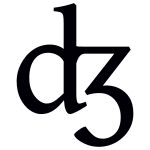| Language | Word | IPA | Meaning | Notes |
| Abkhaz | аџыр | [ad͡ʒər] | 'steel' | See Abkhaz phonology |
| Adyghe | джанэ | [d͡ʒaːna]ⓘ | 'dress' | |
| Albanian | xham | [d͡ʒam] | 'glass' | |
| Amharic | እንጀራ | [ɨnd͡ʒəra] | 'injera' | |
| Arabic | Modern Standard[1] | جَـرَس | [d͡ʒaras] | 'bell' | In other standards and dialects, corresponds to [ɡ] or [ʒ]. See Arabic phonology |
| Hejazi | جــيب/jēb | [d͡ʒe̞ːb] | 'pocket' | Pronounced [ʒ] by some speakers. See Hejazi Arabic phonology |
| Armenian | Eastern[2] | ջուր | [d͡ʒuɾ] | 'water' | |
| Western | ճանճ | [d͡ʒɑnd͡ʒ] | 'musca (fly)' | |
| Assyrian | ܓ̰ܝܪܐ s | [d͡ʒjɑɾɑ] | 'to pee' | Used in native terminology. Used predominantly in Urmia and some Jilu dialects. [ɟ] is used in other varieties. |
| Azerbaijani | can | [d͡ʒɑn] | 'soul' | |
| Bengali | জল | [d͡ʒɔl] | 'water' | Contrasts with the aspirated form. See Bengali phonology |
| Bulgarian | джудже | [d͡ʒʊˈd͡ʒɛ] | 'dwarf' | See Bulgarian phonology |
| Catalan | jutge | [ˈʒu(d).d͡ʒə] | 'judge' | See Catalan phonology |
| Chechen | джерво / jyerwo | [d͡ʒjerwo] | 'previously married woman' | |
| Chinese | Quzhou dialect | 重 / zon | [d͡ʒõ] | 'heavy' | |
| Coptic | ϫⲉ/je | [d͡ʒe] | 'that' | |
| Czech | džbán | [d͡ʒbaːn] | 'jug' | See Czech phonology |
| Dhivehi | ޖަރާސީމު / jarásímu | [d͡ʒaraːsiːmu] | 'germs' | See Dhivehi phonology |
| Dutch | jeans | [d͡ʒiːns] | 'jeans' | Some say [ʒiːns] |
| English | jeans | [ˈd͡ʒiːnz] | 'jeans' | See English phonology |
| Esperanto | manĝaĵo | [manˈd͡ʒaʒo̞] | 'food' | See Esperanto phonology |
| Estonian | džäss | [ˈd̥ʒæsː] | 'jazz' | Rare, occurs only in loanwords. See Estonian phonology |
| Finnish | džonkki | [ˈdʒo̞ŋkːi] | 'junk (ship)' | Rare, occurs only in loanwords. See Finnish phonology |
| French | adjonction | [ad͡ʒɔ̃ksjɔ̃] | 'addition' | Rare. See French phonology |
| Georgian[3] | ჯიბე/jibe | [d͡ʒibɛ] | 'pocket' | |
| German | Standard[4] | Dschungel | [ˈd͡ʒʊŋəl] | 'jungle' | Laminal or apico-laminal and strongly labialized.[4] Some speakers may merge it with /t͡ʃ/. See Standard German phonology |
| Goemai | [example needed] | [d͡ʒaːn] | 'twins' | |
| Hebrew | Standard | ג׳וק/juk | [d͡ʒuk] | 'cockroach' | Only used in loanwords. See Modern Hebrew phonology |
| Temani | גָּדוֹל/jaďol | [d͡ʒaðol] | 'big, great' | Yemenite Hebrew pronunciation of gimel with dageš. See Yemenite Hebrew |
| Hindustani | Hindi | जाना/jānā | [d͡ʒäːnäː] | 'to go' | Contrasts with aspirated form. See Hindustani phonology |
| Urdu | جـانا/jānā |
| Hungarian | lándzsa | [laːnd͡ʒɒ] | 'spear' | Rare, mostly in loanwords. See Hungarian phonology |
| Indonesian | jarak | [ˈd͡ʒaraʔ] | 'distance' | |
| Italian[5] | gemma | [ˈd͡ʒɛmma] | 'gem' | [dʒ] occurs when letter 'G' is before front vowels [e], [i] and [ɛ], while when 'G' is in front of vowels [o], [a], [u] and [ɔ] the phoneme changes to a voiced velar plosive. |
| Kabyle | lǧiran | [id͡ʒiræn] | 'the neighbors' | |
| Kashubian[6] | [example needed] | | |
| Kurdish | Northern | cîger | [d͡ʒiːˈɡɛɾ] | 'lung' | See Kurdish phonology |
| Central | جــەرگ | [d͡ʒɛɾg] | 'liver' |
| Southern | [d͡ʒæɾg] |
| Kyrgyz | жаман / caman | [d͡ʒaman] | 'bad' | See Kyrgyz phonology |
| Ladino | djudyó/גﬞודיו | [d͡ʒudˈjo] | 'Jew' |
| Latvian | dadži | [dad͡ʒi] | 'thistles' | See Latvian phonology |
| Limburgish | Hasselt dialect[7] | djèn | [d͡ʒɛːn²] | 'Eugene' | See Hasselt dialect phonology |
| Lithuanian | džiaugsmingas | [d͡ʒɛʊɡʲsʲˈmʲɪnɡɐs] | 'gladsome' | See Lithuanian phonology |
