- ^ "WHO COVID-19 dashboard". WHO. 14 January 2024. Archived from the original on 6 February 2024. Retrieved 14 January 2024.
- ^ "The pandemic's true death toll". The Economist. Retrieved 2024-02-08.
- ^ "Archived: WHO Timeline - COVID-19". Word Health Organization. 27 April 2020. Archived from the original on 29 April 2020. Retrieved 7 March 2024.
- ^ "COVID is still a pandemic, WHO leader says". TheMessenger. 2024-01-03. Archived from the original on Jan 2, 2024. Retrieved 2024-01-03.
- ^ a b c d Acuna-Soto, R.; Stahle, D. W.; Cleaveland, M. K.; Therrell, M. D. (April 8, 2002). "Megadrought and Megadeath in 16th Century Mexico". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 8 (4): 360–362. doi:10.3201/eid0804.010175. PMC 2730237. PMID 11971767.
- ^ "Antonine Plague". World History Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on 2023-08-28. Retrieved 2021-02-06.
- ^ "Population of Russia". www.tacitus.nu. Archived from the original on 2021-10-18. Retrieved 2021-03-01.
- ^ a b Suzuki, A. (2011). "Smallpox and the epidemiological heritage of modern Japan: Towards a total history". Medical History. 55 (3): 313–318. doi:10.1017/S0025727300005329. PMC 3143877. PMID 21792253.
- ^ Knowable Magazine Staff (July 16, 2020). "Pandemics in recent history". Knowable Magazine. doi:10.1146/knowable-071520-2. Archived from the original on November 29, 2022. Retrieved June 29, 2021.
- ^ a b King, Anthony (May 2020). "An uncommon cold". New Scientist. 246 (3280): 32–35. Bibcode:2020NewSc.246...32K. doi:10.1016/S0262-4079(20)30862-9. PMC 7252012. PMID 32501321.
- ^ "Malaria". World Health Organization. 2023-03-29. Archived from the original on 2020-05-02. Retrieved 2023-05-25.
- ^ Frith, John. "History of Tuberculosis. Part 1 – Phthisis, consumption and the White Plague". Journal of Military and Veterans' Health. Archived from the original on 2021-04-08. Retrieved 2021-02-26.
- ^ Zürcher, Kathrin; Zwahlen, Marcel; Ballif, Marie; Rieder, Hans L.; Egger, Matthias; Fenner, Lukas (2016-10-05). "Influenza Pandemics and Tuberculosis Mortality in 1889 and 1918: Analysis of Historical Data from Switzerland". PLOS ONE. 11 (10): e0162575. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1162575Z. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0162575. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 5051959. PMID 27706149.
- ^ a b c "Tuberculosis". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 2021-04-11. Retrieved 2021-02-26.
- ^ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (2012-07-06). "CDC Grand Rounds: the TB/HIV syndemic". MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 61 (26): 484–489. ISSN 1545-861X. PMID 22763886. Archived from the original on 2021-07-12. Retrieved 2021-02-26.
- ^ a b "Hepatitis B". World Health Organization. 27 July 2021. Archived from the original on 13 May 2020. Retrieved 4 August 2021.
- ^ Franco, Elisabetta; Bagnato, Barbara; Marino, Maria Giulia; Meleleo, Cristina; Serino, Laura; Zaratti, Laura (2012-03-27). "Hepatitis B: Epidemiology and prevention in developing countries". World Journal of Hepatology. 4 (3): 74–80. doi:10.4254/wjh.v4.i3.74. ISSN 1948-5182. PMC 3321493. PMID 22489259.
- ^ "Hepatitis C". World Health Organization. 27 July 2021. Archived from the original on 26 May 2020.
- ^ Shiffman, Mitchell L. (February 2018). "The next wave of hepatitis C virus: The epidemic of intravenous drug use". Liver International. 38 (Suppl 1): 34–39. doi:10.1111/liv.13647. ISSN 1478-3231. PMID 29427493. S2CID 46805810.
- ^ Rodrigo, Chaturaka; Eltahla, Auda A.; Bull, Rowena A.; Grebely, Jason; Dore, Gregory J.; Applegate, Tanya; Page, Kimberly; Bruneau, Julie; Morris, Meghan D.; Cox, Andrea L.; Osburn, William (2016-11-01). "Historical Trends in the Hepatitis C Virus Epidemics in North America and Australia". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 214 (9): 1383–1389. doi:10.1093/infdis/jiw389. ISSN 0022-1899. PMC 5079374. PMID 27571901.
- ^ Palladino, Claudia; Ezeonwumelu, Ifeanyi Jude; Marcelino, Rute; Briz, Verónica; Moranguinho, Inês; Serejo, Fátima; Velosa, José Fernando; Marinho, Rui Tato; Borrego, Pedro; Taveira, Nuno (2018-08-16). "Epidemic history of hepatitis C virus genotypes and subtypes in Portugal". Scientific Reports. 8 (1): 12266. Bibcode:2018NatSR...812266P. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-30528-0. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 6095915. PMID 30116054.
- ^ Amarna Tablet 244 Archived 2023-04-04 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ "Pandemics That Changed History". History.com. Archived from the original on 2020-03-03. Retrieved 2020-04-14.
- ^ "Plague of Athens: Another Medical Mystery Solved at University of Maryland". University of Maryland Medical Center. Archived from the original on 2015-12-04. Retrieved 2016-02-10.
- ^ Papagrigorakis, Manolis J.; Yapijakis, Christos; Synodinos, Philippos N.; Baziotopoulou-Valavani, Effie (2007). "DNA examination of ancient dental pulp incriminates typhoid fever as a probable cause of the Plague of Athens". International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 10 (3): 206–214. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2005.09.001. PMID 16412683.
- ^ Olson, PE; Hames, CS; Benenson, AS; Genovese, EN (1996). "The Thucydides syndrome: Ebola déjà vu? (or Ebola reemergent?)". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 2 (2): 155–156. doi:10.3201/eid0202.960220. PMC 2639821. PMID 8964060.
- ^ Potter, C. W. (2002). "Foreword". Influenza. Elsevier Science. p. vii.
- ^ "Reactions to Plague in the Ancient & Medieval World". World History Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on 2021-04-23. Retrieved 2021-02-06.
- ^ "Past pandemics that ravaged Europe" Archived 2017-10-07 at the Wayback Machine, BBC News, 7 November 2005
- ^ Mazanec, Thomas J. (2020-09-01). "Review: The Halberd at Red Cliff: Jian'an and the Three Kingdoms, by Xiaofei Tian". Studies in Late Antiquity. 4 (3): 353–359. doi:10.1525/sla.2020.4.3.353. ISSN 2470-6469. S2CID 225333779. Archived from the original on 2020-09-03. Retrieved 2021-01-19.
