Max Brödel
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
Max Brödel | |
|---|---|
 Photograph of Max Brödel by Doris Ulmann | |
| Born | 8 June 1870 |
| Died | 26 October 1941 (aged 71) |
| Nationality | German |
| Education | Leipzig Academy of Fine Arts |
| Known for | Medical Illustration |
| Spouse | Ruth Huntington |
| Children | 4, including Elizabeth H. |
| Signature | |
Max Brödel (June 8, 1870 – October 26, 1941) was a medical illustrator. Born in Leipzig, Germany, he began his artistic career after graduating from the Leipzig Academy of Fine Arts, working for Carl Ludwig. Under Ludwig's instruction, Brödel gained a basic knowledge of medicine and became recognized for his detailed medical illustrations. In the late 1890s, he was brought to the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore to illustrate for Harvey Cushing, William Halsted, Howard Kelly, and other notable clinicians. In addition to being a prolific medical illustrator, he developed new artistic techniques such as the carbon dust technique that helped the advancement of the quality and accuracy of medical illustrations for physicians. In 1911, he presided over the creation of the first Department of Art as Applied to Medicine; located at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, it continues to train medical illustrators to this day. His graduates spread out across the world, and have founded a number of other academic programs.
Biography[edit]
Early life and education[edit]
Max Brödel was born on June 8, 1870, in Leipzig, Germany, to Louis Brödel and Henrietta Frenzel Brödel. From the early age of 6, he took piano lessons and by 12, he was playing Beethoven. Not only was he musically inclined, he was also artistically inclined. At age 15, Brödel began to develop his artistic abilities at the Leipzig Academy of Fine Arts in a program for painting and drawing, where he learned artistic techniques reflecting the 19th-century arts education with an emphasis on the development of fine, precise drawings[1][2] This meticulous attention to detail and accuracy was one of the skills that Brödel was later praised for in his medical illustrations. Over the summers, he put his artistic skills to use with part-time jobs drawing landscapes and figures. When Brödel was 18, Carl Ludwig, a famous physiologist of the 19th century, hired Brödel to draw a 150x magnified cortex of the brain. This was his first experience with medical illustrations, which he would make his lifelong career.[3]
Personal life[edit]
Marriage and family[edit]
Brödel was introduced to fellow artist, medical illustrator, and future wife, Ruth Huntington, by Howard Kelly. A graduate of zoology and botany from Smith College, Ruth also received Franklin P. Malls' invitation and had begun illustrating for Charles Bardeen as part of the Hopkins Anatomy Department in 1900.[4] The pair realized their similar musical and artistic interests and married shortly afterwards on December 31, 1902. They lived in the Guilford neighborhood of Baltimore at 320 Suffolk Road.[5] They had four children together: Elizabeth (born October 9, 1903), Ruth (born April 23, 1905), Carl (born June 7, 1908), and Elsa (born February 8, 1911). Ruth suffered from scarlet fever as a child and died on June 1, 1908.[6] Elizabeth later followed her father's footsteps and became a medical illustrator for New York Hospital, and Carl became a geology professor at Johns Hopkins University.[7][8]
Known for his jovial, fun-loving personality, Brödel became close friends with H. L. Mencken, an American journalist and satirist. In 1913, he was invited to join the Saturday Night Club, a group of musicians and intellectuals that played music together, to share drinks.[9] In his free time, he enjoyed hunting trips in the forests of Canada, fishing, and playing the piano.[10] Outside of his profession, he also occasionally made drawings from nature.[4]
Early career[edit]
Despite his minimal scientific background and lack of medical knowledge, Brödel and his artistic potential were well received by esteemed German physician and physiologist, Carl Ludwig. Under Ludwig's mentorship and guidance at the Anatomical Institute at the Institute of Physiology at the University of Leipzig, Brödel was employed with drawing detailed gross anatomical and histological diagrams. Honing his observational skills with detailed notes of the numerous surgeries and autopsies he observed, Brödel's work was credited for topographical accuracy, tissue realism, and attention to the cross-sectional anatomy.[2] Another noticeable feature of his illustrations was the aerial perspective that showed the anatomy as seen through a surgeon's eyes.[11] Some of his early illustrations were also for physicians Spalteholz, His and Braune.[11] His network of medical professionals increased when he met Franklin P. Mall of Johns Hopkins Hospital in 1888.[4]
