Sikh architecture
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (January 2010) |
Sikh architecture ਸਿੱਖ ਸਥਾਪਤਕ ਕਲਾ Sikh monuments and shrines | |
|---|---|
Cultural and religious architectural style | |
| Sikh Architectural Heritage | |
From top, left to right: Harmandir Sahib (Golden Temple), Amritsar; Gurudwara Bangla Sahib, Delhi; Fatehgarh Sahib Sarovar; Interior of Samadhi of Ranjit Singh, Lahore; Tarn Taran Sahib; Takht Sri Patna Sahib, Bihar; Hazur Sahib, Nanded; Kartarpur Sahib, Pakistan; Fateh Burj; Gurdwara Dera Sahib, Lahore; Gurdwara Janam Asthan, Nankana Sahib |
| Part of a series on |
| Sikhism |
|---|
 |
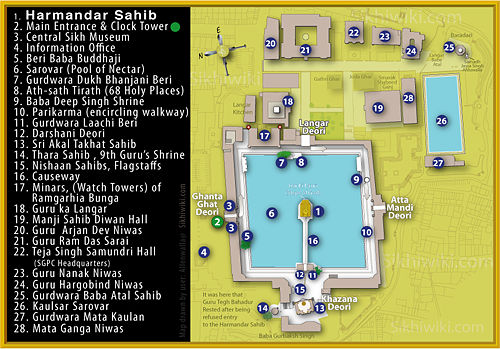
Sikh architecture is a distinctive style of architecture that developed under the Sikh Confederacy and later flourished during the Sikh Empire in the 18th and 19th centuries, primarily in the Punjab region.[1] Due to its progressive nature, Sikh architecture has continued to evolve over time, giving rise to several new branches and influencing various contemporary architectural styles.[2]Although Sikh architecture was originally developed as part of the religious and cultural expression within Sikhism, its aesthetic richness and symbolic elements have led to its adoption in many secular and non-religious buildings as well, admired for their beauty and structural harmony.[3] 300 years ago, Sikh architecture was distinguished for its many curves and straight lines; Keshgarh Sahib and the Harmandir Sahib (Golden Temple) are prime examples of traditional Sikh architecture.[4]
Background
[edit]
Sikh architecture is heavily influenced by elements of Mughal and Islamic styles. Features such as the onion dome, frescoes, inlay work, and multi-foil arches are derived from the Mughal period, particularly during the reign of Shah Jahan. In contrast, features like chattris, oriel windows, bracket-supported eaves at the string-course, and decorative friezes reflect the influence of Rajput architecture.[5]
Description
[edit]
Apart from religious buildings, Sikh architecture includes secular forts, bungas (residential places), palaces, and colleges.[6] The religious structure is called gurdwara (a place where the Guru dwells). The word gurdwara is a compound of guru (guide or master) and dwara (gateway or seat). So, it has an architectural connotation. Sikh gurdwaras are generally commemorative buildings connected with the ten gurus in some way, or with places and events of historical significance. Some examples are Gurdwara Dera Sahib (encampment place), in Batala in Gurdaspur district. It was erected in memory of the brief stay of Guru Nanak along with his companions on the occasion of his marriage. Gurdwara Shahid Ganj (Martyrdom Memorial) in Muktsar in Faridkot district commemorates the cremation spot of Sikhs who were killed in a battle between Guru Gobind Singh and the Mughals in 1705. The Gurdwara Shish Mahal (Palace of Mirrors) in Kiratpur, located in the Ropar district of Punjab, marks the birthplace of the eighth Sikh Guru, Guru Har Krishan.[7]
There are over 500 historical gurdwaras across India and Pakistan, many of which are associated with significant events in the lives of the Sikh Gurus.[8]
There are four broad categories regarding shape and layout of Sikh shrine architecture:[6]
- square
- rectangular
- octagonal (ex. Gurdwara Baba Atal in Amritsar)