- ^ Tian, Xiaofei (2018-10-14). Plague and Poetry: Rethinking Jian'an. Brill. ISBN 978-1-68417-092-0. Archived from the original on 2021-07-12. Retrieved 2021-01-19.
- ^ D. Ch. Stathakopoulos Famine and Pestilence in the late Roman and early Byzantine Empire (2007) 95
- ^ Harper, Kyle (1 November 2017). "Solving the Mystery of an Ancient Roman Plague". The Atlantic. Archived from the original on 21 January 2018. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- ^ Tharoor, Ishaan (2010-10-26). "Top 10 Terrible Epidemics - TIME". Time. ISSN 0040-781X. Archived from the original on 2021-01-16. Retrieved 2020-12-29.
- ^ Maugh, Thomas. "An Empire's Epidemic". University of California, Los Angeles. Archived from the original on 4 August 2002. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- ^ Gregory of Tours. A History of the Franks. Pantianos Classics, 1916
- ^ Frerichs, Ralph R. "An Empire's Epidemic". Ph.ucla.edu. Archived from the original on 13 December 2008. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
- ^ a b Turner, David (November 1990). "The Politics of Despair: The Plague of 746–747 and Iconoclasm in the Byzantine Empire1". Annual of the British School at Athens. 85: 419–434. doi:10.1017/S006824540001577X. ISSN 2045-2403. S2CID 153709117.
- ^ Maddicott, J. R. (1 August 1997). "Plague in seventh century England". Past & Present (156): 7–54. doi:10.1093/past/156.1.7. ISSN 0031-2746. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- ^ Little, Lester K., ed. (2007). Plague and the end of Antiquity. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 104. ISBN 978-0-521-84639-4.
- ^ Kohn, George C. (2002). Encyclopedia of Plague and Pestilence: From Ancient Times to the Present. Princeton, New Jersey: Checkmark Books. p. 213. ISBN 978-0816048939.
- ^ Austin Alchon, Suzanne (2003). A pest in the land: new world epidemics in a global perspective. University of New Mexico Press. p. 21. ISBN 978-0-8263-2871-7. Archived from the original on 2019-04-01. Retrieved 2016-04-22.
- ^ Heyman, Paul; Simons, Leopold; Cochez, Christel (7 January 2014). "Were the English Sweating Sickness and the Picardy Sweat Caused by Hantaviruses?". Viruses. 6 (1): 151–171. doi:10.3390/v6010151. PMC 3917436. PMID 24402305.
- ^ a b "Typhus, War, and Vaccines". historyofvaccines.org. 16 March 2016. Archived from the original on 11 November 2020. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ Morens, David; North, Michael; Taubenberger, Jeffrey (4 December 2011). "Eyewitness accounts of the 1510 influenza pandemic in Europe". Lancet. 367 (9756): 1894–1895. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(10)62204-0. PMC 3180818. PMID 21155080.
- ^ a b "American plague". New Scientist. December 19, 2000. Archived from the original on October 17, 2018. Retrieved October 17, 2018.
- ^ a b Acuna-Soto, R.; Romero, L. C.; Maguire, J. H. (2000). "Large epidemics of hemorrhagic fevers in Mexico 1545–1815". The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 62 (6): 733–739. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.2000.62.733. PMID 11304065.
- ^ a b Acuna-Soto, Rodolfo; Stahle, D. W.; Cleaveland, M. K.; Therrell, M. D. (2002). "Megadrought and Megadeath in 16th Century Mexico". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 8 (4): 360–362. doi:10.3201/eid0804.010175. PMC 2730237. PMID 11971767.
- ^ a b Vågene, Åshild J.; Herbig, Alexander; Campana, Michael G.; Robles García, Nelly M.; Warinner, Christina; Sabin, Susanna; Spyrou, Maria A.; Andrades Valtueña, Aida; Huson, Daniel; Tuross, Noreen; Bos, Kirsten I.; Krause, Johannes (2018). "Salmonella enterica genomes from victims of a major sixteenth-century epidemic in Mexico". Nature Ecology & Evolution. 2 (3): 520–528. Bibcode:2018NatEE...2..520V. doi:10.1038/s41559-017-0446-6. PMID 29335577. S2CID 3358440.
- ^ Alonso de Góngora Marmolejo Historia de Chile desde su descubrimiento hasta el año 1575 Archived 2015-09-24 at the Wayback Machine. Cervantesvirtual.com. Retrieved on 2011-12-06.
- ^ Creighton, Charles (1891). A History of Epidemics in Britain. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. p. 305. Archived from the original on 2021-12-25. Retrieved 2020-05-08.
- ^ "Plague. The fourth horseman – Historic epidemics and their impact in Tenerife" (PDF) (in Spanish). p. 28. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 February 2020. Retrieved 15 May 2020.
- ^ "American Indian Epidemics". Archived from the original on February 14, 2015.
- ^ "Our Heritage Saved: St Roque Chapel". The Malta Independent. 30 May 2007. Archived from the original on 13 March 2020.
- ^ Creighton, Charles (November 1891). A History of Epidemics in Britain: From A.D 664 to the Extinction of Plague. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. pp. 353–354.
- ^ "A History of Spain". Archived from the original on 27 March 2017. Retrieved 16 November 2014.
- ^ "The Death of Queen Elizabeth I, the Return of the Black Plague, the Rise of Shakespeare, Piracy, Witchcraft, and the Birth of the Stuart Era". Archived from the original on 12 July 2021. Retrieved 11 May 2020.
- ^ "Worst Diseases in Shakespeare's London". Archived from the original on 8 May 2020. Retrieved 11 May 2020.
- ^ Bell, Walter George (1951). Belinda Hollyer (ed.). The great Plague in London (folio society ed.). Folio society by arrangement with Random House. pp. 3–5
- ^ Marr, John S.; Cathey, John T. (2010). "New Hypothesis for Cause of Epidemic among Native Americans, New England, 1616–1619". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 16 (2): 281–286. doi:10.3201/eid1602.090276. PMC 2957993. PMID 20113559.
- ^ Mann, Charles C. (December 2005). "Native intelligence". Archived from the original on 2018-11-23. Retrieved 2018-10-17.
- ^ Hays, J. N. (2005). Epidemics and pandemics their impacts on human history. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO. p. 103. ISBN 978-1851096589.
- ^ Eckert, Edward-A. (1978). Annales de Démographie Historique. Vol. 1978. p. 55. doi:10.3406/adh.1978.1378. Archived from the original on 27 November 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ "1633–34 — Smallpox Epidemic, New England Natives, Plymouth Colonists, MA –>1000". usdeadlyevents.com. January 1632. Archived from the original on 8 September 2018. Retrieved 13 May 2020.