Brödel's artistic career was briefly suspended when he was drafted to serve two years on November 8, 1890.[4] Through the auspices of Geheimrat Carl Ludwig, Prince George of Saxony, Brödel served his first year with arms, and the second year with artistic pursuits for the regiment. Upon return to Leipzig after his service, Brödel continued his work as a free-lance artist, specializing in anatomical and scientific illustrations. During this time, Brödel accepted Mall's invitation to illustrate at Johns Hopkins Hospital.[4]
Career at Johns Hopkins University[edit]
Brödel arrived at Johns Hopkins in the winter of January 18, 1894. From here, Brödel had received internal acclaim through his employment by Howard Kelly as the illustrator for Operative Genecology.[12] Highly sought after by anatomist Franklin P. Mall and other physicians for his meticulous attention to detail and realism in his medical illustrations, Brödel's skills were a valuable asset to the Johns Hopkins Hospital. Shortly after his employment, Brödel was joined by fellow medical illustrators, Hermann Becker and August Horn, both of whom had also attended the Leipzig Academy of Fine Arts. Working in conjunction with these two artists, Brödel created an extensive catalog of gross and histological diagrams for the medical staff, including Howard A. Kelly, William S. Halsted, and Thomas S. Cullen, who had proposed Brödel's training of students in medical illustration.[4][11][12] Students of Brödel included Aime M. Awl.[13]
Work with Howard Kelly[edit]
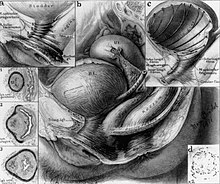
The majority of Brödel's illustrations were for Howard A. Kelly, the Chief of Gynecology, during his employment at Johns Hopkins Hospital. Brödel illustrated for Kelly's two-volume textbook, Operative Gynecology, which was published in 1898. Its release garnered widespread praise and recognition, cemented Kelly's preeminent status in the field of gynecology, and established Brödel's role as a pioneering medical illustrator. Brödel then went on to work on other books authored or co-authored by Kelly, including those on diseases of the kidneys, ureters and bladder, as well as Kelly's journal articles and monographs.[6] Throughout the illustrative process, Brödel worked closely with Kelly, conferring with each other before the first sketch was drawn. After debriefing, with Kelly, Brödel painstakingly conducted independent medical research and experimented to find the best method to communicate information about complex structures to medical professionals. For example, when Kelly asked for some anatomical data about the blood supply of the kidney, Brödel went to the Pathological Laboratories, got a kidney from the autopsies and washed it out by attaching it by a tube to the tap. Then, he filled the arteries with red paint, the veins with blue, and the ureter with yellow. Using the digesting method he had observed Frank Mall use in Carl Ludwig's laboratory in Germany, he could see various sections of the kidney that resembled a tree branch with small apples lining them, which were the glomeruli of the kidney. Brödel also noticed an avascular area and suggested cutting along this line when looking for kidney stones. He developed what is referred today as Brödel's suture, which can be used to repair a prolapsed kidney.[3][14]
Brödel's underlying artistic philosophy is best described in his own words: “The artist must first fully comprehend the subject matter from every standpoint: anatomical, topographical, histological, pathological, medical, and surgical. From this accumulated knowledge grows a mental picture from which again crystallizes the plan for the future drawing. A clear and vivid mental picture must always precede the actual picture on paper. The planning of the picture, therefore, is the all important thing, not the execution.”[4] He developed a technique where he examined every medical sample under a microscope at low, medium, and high (magnification of x40, 100, 400) power to form a complete picture of it in his mind. Just two months prior to his death, he wrote in a journal article that “the artist must know his subject so thoroughly that he can even shut his eyes and coax into existence a mental picture of great clarity.”[15] His emphasis on anatomically accurate visualization prior to artistic actualization was manifested in his incredibly lifelike renderings.
