Malvidin
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
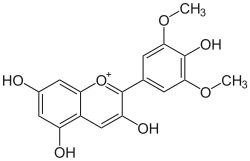 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 3,4′,5,7-Tetrahydroxy-3′,5′-dimethoxyflavylium | |
| Systematic IUPAC name 3,5,7-Trihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxy)-1λ4-benzopyran-1-ylium | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H15O7+ | |
| Molar mass | 331.2968 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Malvidin is an O-methylated anthocyanidin, the 3',5'-methoxy derivative of delphinidin. As a primary plant pigment, its glycosides are highly abundant in nature.
Natural occurrences
[edit]Malvidin is responsible for the blue color found in petals of the Primula plants of the polyanthus group. Blue flowers of the blue pimpernel (Anagallis monelli) have also a higher concentration of malvidin.
It is responsible primarily for the color of red wine, Vitis vinifera being one of its sources.[1] It is also present in other berries, such as blueberries (Vaccinium corymbosum) or the saskatoon berries (Amelanchier alnifolia).[2][3]
Chemistry
[edit]Slightly acidic and neutral solutions of malvidin are characteristically of a red color, while basic solutions of malvidin yield a blue color.
The breakdown of malvidin releases syringic acid.
Use as a marker in archaeology
[edit]The breakdown of malvidin releases syringic acid as revealed in the examination of jars containing shedeh, a drink of Ancient Egypt. Malvidin is also present in the site of the Areni-1 winery, a 6,100-year-old winery discovered in 2007 in the Areni-1 cave complex in the village of Areni in the Vayots Dzor province of Armenia.
Glycosides
[edit]- Malvin is a malvidin diglucoside.
- Oenin is the malvidin-3-glucoside.
- Primulin is the 3-O-galactoside of malvidin.
- Malvidin 3-rutinoside is a pigment responsible for bract color in Curcuma alismatifolia (the Siam tulip).[4] Acylated malvidin 3-rutinosides are responsible for the violet color of Petunia integrifolia subsp. inflata.[5]
- Malvidin-3-O-glucoside-5-O-(6-acetylglucoside) is a pigment responsible for the blue color in 'Johnson's Blue' and other 'blue' geraniums[6]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Phytochemicals: Malvidin". Top Cultures. Archived from the original on April 1, 2010. Retrieved 2009-05-20.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Mazza G (2005). "Compositional and functional properties of saskatoon berry and blueberry". International Journal of Fruit Science. 5 (3): 99–118. doi:10.1300/J492v05n03_10.
- ^ Bakowska-barczak; Marianchuk, M; Kolodziejczyk, P (2007). "Survey of bioactive components in Western Canadian berries". Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology. 85 (11): 1139–52. doi:10.1139/y07-102. PMID 18066116.
- ^ Nakayama, M; Roh, MS; Uchida, K; Yamaguchi, Y; Takano, K; Koshioka, M (2000). "Malvidin 3-rutinoside as the pigment responsible for bract color in Curcuma alismatifolia". Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry. 64 (5): 1093–5. doi:10.1271/bbb.64.1093. PMID 10879491.
- ^ Tatsuzawa, F (1999). "Acylated malvidin 3-rutinosides in dusky violet flowers of Petunia integrifolia subsp. Inflata". Phytochemistry. 52 (2): 351–355. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(99)00095-3.
- ^ Markham, Kenneth R.; Mitchell, Kevin A.; Boase, Murray R. (1997). "Malvidin-3-O-glucoside-5-O-(6-acetylglucoside) and its colour manifestation in 'Johnson's Blue' and other 'Blue' geraniums". Phytochemistry. 45 (2): 417–423. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(96)00831-X.