- ^ Johansen, Bruce E. (2015). American Indian Culture: From Counting Coup to Wampum [2 volumes]: From Counting Coup to Wampum. ABC-CLIO. p. 88. ISBN 978-1-4408-2874-4. Archived from the original on 6 January 2024. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- ^ Newman, Kira L. S. (2012). "Shutt up: bubonic plague and quarantine in early modern England". Journal of Social History. 45 (3): 809–834. doi:10.1093/jsh/shr114. ISSN 0022-4529. JSTOR 41678910. PMID 22611587. S2CID 24952354.
- ^ Ch'iu, Chung-lin. "The Epidemics in Ming Beijing and the Responses from the Empire's Public Health System". 中央研究院歷史語言研究所集刊 (in Chinese): 331–388. Archived from the original on 2021-01-02. Retrieved 2021-01-18.
- ^ Timothy Brook (1999). The Confusions of Pleasure: Commerce and Culture in Ming China. University of California Press. p. 163. ISBN 978-0-520-22154-3. Retrieved 31 March 2011.
- ^ Stanley G. Payne: A History of Spain and Portugal Volume 1, Ch 15 The Seventeenth-Century Decline Archived 2017-03-27 at the Wayback Machine THE LIBRARY OF IBERIAN RESOURCES ONLINE, accessed 26 May 2020
- ^ Rogers, D.J.; Wilson, A.J.; Hay, S.I.; Graham, A.J. (2006). "The Global Distribution of Yellow Fever and Dengue". Advances in Parasitology. 62: 181–220. doi:10.1016/S0065-308X(05)62006-4. ISBN 9780120317622. ISSN 0065-308X. PMC 3164798. PMID 16647971.
- ^ Scasciamacchia, Silvia; Serrecchia, Luigina; Giangrossi, Luigi; Garofolo, Giuliano; Balestrucci, Antonio; Sammartino, Gilberto; Fasanella, Antonio (2012). "Plague Epidemic in the Kingdom of Naples, 1656–1658". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 18 (1): 186–188. doi:10.3201/eid1801.110597. PMC 3310102. PMID 22260781.
- ^ "De pest" (in Dutch). 23 April 2019. Archived from the original on 11 April 2020. Retrieved 13 May 2020.
- ^ Ross, David. "UK travel and heritage – Britain Express UK travel guide". The London Plague of 1665. Archived from the original on 26 May 2019. Retrieved 14 July 2011.
- ^ Archives, The National. "Great Plague of 1665–1666 – The National Archives". Archived from the original on 28 April 2016. Retrieved 4 July 2016.
- ^ Jones, Colin (1996). "Plague and Its Metaphors in Early Modern France". Representations. 53 (53): 97–127. doi:10.2307/2928672. ISSN 0734-6018. JSTOR 2928672.
- ^ Grima, Noel (19 June 2017). "The 1676 plague in Malta". The Malta Independent. Archived from the original on 12 November 2017.
- ^ Casey, James (1999). Early Modern Spain: A Social History. Psychology Press. p. 37. ISBN 978-0-415-13813-0. Archived from the original on 6 January 2024. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- ^ "1677–1678 — Smallpox Epidemic, Massachusetts Bay Colony, esp. Boston & vic. –750-1,000". usdeadlyevents. January 1676. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- ^ Payne, Joseph Frank (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 21 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 696.
- ^ "Plague". britannica. Archived from the original on 16 January 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ History of South Africa 1486–1691, George McCall Theal, London, pub. Swan Sonnenschein, 1888. p. 332 "Towards the beginning of the winter of 1687 the colony was visited by a destructive disease, a kind of fever which carried off many of the inhabitants. The natives suffered very..."
- ^ "1693 — June 17 start, Yellow Fever, Boston, British fleet arrival from Martinique[1]—<10?". 17 June 1693. Archived from the original on 12 July 2021. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ "1699 — Yellow Fever Epidemics Charleston, SC(170–311); Philadelphia (220) –390 – 531". January 1699. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ "1702 — Summer to late Fall, Yellow Fever Epidemic, New York City, NY −500-570". June 1702. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ Desjardins, Bertrand (1996). "Demographic Aspects of the 1702–1703 Smallpox Epidemic in the St. Lawrence Valley". Canadian Studies in Population. 23 (1): 49–67. doi:10.25336/P6459C.
- ^ J. N. Hays (2005). Epidemics and pandemics: their impacts on human history. ABC-CLIO. p. 131. ISBN 978-1-85109-658-9. Retrieved 29 March 2011.
- ^ Sticker, Georg (1908). Die Pest. Abhandlungen aus der Seuchengeschichte und Seuchenlehre. Vol. 1. Gießen: A. Töpelmann (vormals J. Ricker). p. 213.
- ^ Kroll, Stefan; Grabinsky, Anne. "Städtesystem und Urbanisierung im Ostseeraum in der Neuzeit – Historisches Informationssystem und Analyse von Demografie, Wirtschaft und Baukultur im 17. und 18. Jahrhundert. B: Komplexe Historische Informationssysteme. B2: Der letzte Ausbruch der Pest im Ostseeraum zu Beginn des 18. Jahrhunderts. Chronologie des Seuchenzugs und Bestandsaufnahme überlieferter Sterbeziffern. Karte". University of Rostock. Archived from the original on 2007-07-03. Retrieved 2012-08-14.
Specific sections: Danzig Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Königsberg Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Stettin Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Memel Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Tilsit Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Narva Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Stargard Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Riga Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Pernau Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Reval Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Stralsund Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Stockholm Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Visby Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Linköping Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Jönköping Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Ystad Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Malmö Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Helsingør Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Kopenhagen Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine; Hamburg Archived 2007-07-03 at the Wayback Machine - ^ Morens, David M. (2015). "The Past Is Never Dead – Measles Epidemic, Boston, Massachusetts, 1713". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 21 (7): 1257–1260. doi:10.3201/eid2107.150397. PMC 4480406. PMID 26277799.
- ^ Mazan, Ryan; Gagnon, Alain; Desjardins, Bertrand (2009). "The Measles Epidemic of 1714–1715 in New France". Canadian Studies in Population. 36 (3–4): 295–323. doi:10.25336/P63P5Q.
- ^ Devaux, Christian A. (2013). "Small oversights that led to the Great Plague of Marseille (1720–1723): Lessons from the past". Infection, Genetics and Evolution. 14: 169–185. Bibcode:2013InfGE..14..169D. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2012.11.016. PMID 23246639.
- ^ "Zabdiel Boylston and inoculation". Archived from the original on 5 September 2015. Retrieved 16 November 2014.