The seamless translation of medical knowledge into his illustrations is credited with his strong investigative drive. Brödel understood the essential role medical illustrations played in teaching medical students the complexities and functions of anatomical structures, and was therefore keen on educating himself by poring over medical texts, attending lectures, and dissecting cadavers.[16] In a bulletin to Johns Hopkins, Brödel wrote "No drawing was made by me without original study through injection, dissection, frozen section, or reconstruction.[15]
Other medical fields he worked extensively in are Otolaryngology, Urology, and Neurosurgery.[16][17][18]
Setbacks[edit]
On March 24, 1899, Brödel was diagnosed with a streptococcus infection on his hand and arm, caused by improper practice of handling anatomical dissections without gloves.[4] He required several operations on his left arm, including one to separate nerve fibers from the scar tissue. These operations were performed by William S. Halsted, Chief of Surgery at Johns Hopkins Hospital. Capitalizing on this experience, Brödel illustrated and detailed his medical condition and the resulting numbness of his nondominant left hand. Despite encouragement by Halsted, these drawings remained unpublished.[4]
In December 1904, Brödel sustained severe injuries to the middle finger of his right hand. Another Johns Hopkins physician, John Miller Turpin Finney, was able to help recover normal functioning, allowing Brödel to continue his artistic and musical pursuits.[4]
War years[edit]
With the onset of World War I, Brödel experienced alienation and disillusion living amongst anti-German sentiment in the United States along with his mother's declining health back in Germany. Henriette Brödel would end up dying November 2, 1915, and Max would become more introverted as the years went on, realizing he had overestimated the amount of importance and growth his medical illustration training program was to receive, expecting it to grow in stature in ways it never did.
Brödel's program was to be plagued by low student enrollment during the war years and the persistent troubles of meager compensation in the profession of medical illustration, with two of his pupils turning down offers to work with Brödel's former colleague Harvey Cushing, now at Harvard Medical School, over the issue of salary.[6]
Death[edit]
Brödel died on October 26, 1941, of pancreatic cancer in Baltimore, Maryland.[16] Approximately two months before he died, he had published a paper in the Journal of the American Medical Association titled "Medical Illustration." This provided a first-hand account and insight into his long illustrative career.[4] A few months after his death, an intensive study of the human ear was published, in which two of the series of three drawings had been completed by Brödel and the third, being preliminary sketches at the time of his death, was later completed by P. D. Malone.[19]
Legacy[edit]
Carbon dust technique[edit]
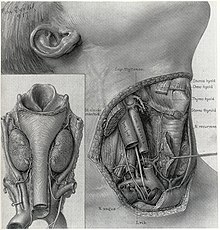
Brödel is credited with the development of the carbon dust technique for medical and scientific illustrations. He had been looking for an acceptable medium able to show the vividness and detail characteristic of living tissue, and made the breakthrough using clay-surfaced lithographic transfer paper.[20] Using a wide variety of media, realistic multi-dimensional representations of complex anatomical structures are able to be constructed. The dust is made by shaving carbon pencils against abrasive surfaces, and then applying this fine dust onto textured, calcium-coated paper with dry brushes. Increasing the depth and dimension of the image, the carbon dust technique was able to add highlights, shadows, and texture to Brödel's work. Due to the limitations of the black and white printing era, the relative ease of reprinting artwork created with carbon dust made this a highly suitable technique for a wide variety of scientific illustrations.[21] Popularized in the 1900s, this method is applied with various different materials and techniques, but the same principles are still used today. This is because of its ability to capture a remarkable amount of fine visual detail, as well as a bridge allowing for close collaboration with physicians.[22]
Department of Art as Applied to Medicine[edit]