- cruciform (ex. Gurdwara Nanak Jhira in Bidar, Karnataka)
Conservation
[edit]Many priceless Sikh heritage sites (including their architecture) have been destroyed or altered beyond recognition under the guise of "kar seva" renovations by various institutions and groups in recent-times,[9][10][11][12][13][14] especially vulnerable are Sikh heritage sites in both India and Pakistan according to one scholar, who states it is due to "...the lack of will on the part of the authorities concerned to preserve them".[15] An example of these haphazard and destructive renovations is an incident involving the top section of the historical Darshani Deori gatehouse at the Gurdwara Tarn Taran Sahib complex, which was demolished by Kar Seva groups in March 2019.[16][17][18][19] Many groups are rushing to digitize what historical architecture and structures remains for posterity before they are lost, such as Panjab Digital Library.[20] In July 2021, the SGPC launched a project to archive and document the heritage structures of the community and have set up the old doors of the Golden Temple as museum display when they were replaced.[21][22][23] However, around the same time the SGPC denied the importance of a historical Sikh structure discovered underground near the Golden Temple complex, which experts at the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) deemed as 'historic'.[24] Also, the SGPC made plans to raze a historical building known as Guru Ram Das Sarai, even in the face of criticism of the decision by experts.[25][26] As many as ninety percent of Sikh heritage monuments have been destroyed in Punjab in the name of renovation and kar seva.[27] Many historical Sikh structures that were destroyed by Kar Seva renovations include original houses of the Sikh gurus and their relatives.[28]
According to the Sikh historian, Harjinder Singh Dilgeer:[28]
Though kar seva babas had been renovating gurudwaras ever since anyone can remember, it was after Operation Bluestar, when the Sikh community donated generously for the massive rebuilding of the Golden Temple premises, that 'babas' began to appreciate the money-making opportunities such rebuilding threw up. The trend then spread across Punjab and in the last two decades, old heritage structures began to be demolished and replaced by garish, opulent marble gurudwaras. These pseudo-babas are armed with so much money but they spend it foolishly on rebuilding instead of restoration, because they are absolutely ignorant about the historical value of these old monuments. Somewhere along the line, the original, unpretentious Sikh architecture has begun to be perceived as something to be ashamed of. Our Gurus were simple, down-to-earth men of the soil, and their buildings reflect the simplicity and harmony which Sikhism is all about.
— Harjinder Singh Dilgeer, Sikh historian
According to Sikh scholar, Gurtej Singh, on who is to blame for the plight of Sikh historical heritage:[28]
Whether it is the Shiromani Gurudwara Prabandhak Committee or the Akal Takht or even the political Akali Dal which draws its strength from the former two, there is no appreciation for our heritage. Scholars like us do not matter in the scheme of things, because we obstruct their commercial aspirations. The SGPC patronises these babas and they do not realise that they are converting history into mythology by destroying historical evidence.