- ^ Brink, Susan (28 August 2016). "Yellow Fever Timeline: The History Of A Long Misunderstood Disease". NPR. Archived from the original on 28 May 2020. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ "Ambrosevideo.com". Archived from the original on 2016-04-17. Retrieved 2011-03-27.
- ^ Gagnon, Alain; Mazan, Ryan (2009). "Does exposure to infectious diseases in infancy affect old-age mortality? Evidence from a pre-industrial population". Social Science & Medicine. 68 (9): 1609–1616. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2009.02.008. PMID 19269727.
- ^ Purvis, Thomas L. (2014). Colonial America To 1763. Infobase. p. 173. ISBN 9781438107998. Archived from the original on 6 January 2024. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- ^ "Banat's historical chronology for the last millennium- XVIII Century". www.genealogy.ro. Genealogy RO Group. Archived from the original on 4 June 2002. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- ^ "1738–39 — Smallpox, Catawba (NC/SC) and Cherokee Natives (NC) –7,700–11,700". usdeadlyevents.com. January 1738. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 13 May 2020.
- ^ a b "The Early History of Yellow Fever". jdc.jefferson.edu. Thomas Jefferson University. September 2009. p. 3. Archived from the original on 6 January 2024. Retrieved 16 May 2020.
- ^ Tognotti, Eugenia (February 2013). "Lessons from the History of Quarantine, from Plague to Influenza A". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 19 (2): 254–259. doi:10.3201/eid1902.120312. PMC 3559034. PMID 23343512.
- ^ Wyman, Walter (April 1897). "The North American Review". The Black Plague. 164 (485). University of Northern Iowa: 442. JSTOR 25118799.
- ^ LeMay, Michael C. (2016). Global Pandemic Threats: A Reference Handbook: A Reference Handbook. ABC-CLIO. p. 227. ISBN 978-1-4408-4283-2. Archived from the original on 6 January 2024. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- ^ Krebsbach, Suzanne (1996). "The Great Charlestown Smallpox Epidemic of 1760". The South Carolina Historical Magazine. 97 (1): 30–37. ISSN 0038-3082. JSTOR 27570134.
- ^ "1760 — Smallpox Epidemic, Charleston, SC (as well as undocumented Native deaths)–730-940". usdeadlyevents.com. January 1760. Archived from the original on 9 March 2021. Retrieved 13 May 2020.
- ^ Ranlet, Philip (2000). "The British, the Indians, and Smallpox: What Actually Happened at Fort Pitt in 1763?". Pennsylvania History: A Journal of Mid-Atlantic Studies. 67 (3): 427–441. ISSN 0031-4528. JSTOR 27774278.
- ^ Melikishvili, Alexander (2006). "Genesis of the anti-plague system: the Tsarist period" (PDF). Critical Reviews in Microbiology. 36 (1): 19–31. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.204.1976. doi:10.1080/10408410500496763. PMID 16610335. S2CID 7420734. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2009-11-23. Retrieved 2020-05-26.
- ^ "1772 — Measles Epidemics, Charleston, SC (800–900), Philadelphia, PA (180) –980-1,080". usdeadlyevents.com. January 1772. Archived from the original on 22 January 2021. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ^ Hashemi Shahraki A; Carniel E; Mostafavi E (2016). "Plague in Iran: its history and current status". Epidemiol Health. 38: e2016033. doi:10.4178/epih.e2016033. PMC 5037359. PMID 27457063.
- ^ Prichard, Augustin; Fothergill, John (1894). "Influenza in 1775". The Lancet. 143 (3673): 175–176. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(01)66026-4. Archived from the original on 2020-01-03. Retrieved 2019-07-05.
- ^ Greg Lange,"Smallpox epidemic ravages Native Americans on the northwest coast of North America in the 1770s" Archived 2008-05-26 at the Wayback Machine, 23 Jan 2003, HistoryLink.org, Online Encyclopedia of Washington State History, accessed 2 Jun 2008
- ^ Houston, C. S.; Houston, S. (2000). "The first smallpox epidemic on the Canadian Plains: In the fur-traders' words". The Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases. 11 (2): 112–115. doi:10.1155/2000/782978. PMC 2094753. PMID 18159275.
- ^ Rohé, George Henry; Robin, Albert (1908). Text-book of Hygiene: A Comprehensive Treatise on the Principles and Practice of Preventive Medicine from an American Standpoint. Davis. p. 428. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
spain 1788 dengue fever.
- ^ Waldman, Carl; Braun, Molly (2009). Atlas of the North American Indian. Infobase Publishing. p. 295. ISBN 978-1-4381-2671-5. Archived from the original on 6 January 2024. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- ^ The History of Small-Pox in Australia, 1788–1908, JHL Cumpston, (1914, Government Printer, Melb.)This epidemic is unlikely to have been a natural event. see, Warren (2013) doi:10.1080/14443058.2013.849750 After Cook and coinciding with Colonisation "With the arrival of the Europeans, the Gadigal population was virtually wiped. In 1789 and 1790 a smallpox epidemic swept through the Aboriginal population around Sydney" Archived 2008-06-25 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "The origin of the smallpox outbreak in Sydney in 1789". thefreelibrary. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ "Epidemics". Archived from the original on 2013-07-22. Retrieved 2008-06-08.
- ^ "Tiger mosquitoes and the history of yellow fever and dengue in Spain". Archived from the original on 4 August 2017. Retrieved 16 November 2014.
- ^ Andrew Davidson (1893). Hygiene & diseases of warm climates. Pentland. p. 337. Retrieved 31 March 2011.
- ^ a b c "The 1802 Saint-Domingue Yellow Fever Epidemic and the Louisiana Purchase (page 78)" (PDF). 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 February 2016. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ Lynch, Lily (5 December 2015). "Odessa, 1812: Plague and Tyranny at the Edge of the Empire". Balkanist. Archived from the original on 13 February 2020.
- ^ Mangion, Fabian (19 May 2013). "Maltese islands devastated by a deadly epidemic 200 years ago". Times of Malta. Archived from the original on 12 March 2020. Retrieved 28 May 2020.
- ^ Ştefan Ionescu, Bucureştii în vremea fanarioţilor (Bucharest in the time of the Phanariotes), Editura Dacia, Cluj, 1974. p. 287-293
- ^ Fenning, Hugh (1999). "Typhus Epidemic in Ireland, 1817–1819: Priests, Ministers, Doctors". Collectanea Hibernica. 41 (41): 117–152. JSTOR 30004680.
- ^ J. N. Hays (2005). Epidemics and pandemics: their impacts on human history. ABC-CLIO. p. 193. ISBN 978-1-85109-658-9. Retrieved 29 March 2011.
- ^ "The Autumnal Fever: The Outbreak of the Yellow Fever in Savannah, Georgia in 1820". projects.leadr.msu.edu. Archived from the original on 24 February 2021. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ a b c Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 28 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 910–911.
- ^ "Yellow fever in Barcelona". 14 May 2009. Archived from the original on 10 March 2021. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ J. N. Hays (2005). Epidemics and pandemics: their impacts on human history. ABC-CLIO. p. 211. ISBN 978-1-85109-658-9. Retrieved 29 March 2011.
- ^ "Aboriginal Health History". Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 16 November 2014.
- ^ "The smallpox holocaust that swept Aboriginal Australia – Red hot echidna spikes are burning me". candobetter. Archived from the original on 3 August 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ "Epidemieën in Groningen: De Groninger ziekte (1826)". rtvnoord (in Dutch). 22 March 2020. Archived from the original on 1 April 2020. Retrieved 18 April 2020.
- ^ "A Listing Of Some Worldwide Epidemics". raogk. 16 June 2015. Archived from the original on 14 March 2020. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- ^ "Disease Epidemics among Indians, 1770s–1850s (essay)". oregonencyclopedia. Archived from the original on 24 March 2020. Retrieved 18 April 2020.
- ^ A History of the Human Plague in Iran Archived 2011-07-19 at the Wayback Machine, Mohammad Azizi, Farzaneh Azizi
- ^ a b c d Kuhnke, Laverne. Lives at Risk: Public Health in Nineteenth-Century Egypt. ark.cdlib.org Archived 2008-11-20 at the Wayback Machine, Berkeley: University of California Press, c1990.
- ^ "Smallpox decimates tribes; survivors join together – Timeline – Native Voices". www.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 16 August 2016. Retrieved 4 July 2016.
- ^ "1841 — Yellow Fever, esp. FL & LA, esp. New Orleans, also Vicksburg, Charleston −3,498". usdeadlyevents.com. January 1840. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ Gallagher, The Reverend John A. (1936). "The Irish Emigration of 1847 and Its Canadian Consequences". Canadian Catholic Historical Association Report, University of Manitoba Web Site. Archived from the original on 2007-10-11. Retrieved 2008-03-23.
- ^ "1847 –Yellow Fever, esp. New Orleans, also Galveston, Mobile, Pensacola, Vicksburg >3,400". usdeadlyevents.com. January 1846. Archived from the original on 9 March 2021. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ a s, &NA (1849). "On the Influenza, or Epidemic Catarrhal Fever of 1847–8". The American Journal of the Medical Sciences. 18 (35): 148–154. doi:10.1097/00000441-184907000-00018. PMC 5277660.
- ^ Schmitt, Robert C.; Nordyke, Eleanor C. (2001). "Death in Hawai'i: the Epidemics of 1848 – 1849". Hawaiian Journal of History. 35. hdl:10524/339.
- ^ J. N. Hays (2005). Epidemics and pandemics: their impacts on human history. ABC-CLIO. p. 236. ISBN 978-1-85109-658-9. Retrieved 29 March 2011.
- ^ Practitioner. 1877. Retrieved 29 March 2011.
- ^ "Efterhistorien". wayback-01.kb.dk. Archived from the original on January 3, 2015.
- ^ John Snow (1855). On the mode of communication of cholera. John Churchill. Retrieved 29 March 2011.
- ^ "Norfolk's Yellow Fever Epidemic of 1855". historicforrest.com. Archived from the original on 25 June 2020. Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- ^ Pryor, E. G. (1975). "The Great Plague of Hong Kong". Journal of the Hong Kong Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society. 15: 61–70. ISSN 0085-5774. JSTOR 23881624. PMID 11614750. Archived from the original on 2023-02-14. Retrieved 2021-05-25.
- ^ Stenseth, Nils Chr (8 August 2008). "Plague Through History". Science. 321 (5890): 773–774. doi:10.1126/science.1161496. S2CID 161336516.
- ^ "La fiebre amarilla en el siglo XIX" (in Spanish). 13 August 2019. Archived from the original on 24 July 2021. Retrieved 24 July 2021.
- ^ "Australian Medical Pioneers Index (AMPI) – Colonial Medical Life". Archived from the original on 29 June 2017. Retrieved 16 November 2014.
- ^ Beveridge, W.I.B. Influenza, the Last Great Plague (Heinemann, London, 1977)[page needed]
- ^ Creating Canada: 1850–1890 (PDF). p. 42. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 August 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ "How a smallpox epidemic forged modern British Columbia". macleans.ca. August 2017. Archived from the original on 18 January 2021. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ Boyd, Robert; Boyd, Robert Thomas (1999). "A final disaster: the 1862 smallpox epidemic in coastal British Columbia". The Coming of the Spirit of Pestilence: Introduced Infectious Diseases and Population Decline Among Northwest Coast Indians, 1774–1874. University of British Columbia Press. pp. 172–201. ISBN 978-0-295-97837-6. Archived from the original on 6 January 2024. Retrieved 10 February 2021.
- ^ "Typhoid Fever History". news-medical.net. 22 April 2010. Archived from the original on 13 May 2020. Retrieved 13 May 2020.
- ^ J. N. Hays (2005). Epidemics and pandemics: their impacts on human history. ABC-CLIO. p. 267. ISBN 978-1-85109-658-9. Retrieved 29 March 2011.
- ^ a b "Epidemics". dictionaryofsydney.org. 2008. Archived from the original on 28 March 2020. Retrieved 16 May 2020.
- ^ "The Yellow Fever Outbreak of 1871". Archived from the original on 29 September 2019. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ "Franco-Prussian War". strategypage.com. Archived from the original on 3 August 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ Jorland, Gerard (2011). "Smallpox and the Franco-Prussian War of 1870". Les Tribunes de la Santé. 33 (4): 25–30. doi:10.3917/seve.033.0025. Archived from the original on 2023-04-04. Retrieved 2020-05-14.
- ^ "Death of Forty Thousand Fijians from Measles". Liverpool Mercury. 29 Sep 1875. Retrieved 9 Nov 2012.
- ^ "Plague in the 19th Century: (2) 1853–84". 1902encyclopedia. Archived from the original on 3 June 2020. Retrieved 16 May 2020.
- ^ J. N. Hays (2005). Epidemics and pandemics: their impacts on human history. ABC-CLIO. p. 303. ISBN 978-1-85109-658-9. Retrieved 29 March 2011.