In 1910, Brödel received an inviting offer for a position at the Mayo Clinic. Gynecologist and close friend of Brödel, Thomas S. Cullen, began raising funds for a department where Brödel could remain content at Johns Hopkins and train the next generation of medical illustrators with the necessary skills and background.[20] Henry Walters, a Baltimore financier, philanthropist and art collector, agreed to fund the creation of this endeavor.[23] In 1911, Brödel became the inaugural director for the Department of Art as Applied to Medicine at Johns Hopkins. His goal was to train medical illustrators to work in conjunction with physicians to increase understanding of how the body works. The program was the first medical illustration program, and attracted both medical and art students from all around the world.[24]
In an article published in the September 1911 edition of The Johns Hopkins Hospital Bulletin, Brödel laid out his case for the creation of the department. “Its purpose,” he wrote, “is to bridge over the gap existing between art and medicine, and to train a new generation of artists to illustrate medical journals and books in the future and to spare them the years of trial and disappointment of their self-taught predecessors.”[25]
The Department of Art as Applied to Medicine is still recognized for their excellence in visual communication in science and medicine. Many former students at the Department of Art as Applied to Medicine would later make up a large percentage of the founding members of the Association of Medical Illustrators, which began in 1945.[20] Several notable artists who were heavily influenced by Brödel include the following:[20]
- Annette Smith Burgess – Taught by Brödel at the Maryland Institute College of Art, she became the first medical illustrator at the Wilmer Eye Institute at Johns Hopkins.[26]
- Elizabeth Brödel - She was one of Max Brödel's daughters who worked at the Woman's Clinic in the New York Hospital and later became the first elected Treasurer for the Association of Medical Illustrators.[27]
- James F. Didusch - He was the first student under Max Brödel from 1911 to 1913 and worked as the illustrator for the Carnegie Institute of Embryology at Johns Hopkins University until his death in 1955.[28]
- Dorcas Hager Padget - She was a self-taught artist who received training from Max Brödel before working for neurosurgeon Walter Dandy and eventually became a scientific researcher at the Department of Embryology at the Carnegie Institution of Washington and later at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.[29]
- Muriel McLatchie - She was another student of Max Brödel at Johns Hopkins University. In the early 1930s she went to Boston and later established a department of Medical Art at the Massachusetts General Hospital. McLatchie was also one of the founding members of the Association of Medical Illustrators.[27]
- Leon Schlossberg - After graduating from City College and studying Max Brödel's work at the Maryland Institute College of Art, he sought out mentorship from Max Brödel. From 1942 to 1946, he worked at the Bethesda Naval Hospital and then became a professor at the Johns Hopkins University teaching anatomical sketching for more than fifty years until his death in 1999.[30]
Institutions that have been influenced by Brödel's work in medical illustrations include the Wilmer, Brady, Mayo and Lahey clinics, the American Museum of Natural History, and Yale, Minnesota, Rochester, Toronto and Tulane Universities.[31]
Notable textbooks[edit]
- Operative Gynecology (Vols. I&II), (New York: D. Appleton and company, 1898), Howard A. Kelly
- Gynecology, (New York, London: D. Appleton and Company, 1928), Howard A. Kelly
- Medical Gynecology, (New York: Appleton, 1908), Howard A. Kelly
- "The Vermiform Appendix and Its Diseases" The Indian Medical Gazette 41, no. 2 (February 1906): 70–71. Kelly, and Elizabeth Herndon.
- Gynecology and Abdominal Surgery (Vols. I&II) (Philadelphia and London: W. B. Saunders company, 1907), Howard A. Kelly and Charles P. Noble
- Myomata of the Uterus, (Philadelphia: Saunders, 1909), Howard A. Kelly and Thomas Stephen Cullen
- Diseases of the Kidneys, Ureters and Bladder (Vols. I&II), Howard A. Kelly and Charles Burnham
Johns Hopkins Hospital[edit]
In 1938, a portrait of Brödel by artist Thomas C. Corner, was presented and displayed in the halls of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine alongside portraits of medical pioneers, William Osler, William Stewart Halsted, Howard Atwood Kelly, and William H. Welch.[11] This display of recognition was initiated by the vice president of the W.B. Saunders medical publishing company, Mr. R.W. Greene.