| Macedonian | џемпер/džemper | [ˈd͡ʒɛmpɛr] | 'sweater' | See Macedonian phonology |
| Malay | jahat | [d͡ʒahat] | 'evil' | |
| Maltese | ġabra | [d͡ʒab.ra] | 'collection' | |
| Manchu | ᠵᡠᠸᡝ/juwe | [d͡ʒuwe] | 'two' | |
| Marathi | जय/jay | [d͡ʒəj] | 'victory' | Contrasts with the aspirated form. Allophone [dʑ] and [d̪z]. See Marathi phonology |
| Occitan | Languedocien | jove | [ˈd͡ʒuβe] | 'young' | See Occitan phonology |
| Provençal | [ˈd͡ʒuve] |
| Odia | ଜମି/jami | [d͡ʒɔmi] | 'land' | Contrasts with aspirated form.See Odia phonology |
| Ojibwe | iijikiwenh | [iːd͡ʒikiwẽːʔ] | 'brother' | See Ojibwe phonology |
| Pashto | جــګ/jeg | [d͡ʒeɡ] | 'high' | |
| Persian | کـجـا/koja | [kod͡ʒɒ] | 'where' | See Persian phonology |
| Polish | Standard | liczba | [ˈlid͡ʐ.ba] | 'number' | |
| Gmina Istebna | dziwny | [ˈd͡ʒivn̪ɘ] | 'strange' | /ɖ͡ʐ/ and /d͡ʑ/ merge into [d͡ʒ] in these dialects. In standard Polish, /d͡ʒ/ is commonly used to transcribe what actually is a laminal voiced retroflex affricate. |
| Lubawa dialect[8] |
| Malbork dialect[8] |
| Ostróda dialect[8] |
| Warmia dialect[8] |
| Portuguese | Most Brazilian dialects[9] | grande | [ˈɡɾɐ̃d͡ʒ(i)] | 'big' | Allophone of /d/ before /i, ĩ/ (including when the vowel is elided) and other instances of [i] (e.g. epenthesis), marginal sound otherwise. |
| Most dialects | jambalaya | [d͡ʒɐ̃bɐˈlajɐ] | 'jambalaya' | In free variation with /ʒ/ in a few recent loanwords. See Portuguese phonology |
| Romanian | ger | [ˈd͡ʒɛ̝r] | 'frost' | See Romanian phonology |
| Sardinian | Campidanese | géneru | [ˈd͡ʒɛneru] | 'son-in-law' | |
| Scottish Gaelic | Dia | [d͡ʒia] | 'God' | See Scottish Gaelic phonology |
| Serbo-Croatian | Some speakers | џем / džem | [d͡ʒê̞m] | 'jam' | May be laminal retroflex instead, depending on the dialect. See Serbo-Croatian phonology |
| Bosnian | ђаво / đavo | [d͡ʒâ̠ʋo̞ː] | 'devil' | Most Croatian and some Bosnian speakers merge /d͡ʒ/ and /d͡ʑ/, either to [d͡ʒ] or laminal [ɖ͡ʐ]. |
| Croatian |
| Silesian | Gmina Istebna[10] | [example needed] | | | These dialects merge /ɖ͡ʐ/ and /d͡ʑ/ into [d͡ʒ]. |
| Jablunkov[10] | [example needed] | | |
| Slovene | enačba | [eˈnáːd͡ʒbà] | 'equation' | Allophone of /t͡ʃ/ before voiced obstruents in native words. As a phoneme present only in loanwords. See Slovene phonology |
| Somali | joog | [d͡ʒoːɡ] | 'stop' | See Somali phonology |
| Tagalog | diyan | [d͡ʒän] | 'there' | Used to pronounce the multigraphs ⟨dy⟩ and ⟨diy⟩ in native words and ⟨j⟩ in loanwords outside Spanish. For more information, see Tagalog phonology. |
| Tatar | Mishar Dialect[11] | can / җан | [d͡ʒɑn] | 'soul' | In standard Tatar (Kazan dialect), the sound for letter c (җ) is ⟨ʑ⟩. |
| Turkish | acı | [äˈd͡ʒɯ] | 'pain' | See Turkish phonology |
| Turkmen | jar | [d͡ʒär] | 'ravine' | |
| Tyap | jem | [d͡ʒem] | 'hippopotamus' | |
| Ubykh | [amd͡ʒan] | '?' | See Ubykh phonology |
| Ukrainian | джерело/džerelo | [d͡ʒɛrɛˈlɔ] | 'source' | See Ukrainian phonology |
| Uyghur | coza / جوزا | [d͡ʒozɑ] | 'desk' | See Uyghur phonology |
| Uzbek | jahon / жаҳон | [d͡ʒaˈhɒn] | 'world' |
| Welsh | siop jips | [ʃɔp d͡ʒɪps] | 'chip shop' | Occurs as the colloquial soft mutation of /t͡ʃ/. See Colloquial Welsh morphology |
| West Frisian | siedzje | [ˈʃɪd͡ʒə] | 'to sow' | See West Frisian phonology |
| Yiddish | דזשוכע/juche | [d͡ʒʊxə] | 'insect' | See Yiddish phonology |
| Zapotec | Tilquiapan[13] | dxan | [d͡ʒaŋ] | 'god' | |
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia