Sobrerol
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
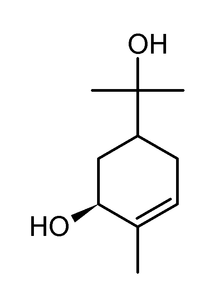 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | trans-p-Menth-6-ene-2,8-diol; trans-sobrerol |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.050.692 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H18O2 |
| Molar mass | 170.252 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 130–132 °C (266–270 °F) |
| Boiling point | 270–271 °C (518–520 °F) |
| |
| (verify) | |
Sobrerol is a mucolytic.
History
[edit]Sobrerol was discovered by Ascanio Sobrero as an oxidation product of terpenes. Later the oxidation and reduction reactions of chiral pinene lead also to several possible isomers of carvone (the corresponding cyclohexyl ketone dehydrated at the isopropyl) and sobrerol, making it possible to determine reaction mechanism and the structural properties of pinene and of other terpenes.
References
[edit]- Henderson GG, Eastburn WJ (1909). "CLXIV — The conversion of pinene into sobrerol". Journal of the Chemical Society, Transactions. 95: 1465–1466m. doi:10.1039/CT9099501465.
- Armstrong HE, Pope WJ (1891). "XXXVI — Studies of the terpenes and allied compounds. Sobrerol, a product of the oxidation of terebenthene (oil of turpentine) in sunlight". Journal of the Chemical Society, Transactions. 59: 315–320. doi:10.1039/CT8915900315.
- Schmidt H (November 1953). "Über cis-und trans-Sobrerol (optisch-aktives Pinolhydrat)" [About cis- and trans-sobrerol (optically active pinol hydrate)]. Chemische Berichte (in German). 86 (11): 1437–1444. doi:10.1002/cber.19530861112.
- Allegra L, Bossi R, Braga PC (1981). "Action of sobrerol on mucociliary transport". Respiration; International Review of Thoracic Diseases. 42 (2): 105–109. doi:10.1159/000194412. PMID 7313328.