— Gurtej Singh
Peter Bance, when evaluating the status of Sikh sites in present-day India, where the majority of Sikhs live today, criticizes the destruction of the originality of 19th-century-era Sikh sites under the guise of "renovation", whereby historical structures are toppled and new buildings take their former place.[29] An example cited by him of sites losing their originality relates to nanakshahi bricks, which are characteristic of Sikh architecture from the 19th century, being replaced by renovators of historical Sikh sites in India by marble and gold.[29] Bance advocates that a grassroots movement advocating for the proper restoration and preservation of historical Sikh sites and their original architecture is necessary, which works together with private enthusiasts and government bodies in-cooperation with one another.[29] Bance further claims that a lack of willpower rather than a lack of funds is responsible for the poor conservation of Sikh historical sites.[29] Bance believes that the way forward in the modern-age to conserve Sikh heritage must be a digital approach, where social networking and technology is utilized to share research, build-up archives, and promote tourism to these sites.[29] Increased tourism has the potential to increase efforts to preserve and restore Sikh heritage sites.[29] Bance uses the Instagram platform to bring light to forgotten Sikh heritage lying in Pakistan with the wider community, using engagements there to generate social awareness and passion.[29] Through his Instagram account, Bance has been contacted by persons interested in restoring Sikh heritage sites, which have allowed them to be connected with others who specialize in this field.[29] Furthermore, he claims that on a weekly-basis hundreds of members of the general public from both India and Pakistan contact him through social media requesting him to visit their locality to document the Sikh heritage located there, as they lack the know-how on how to do this themselves.[29]
Shahid Shabbir is a Pakistani historian and journalist who has documented countless Sikh heritage sites (most often neglected, dilapidated, or abandoned) located in his country, including their extant artwork and architecture.[30][31] Sikh architecture remains a seldom studied or researched subject.[32]
Gallery
[edit]- Golden dome of Gurdwara Dera Sahib in Lahore
- The Gurdwara Janam Asthan in Nankana Sahib, Pakistan, commemorates the site where Guru Nanak is believed to have been born. It was rebuilt by the Pakistani Government
- Gurudwara Bangla Sahib is one of the most prominent Sikh gurdwara in Delhi, India and known for its association with the eighth Sikh Guru, Guru Har Krishan, as well as the pool inside its complex, known as the "sarovar."
- Original structure of Gurudwara Sri Sheesh Mahal Sahib, Kiratpur Sahib
- True-colour photograph of Gurdwara Dera Sahib in Lahore, India (now Pakistan), taken in 1914 by Stéphane Passet.
- True-colour photograph titled ‘Interior decoration of the western door of the Darbar Sahib’, taken on 15 January 1914 by Stéphane Passet.
See also
[edit]- Sikh architecture in Karnataka
- Nanak Shahi bricks
- Sikh art and culture
- Sikh scriptures
- History of Sikhism
- Sikh Ajaibghar
- Mehdiana Sahib
References
[edit]- ^ Singh, Khushwant (2004). A History of the Sikhs, Volume 1: 1469–1839. Oxford University Press. p. 331. ISBN 978-0-19-567308-1.
- ^ Subhash Parihar (2001). Golden Temple: History, Art, and Architecture. Aryan Books International. p. 102.
- ^ Malik Arshi (2012). Sikh Architecture. Himalaya Publishing House. p. 47.
- ^ Kartar Singh. "Sikh Architecture". SikhMuseum.com. Retrieved 2 July 2025.
- ^ Subhash Parihar (1996). The Golden Temple: Past and Present. Publication Bureau, Punjabi University. p. 58.
- ^ a b Singh, Gurmukh (2004). "SIKH ARCHITECTURE". In Singh, Harbans (ed.). The Encyclopedia of Sikhism. Vol. IV: S–Z (2nd ed.). Punjabi University. pp. 131–133. ISBN 817380530X.
- ^ Harbans Singh (1998). The Encyclopaedia of Sikhism. Vol. 2. Punjabi University. p. 228.
- ^ "List of Historical Gurdwaras". World Gurudwaras. Retrieved 2 July 2025.
