Pyrone
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia

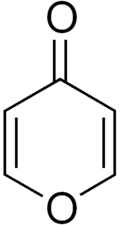
Pyrones or pyranones are a class of heterocyclic chemical compounds. They contain an unsaturated six-membered ring, which has one oxygen atom and a carbonyl functional group.[1] There are two isomers, denoted as 2-pyrone and 4-pyrone. The 2-pyrone (or α-pyrone) structure is a lactone and is found in nature as part of the coumarin ring system. The 4-pyrone (or γ-pyrone) structure is an ether–ketone found in some natural chemical compounds such as chromone, maltol and kojic acid.
See also
[edit]- Furanone, which has one fewer carbon atom in the ring.
- Pyridones, which contain a nitrogen in place of the oxygen that is part of the ring
References
[edit]- ^ Streitwieser, Andrew Jr.; Heathcock, Clayton H. (1985). Introduction to Organic Chemistry (Third ed.). pp. 1038–1040. ISBN 978-0-02-418140-4.