Brödel Archives[edit]
The majority of Brödel's illustrations and his uncompleted manuscript are housed in the Brödel archives located at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.[2] Visitors and researchers are allowed to reproduce a selection of his works with special permission. All of Brödel's work for Kelly and Thomas S. Cullen are numbered from 1 to 989.
See also[edit]
- Medical Illustration
- Association of Medical Illustrators
- Johns Hopkins School of Medicine
- Johns Hopkins Hospital
References[edit]
- ^ Pace-Asciak, P.; Gelfand, T. (2007-08-01). "38. Max Brodel (1870-1941): His artistic influence on surgical learning at Johns Hopkins Medical School". Clinical and Investigative Medicine. 30 (4): 47. doi:10.25011/cim.v30i4.2798. ISSN 1488-2353.
- ^ a b c Medicine, Faculty of. "Max Brodel (1870-1941): His Artistic Influence on Surgical Learning at Johns Hopkins Medical School". www.med.uottawa.ca. Retrieved 2017-04-23.
- ^ a b THIERY M (2006-01-01). "Max Brödel (1870-1941) en de Brödel-operatie". Tijdschrift voor Geneeskunde. 62 (4): 333–335. doi:10.2143/tvg.62.4.5002407. ISSN 0371-683X.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Cullen, Thomas S. (2017-04-23). "Max Brödel, 1870-1941 Director of the First Department of Art as Applied to Medicine in the World". Bulletin of the Medical Library Association. 33 (1): 4.1–29. ISSN 0025-7338. PMC 200894.
- ^ "Notable Residents — the Arts and Letters" (PDF). GuilfordAssociation.org. Summer 2019. Retrieved April 11, 2024.
- ^ a b c Crosby, Ranice (1991). Max Brödel: The Man Who Put Art Into Medicine. Springer. ISBN 0-387-97563-2.
- ^ "45555a, 1886-03-24, A residence, Lowndes Street; [EASTON], [MIDDLETON], [NEWDEGATE], and others". doi:10.1163/2210-7886_asc-45555a.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Crosby, Ranice W. (1991). Max Brödel : the man who put art into medicine. Cody, John, 1925-. New York: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-97563-2. OCLC 23902250.
- ^ "Max Brodel". Johns Hopkins Magazine. Retrieved 2017-03-27.
- ^ Cullen, Thomas (1945). "Max Brödel, 1870-1941, Director of the First Department of Art as Applied to Medicine in the World". Bulletin of the Medical Library Association. 33 (1): 4.1–29. PMC 200894.
- ^ a b c d "Max Brodel and Medical Illustration". Journal of the American Medical Association. 110 (11): 817. 1938-03-12. doi:10.1001/jama.1938.02790110043013. ISSN 0002-9955.
- ^ a b Morman, Edward T. (February 2000). Brödel, Paul Heinrich Max (18 June 1870–26 October 1941), medical illustrator and anatomist. American National Biography Online. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/anb/9780198606697.article.1200107.
- ^ Rosencrantz, Pat (1960-10-14). "Local Woman's Scientific Illustrations In Britannica". The News (Frederick, Maryland). p. 1. Retrieved 2023-01-10.
- ^ Schultheiss, Dirk; Engel, Rainer M.; Crosby, Ranice W.; Lees, Gary P.; Truss, Michael C.; Jonas, Udo (October 2000). "Max Brödel (1870-1941) and Medical Illustration in Urology". Journal of Urology. 164 (4): 1137–1142. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(05)67128-5. ISSN 0022-5347. PMID 10992353.