- ^ Plague A Story of Smallpox in Montreal Archived 2023-04-04 at the Wayback Machine Michael Bliss, 1991, accessed 8 May 2020
- ^ Huynh, Jeremy; Li, Shimena; Yount, Boyd; Smith, Alexander; Sturges, Leslie; Olsen, John C.; Nagel, Juliet; Johnson, Joshua B.; Agnihothram, Sudhakar; Gates, J. Edward; Frieman, Matthew B.; Baric, Ralph S.; Donaldson, Eric F. (1 December 2012). "Evidence Supporting a Zoonotic Origin of Human Coronavirus Strain NL63". Journal of Virology. 86 (23): 12816–12825. doi:10.1128/JVI.00906-12. PMC 3497669. PMID 22993147.
- ^ Great Britain. Local Government Board (1893). Further report and papers on epidemic influenza, 1889–92: with an introduction by the medical officer of the Local Government Board. Eyre. p. 49. Retrieved 29 March 2011.
- ^ "A lesson from history – Hong Kong's plague epidemic points way ahead in face of crisis". South China Morning Post. 2016-01-11. Archived from the original on 2020-11-09. Retrieved 2021-01-16.
- ^ "The 1896 Bombay Plague: Lessons In What Not To Do". outlookindia. 9 April 2020. Archived from the original on 16 April 2020. Retrieved 13 May 2020.
- ^ a b "The history of sleeping sickness". WHO. Archived from the original on March 23, 2008. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ Pontes, David (2012). O cerco da peste no Porto: Cidade, imprensa e saúde pública na crise sanitária de 1899 (PDF) (master's degree) (in Portuguese). Faculdade de Letras da Universidade do Porto. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 March 2020. Retrieved 2 March 2020.
- ^ J. N. Hays (2005). Epidemics and pandemics: their impacts on human history. ABC-CLIO. p. 345. ISBN 978-1-85109-658-9. Retrieved 29 March 2011.
- ^ Echenberg, Myron (2007). Plague Ports: The Global Urban Impact of Bubonic Plague: 1894–1901. Sacramento: New York University Press. p. 231. ISBN 978-0-8147-2232-9.
- ^ "The day bubonic plague hit Sydney". www.dailytelegraph.com.au. 2015-09-03. Archived from the original on 2020-02-12. Retrieved 2020-07-26.
- ^ Liberski, Pawel; Gajos, Agata; Sikorska, Beata; Lindenbaum, Shirley (2019). "Kuru, the First Human Prion Disease †". Viruses. 11 (3): 232. doi:10.3390/v11030232. PMC 6466359. PMID 30866511.
- ^ Zafar Khan, Zartash (20 July 2021). Kuru: Background, Pathophysiology, Epidemiology (Report). Archived from the original on 9 October 2023. Retrieved 31 July 2020 – via emedicine.medscape.com.
- ^ Blackburne, George Hugh Spencer; Anderson, T. L. (1903). – via Wikisource.
- ^ Wijesundere, Dilkushi Anula; Ramasamy, Ranjan (2017-08-28). "Analysis of Historical Trends and Recent Elimination of Malaria from Sri Lanka and Its Applicability for Malaria Control in Other Countries". Frontiers in Public Health. 5: 212. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2017.00212. ISSN 2296-2565. PMC 5581355. PMID 28894732.
- ^ Meiklejohn, Iain. "Manchurian plague, 1910–11". Disaster History. Archived from the original on 8 March 2018. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ a b Ochman, Sophie; Roser, Max (9 November 2017). "Polio (graph "Reported paralytic polio cases and deaths in the United States since 1910")". Our World in Data. OurWorldInData.org. Archived from the original on 28 March 2018. Retrieved 15 May 2020.
- ^ a b c "Pandemic Influenza Risk Management WHO Interim Guidance" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2013. p. 19. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-01-21. Retrieved 7 December 2020.
- ^ P. Spreeuwenberg; et al. (1 December 2018). "Reassessing the Global Mortality Burden of the 1918 Influenza Pandemic". American Journal of Epidemiology. 187 (12): 2561–2567. doi:10.1093/aje/kwy191. PMC 7314216. PMID 30202996.
- ^ Borza, T. (2001-12-10). "[Spanish flu in Norway 1918-19]". Tidsskrift for den Norske Laegeforening. 121 (30): 3551–3554. ISSN 0029-2001. PMID 11808016. Archived from the original on 2020-08-20. Retrieved 2020-12-30.
- ^ Patterson KD (1993). "Typhus and its control in Russia, 1870–1940". Med Hist. 37 (4): 361–381 [378]. doi:10.1017/s0025727300058725. PMC 1036775. PMID 8246643.
- ^ Ravenholt, R. T; Foege, WilliamH (1982-10-16). "1918 Influenza, Encephalitis Lethargica, Parkinsonism". The Lancet. Originally published as Volume 2, Issue 8303. 320 (8303): 860–864. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(82)90820-0. ISSN 0140-6736. PMID 6126720. S2CID 45138249. Archived from the original on 2021-07-12. Retrieved 2020-12-23.
- ^ McCall, Sherman; Vilensky, Joel A; Gilman, Sid; Taubenberger, Jeffery K (May 2008). "The relationship between encephalitis lethargica and influenza: A critical analysis". Journal of Neurovirology. 14 (3): 177–185. doi:10.1080/13550280801995445. ISSN 1355-0284. PMC 2778472. PMID 18569452.
- ^ Foster, Harold D.; Hoffer, Abram (1 January 2007). "Hyperoxidation of the Two Catecholamines, Dopamine and Adrenaline: Implications for the Etiologies and Treatment of Encephalitis Lethargica, Parkinson's Disease, Multiple Sclerosis, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, and Schizophrenia". Chapter 16 – Hyperoxidation of the Two Catecholamines, Dopamine and Adrenaline: Implications for the Etiologies and Treatment of Encephalitis Lethargica, Parkinson's Disease, Multiple Sclerosis, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, and Schizophrenia. Elsevier Science B.V. pp. 369–382. doi:10.1016/B978-044452809-4/50157-5. ISBN 9780444528094. Archived from the original on 24 February 2020. Retrieved 11 February 2020.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ Viseltear A.J. (March 1974). "The Pneumonic Plague Epidemic of 1924 in Los Angeles". Yale J. Biol. Med. 47 (1): 40–54. PMC 2595158. PMID 4596466.
- ^ Nelson, Paul (2018-01-02). "Smallpox Epidemic, 1924–1925". MNopedia. Archived from the original on 2014-11-04. Retrieved 2019-07-25.
- ^ Berger, Stephen (20 January 2017). Typhoid and Enteric Fever: Global Status: 2017 edition. GIDEON Informatics, Incorporated. ISBN 9781498816878. Archived from the original on 6 January 2024. Retrieved 16 May 2020.