- ^ Singh, Gurnam (2021-04-21). "Who's really destroying Sikh heritage?". Asia Samachar. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
- ^ Singh, I. P.; Rana, Yudhvir (August 23, 2021). "Sikhs wake up late to the loss of religious heritage". The Times of India. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
- ^ "Stop 'kar seva': SAD-A to SGPC". The Times of India. TNN. Apr 15, 2003. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
- ^ "Sikhs aghast with tearing down of historic Sikh site in name of 'kar seva'". asiasamachar.com. Asia Samachar Team. April 2019. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ "UPDATE: Kar Seva's Baba Jagtar Singh Evicted from Sri Tarn Taran Sahib". Sikh24.com. Sikh24 Editors. 2019-04-01. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ IP Singh (Oct 7, 2018). "Heritage under the hammer". The Times of India. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
- ^ "Sikh heritage sites in India, Pak facing ruin, says scholar". Tribuneindia News Service. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
- ^ Yudhvir Rana (Mar 31, 2019). "Karsewa group demolish historical darshani deori". The Times of India. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
- ^ "Historic Tarn Taran gurdwara's 'darshani deori' razed, row erupts". Hindustan Times. 2019-04-01. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
- ^ "10 months on, no progress on restoration of Darshani Deori in Tarn Taran gurdwara". Hindustan Times. 2020-01-25. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
- ^ Kaur, Mejindarpal (2019-04-05). "Stop the Destruction of Sikh Heritage". United Sikhs. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
- ^ Sethi, Chitleen K. (2018-12-19). "In Punjab, a library's silent digital revolution is preserving the state's heritage". ThePrint. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
- ^ "Beleaguered over Destruction of Heritage, SGPC Plans to Initiate Sikh Archives Project". Sikh24.com. Sikh24 Punjab Bureau. 2021-07-31. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ Paul, G.S. "200-year-old doors of Golden Temple's 'Darshani Deori' on display". Tribuneindia News Service. Tribune News Service. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
- ^ "Jathedar dispels rumours on Darshani Deori doors". Tribuneindia News Service. Tribune News Service. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ "SGPC Continues to Deny Historic Importance of Old Structure Found at Darbar Sahib". Sikh24.com. Sikh24 Editors. 2021-07-31. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ "SGPC Revives Plan of Razing Darbar Sahib Sarai Where Sikhs Were Martyred During '84 Holocaust". Sikh24.com. Sikh24 Editors. 2021-07-20. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ "SGPC plans to demolish Guru Ram Dass Sarai near Darbar Sahib; Sikh groups obejct". Sikh Siyasat News. Sikh Siyasat Bureau. 2016-06-29. Retrieved 2023-01-08.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ Glover, William J. "Shiny new buildings: rebuilding historic sikh gurdwaras in Indian Punjab." Future Anterior, vol. 9, no. 1, summer 2012, pp. 32+. Gale Academic OneFile, link.gale.com/apps/doc/A313972601/AONE?u=anon~bc4b7e36&sid=googleScholar&xid=807b241c. Accessed 8 Jan. 2023.
- ^ a b c Dogra, Chander Suta (3 May 2016). "Have You the Eyes for It?". SikhNet (republished, originally published by Outlook Magazine). Retrieved 21 September 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Bakshi, Artika Aurora (2023). "Discovering the Forgotten Heritage of the Panjabs With Peter Bance". Nishaan Nagaara (11): 28–37.
- ^ Aslam, Irfan (28 May 2019). "Narowal haveli has nothing to do with Baba Guru Nanak". Dawn. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ^ Singh, Inderjeet (18 September 2015). "Research Into Sikh Heritage in Pakistan – Shahid Shabbir (aka Baba Ji)". Sikh Net. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ^ Kang, Kanwarjit Singh (1988). "16. The Sikh Shrines of Anandpur Sahib". Punjab Art and Culture. Atma Ram & Sons. p. 82. ISBN 9788170430964.
Bibliography
[edit]- Arshi, Pardeep Singh, Sikh Architecture in the Punjab, Intellectual Pub. House, 1986.
- Brown, Percy, Indian Architecture (Islamic Period), Fifth Edition, 1965, Bombay.
- Brown, Percy, Indian Architecture (Hindu and Buddhist Period), Fifth Edition, 1965, Bombay.
- Singh, Mehar, Sikh Shrines In India, Publications Division, Government of India, 1974, New Delhi.
- Singh, Darshan, The Sikh art and architecture, Dept. of Guru Nanak Sikh Studies, Panjab University, 1987.
- Marg, Volume XXX, Number 3, June 1977, Bombay.
Further reading
[edit]- Rajwant Singh Chilana (2005). International Bibliography of Sikh Studies. Springer Netherlands. ISBN 978-1-4020-3043-7.
- Kerry Brown, ed. (1999). Sikh Art and Literature. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-20289-3.


