- ^ a b "45555a, 1886-03-24, A residence, Lowndes Street; [EASTON], [MIDDLETON], [NEWDEGATE], and others". doi:10.1163/2210-7886_asc-45555a.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b c Medicine, Faculty of. "Max Brodel (1870-1941): His Artistic Influence on Surgical Learning at Johns Hopkins Medical School". www.med.uottawa.ca. Retrieved 2017-04-23.
- ^ Patel, Smruti K.; Couldwell, William T.; Liu, James K. (July 2011). "Max Brödel: his art, legacy, and contributions to neurosurgery through medical illustration". Journal of Neurosurgery. 115 (1): 182–190. doi:10.3171/2011.1.jns101094. ISSN 0022-3085. PMID 21294618.
- ^ Schultheiss, Dirk; Jonas, Udo (September 1999). "Max Brödel (1870–1941) and Howard A. Kelly (1858–1943) – Urogynecology and the birth of modern medical illustration". European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology. 86 (1): 113–115. doi:10.1016/s0301-2115(99)00028-7. ISSN 0301-2115. PMID 10471153.
- ^ Morman, Edward T. (February 2000). Brödel, Paul Heinrich Max (18 June 1870–26 October 1941), medical illustrator and anatomist. American National Biography Online. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/anb/9780198606697.article.1200107.
- ^ a b c d Crosby, Ranice (1991). Max Brödel: The Man Who Put Art Into Medicine. Springer. ISBN 0-387-97563-2.
- ^ Hodges, Elaine R. S.; (U.S.), Guild of Natural Science Illustrators (1989-01-01). The Guild handbook of scientific illustration. Wiley. ISBN 9780471288961. OCLC 41168198.
- ^ michellekim (2015-10-19). "Biomedical Illustrators: Masters of Art and Science | Biomedical Odyssey". Retrieved 2020-03-25.
- ^ Melloni, Ida Dox (1990). Max Brödel and visual communication: The effect of the Hopkins intellectual context in the genesis of modern medical illustration. University of Maryland College Park: UMI.
- ^ Wolff, M.; Radwan, Hildegard (1997-08-01). "Max Brödel (1870–1941): his life and his role in the development of surgery". Der Chirurg. 68 (8): 840–847. doi:10.1007/s001040050283. ISSN 1433-0385. PMID 9378000. S2CID 31330006.
- ^ Johns Hopkins Hospital. Bulletin of the Johns Hopkins Hospital. Baltimore: The Hospital, 1891.
- ^ Shaner, Arlene (2017-03-21). "Annette Smith Burgess: Ophthalmological Illustrator". New York Academy of Medicine. Retrieved 2021-05-09.
- ^ a b "History of the AMI". AMI. Retrieved 2020-04-06.
- ^ Altemus, A. R. (1992). "The life and work of James F. Didusch". The Journal of Biocommunication. 19 (2): 8–21. ISSN 0094-2499. PMID 1624478.
- ^ Kretzer, Ryan M.; Crosby, Ranice W.; Rini, David A.; Tamargo, Rafael J. (April 2004). "Dorcas Hager Padget: neuroembryologist and neurosurgical illustrator trained at Johns Hopkins". Journal of Neurosurgery. 100 (4): 719–730. doi:10.3171/jns.2004.100.4.0719. ISSN 0022-3085. PMID 15070132.
- ^ Lyons, Sheridan. "Leon Schlossberg, 87, JHU professor, expert in medical illustration". baltimoresun.com. Retrieved 2020-04-06.
- ^ "Max Brodel and Medical Illustration". Journal of the American Medical Association. 110 (11): 817. 1938-03-12. doi:10.1001/jama.1938.02790110043013. ISSN 0002-9955.
Further reading[edit]
- Ranice W. Crosby; John Cody (1991). Max Brödel: The Man Who Put Art Into Medicine. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 0-387-97563-2.
- Brödel, Max (1946). Three Unpublished Drawings of the Anatomy of the Human Ear. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co.