- ^ Honigsbaum, Mark (2020). "3. The Great Parrot Fever Pandemic". The Pandemic Century: One Hundred Years of Panic, Hysteria and Hubris (PDF). London: Hurst & Company. pp. 67–98. ISBN 9781787381216. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-07-12. Retrieved 2020-06-27.
- ^ Ravenel, Mazÿk P. (May 1938). "The Croydon Epidemic of Typhoid Fever". American Journal of Public Health and the Nation's Health. 28 (5): 644–646. doi:10.2105/AJPH.28.5.644. PMC 1529192. PMID 18014847.
- ^ Professor Joan McMeeken (University of Melbourne) (2018-01-18). "Remembering Australia's polio scourge". Pursuit. Archived from the original on 2020-07-24. Retrieved 2020-07-26.
- ^ "Yellow Fever in Sudan" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 February 2021. Retrieved 13 May 2020.
- ^ a b c Gallagher, Nancy. Egypt's Other Wars: Epidemics and the Politics of Public Health. Syracuse University Press, c1990. American University in Cairo Press. ISBN 977-424-295-5 pp. 4–6
- ^ Shousha AT (1948). "Cholera Epidemic in Egypt (1947): A Preliminary Report". Bull. World Health Organ. 1 (2): 353–81. PMC 2553924. PMID 20603928.
- ^ a b William E. Paul (2008). Fundamental Immunology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-6519-0. Archived from the original on 2 July 2014. Retrieved 29 March 2011.
- ^ a b "Report of the Review Committee on the Functioning of the International Health Regulations (2005) in relation to Pandemic (H1N1) 2009" (PDF). 2011-05-05. p. 37. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 May 2015. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ Lilay, Abrham; Asamene, Negga; Bekele, Abyot; Mengesha, Mesfin; Wendabeku, Milliyon; Tareke, Israel; Girmay, Abiy; Wuletaw, Yonas; Adossa, Abate; Ba, Yamar; Sall, Amadou; Jima, Daddi; Mengesha, Debritu (15 May 2017). "Reemergence of yellow fever in Ethiopia after 50 years, 2013: epidemiological and entomological investigations". BMC Infectious Diseases. 17 (1): 343. doi:10.1186/s12879-017-2435-4. PMC 5432991. PMID 28506254. S2CID 21276606.
- ^ J. N. Hays (2005). Epidemics and pandemics: their impacts on human history. ABC-CLIO. p. 421. ISBN 978-1-85109-658-9. Retrieved 29 March 2011.
- ^ "Polio in Staphorst". anderetijden (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 20 April 2020. Retrieved 15 May 2020.
- ^ Ehrengut W (1974). "[Smallpox in Yugoslavia in 1972 (author's transl)]". Med Klin. 69 (8): 350–352. PMID 4826683.
- ^ "New, Deadly Flu Strain Detected in Albany Co". Schenectady Gazette. Associated Press. January 24, 1975. p. 3. Archived from the original on May 22, 2022. Retrieved August 3, 2012.
- ^ De Lorenzo F.; Manzillo G.; Soscia M.; Balestrieri G.G. (1974). "Epidemic of Cholera el Tor in Naples, 1973". The Lancet. 303 (7859): 669. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(74)93214-0. PMID 4132328.
- ^ "The control and eradication of smallpox in South Asia". www.smallpoxhistory.ucl.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 2008-10-19. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ^ Michaelis, Martin; Doerr, Hans Wilhem; Cinatl, Jindrich (2009-08-01). "Novel swine-origin influenza A virus in humans: another pandemic knocking at the door". Medical Microbiology and Immunology. 198 (3): 175–183 (Table 1). doi:10.1007/s00430-009-0118-5. ISSN 1432-1831. PMID 19543913. S2CID 20496301.
- ^ "You're more likely to die from the H1N1 flu if you were born in 1957". University of Montreal. 2020-11-18. Archived from the original on 2019-01-31. Retrieved 2021-01-24.
- ^ Meselson, Matthew; Guillemin, J; Hugh-Jones, Martin; Langmuir, A; Popova, I; Shelokov, A; Yampolskaya, O (1994-12-01). "The Sverdlovsk anthrax outbreak of 1979". Science. 266 (5188): 1202–8. Bibcode:1994Sci...266.1202M. doi:10.1126/science.7973702. PMID 7973702. Archived from the original on 2021-07-12. Retrieved 2020-07-31.
- ^ "Global HIV and AIDS statistics". UNAIDS. Archived from the original on 2019-12-04. Retrieved 2021-08-23.
- ^ De Cock KM; Monath TP; Nasidi A; Tukei PM; Enriquez J; Lichfield P; Craven RB; Fabiyi A; Okafor BC; Ravaonjanahary C (1988). "Epidemic yellow fever in eastern Nigeria, 1986". Lancet. 1 (8586): 630–3. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91425-0. PMID 2894558. S2CID 31563771.
- ^ "Yellow fever in Mali". who.int. Archived from the original on January 9, 2005. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ Cooksley, W. G. (May 2000). "What did we learn from the Shanghai hepatitis A epidemic?". Journal of Viral Hepatitis. 7 (Suppl 1): 1–3. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2893.2000.00021.x. ISSN 1352-0504. PMID 10870174. S2CID 34673718. Archived from the original on 2021-08-04. Retrieved 2021-08-04.
- ^ "City getting tougher on blood clam ban". Shanghai Daily. 2013-07-23. Archived from the original on 2019-07-19. Retrieved 2021-08-04.
- ^ Halliday, Mabel L.; Kang, Lai-Yi; Zhou, Ting-Kui; Hu, Meng-Dong; Pan, Qi-Chao; Fu, Ting-Yuan; Huang, Yu-Sheng; Hu, Shan-Lian (1991). "An Epidemic of Hepatitis A Attributable to the Ingestion of Raw Clams in Shanghai, China". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 164 (5): 852–859. doi:10.1093/infdis/164.5.852. ISSN 0022-1899. JSTOR 30111993. PMID 1658157. Archived from the original on 2023-07-02. Retrieved 2021-08-04.
- ^ Summary of cholera cases and deaths reported in the literature, by date, country and World Health Organization (WHO) mortality stratum Mohammad Ali, Anna Lena Lopez, Young Ae You, Young Eun Kim, Binod Sah, Brian Maskery & John Clemens, Bulletin of the World Health Organization, Volume 90, Number 3, March 2012, 209-218A www.who.int, accessed 4 May 2020
- ^ Tickner, Joel; Gouveia-Vigeant, Tami (June 2005). "The 1991 Cholera Epidemic in Peru: Not a Case of Precaution Gone Awry". Risk Analysis. 25 (3): 495–502. Bibcode:2005RiskA..25..495T. doi:10.1111/j.1539-6924.2005.00617.x. PMID 16022685. S2CID 15792284.
- ^ "Cholera in the Americas". Bulletin of the Pan American Health Organization. 25 (3): 267–273. 1991. ISSN 0085-4638. PMID 1742573.
- ^ Dutt, Ashok (2006). "Surat Plaque of 1994 re-examined" (PDF). Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health. 37 (4): 755–760. PMID 17121302. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 February 2016. Retrieved 19 June 2016.
- ^ "'Mad cow disease': What is BSE?". BBC. 18 October 2018. Archived from the original on 3 May 2020. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ "Variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease, Current Data (July 2012)". The National Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease Surveillance Unit (NCJDSU), University of Edinburgh. Archived from the original on 21 July 2012. Retrieved 20 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link); - ^ Wide Epidemic of Meningitis Fatal to 10,000 in West Africa Archived 2023-07-11 at the Wayback Machine Eoward W. French, 8 May 1996 www.nytimes.com, accessed 26 April 2020
- ^ Lai-Meng Looi; Kaw-Bing Chua (2007). "Lessons from the Nipah virus outbreak in Malaysia" (PDF). The Malaysian Journal of Pathology. 29 (2). Department of Pathology, University of Malaya and National Public Health Laboratory of the Ministry of Health, Malaysia: 63–7. PMID 19108397. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 August 2019.
- ^ a b "Outbreak Table | Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever | CDC". Archived from the original on 2015-01-21. Retrieved 2021-08-13.
- ^ "Dengue in the Americas: The Epidemics of 2000". Archived from the original on 2017-10-17. Retrieved 2008-08-05.
- ^ "Nigeria cholera outbreak kills 400". 2001-11-26. Archived from the original on 19 December 2003. Retrieved 16 November 2014.
- ^ "Cholera Spreads Through South Africa Townships". Archived from the original on 3 June 2009. Retrieved 16 November 2014.
- ^ 2001 – Cholera in South Africa 16 March 2001 www.who.int, accessed 28 April 2020
- ^ "WHO | Summary of probable SARS cases with onset of illness from 1 November 2002 to 31 July 2003". Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Retrieved 5 April 2020.
- ^ "Cumulative number of confirmed human cases for avian influenza A(H5N1) reported to WHO, 2003 – 2020" (PDF). 8 May 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 June 2020. Retrieved 4 January 2020.
- ^ Dengue fever in Indonesia – update 4 11 May 2004 www.who.int, accessed 16 February 2020
- ^ a b "Ebola virus disease" (Press release). World Health Organization (WHO). 12 February 2018. Archived from the original on 18 April 2018. Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- ^ Koh, B. K.; Ng, L. C.; Kita, Y.; Tang, C. S.; Ang, L. W.; Wong, K. Y.; James, L.; Goh, K. T. (2008). "The 2005 dengue epidemic in Singapore: Epidemiology, prevention and control" (PDF). Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore. 37 (7): 538–545. doi:10.47102/annals-acadmedsg.V37N7p538. PMID 18695764. S2CID 31640849. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-07-06. Retrieved 2018-10-17.
- ^ Worst cholera outbreak in Angola Archived 2017-04-29 at the Wayback Machine, BBC
- ^ Plague in the Democratic Republic of the Congo 14 June 2006 www.who.int, accessed 26 February 2020
- ^ Plague in the Democratic Republic of the Congo 13 October 2006 www.who.int, accessed 26 February 2020
- ^ "Malaria Epidemic Sweeps Northeast India". Archived from the original on 2017-02-03. Retrieved 2008-07-01.
- ^ "Dengue epidemic threatens India's capital". News-Medical.net. 2 October 2006. Archived from the original on 15 January 2009. Retrieved 16 November 2014.
- ^ Khan, E.; Siddiqui, J.; Shakoor, S.; Mehraj, V.; Jamil, B.; Hasan, R. (2007). "Dengue outbreak in Karachi, Pakistan, 2006: Experience at a tertiary care center". Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 101 (11): 1114–1119. doi:10.1016/j.trstmh.2007.06.016. PMID 17706259.
- ^ Epidemiology of Dengue Disease in the Philippines (2000–2011): A Systematic Literature Review Archived 2023-07-11 at the Wayback Machine November 2014 PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases via www.researchgate.net, accessed 16 February 2020
- ^ Rift Valley fever Archived 2021-10-09 at the Wayback Machine 19 February 2018 www.who.int, accessed 26 April 2020
- ^ "Mourners die as fever grips Congo." Archived 2012-10-23 at the Wayback Machine Sydney Morning Herald, August 30, 2007
- ^ Xan Rice (2007-02-22). "Fatal outbreak not a cholera epidemic, insists Ethiopia". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 26 October 2017. Retrieved 16 November 2014.
- ^ Cholera outbreak in Iraq growing Archived 2017-02-04 at the Wayback Machine, Associated Press
- ^ Dengue fever epidemic hits Caribbean, Latin America Archived 2009-08-03 at the Wayback Machine, Reuters
- ^ "Q-koorts nog niet voorbij: In totaal al 95 doden". nu.nl (in Dutch). 3 November 2018. Archived from the original on 9 February 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ Thousands hit by Brazil outbreak of dengue Archived 2023-07-11 at the Wayback Machine edition.cnn.com, accessed 16 February 2020
- ^ Cambodia suffers worst dengue epidemic, 407 dead Archived 2009-11-11 at the Wayback Machine, Reuters
- ^ "Cholera epidemic in western Chad kills 123". 2004-09-02. Archived from the original on 2009-01-12. Retrieved 2008-06-08.
- ^ Huang, Jiao; Liao, Qiaohong; Ooi, Mong How; Cowling, Benjamin J.; Chang, Zhaorui; Wu, Peng; Liu, Fengfeng; Li, Yu; Luo, Li; Yu, Shuanbao; Yu, Hongjie; Wei, Sheng (2018). "Epidemiology of Recurrent Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease, China, 2008–2015". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 24 (3): 432–442. doi:10.3201/eid2403.171303. PMC 5823341. PMID 29460747.2008–2015, ≈13 million HFMD cases were reported, including 123,261 severe cases and 3,322 deaths in 31 provinces of mainland China
- ^ Cholera death toll in India rises Archived 2017-11-11 at the Wayback Machine, BBC News
- ^ "Madagascar: eighteen dead from Bubonic Plague, five in hospital since 1 January 2008". Archived from the original on May 9, 2009.
- ^ "Dengue cases in Philippines rise by 43 percent: government". Archived from the original on 17 October 2017. Retrieved 16 November 2014.