Gombak District
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
Gombak District | |
|---|---|
| Daerah Gombak | |
| Other transcription(s) | |
| • Jawi | ڬومبق |
| • Chinese | 鹅唛县 (Simplified) 鵝嘜縣 (Traditional) |
| • Tamil | கோம்பாக் மாவட்டம் |
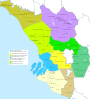
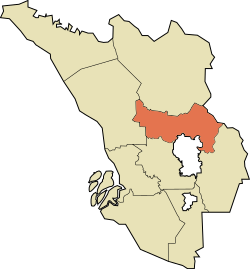 Location of Gombak District in Selangor Darul Ehsan | |
 | |
Location of Gombak District in Malaysia | |
| Coordinates: 3°16′27.3″N 101°34′14.6″E / 3.274250°N 101.570722°E | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Seat | Bandar Baru Selayang |
| Local area government(s) | Selayang Municipal Council (West) Ampang Jaya Municipal Council (East) |
| Government | |
| • District officer | Amirul Azizan Abdul Rahim[1] |
| • Sultan's Representative | Wan Mahmood Pawanteh[2] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 650.08 km2 (251.00 sq mi) |
| Population (2020)[4] | |
| • Total | 942,336 |
| • Density | 1,400/km2 (3,800/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (MST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+8 (Not observed) |
| Postcode | 48xxx, 52xxx-54xxx, 68xxx |
| Calling code | +6-03-41, +6-03-60, +6-03-61, +6-3-62 |
| Vehicle registration plates | B |
The Gombak District is an administrative district located in the state of Selangor, Malaysia. The district was created on February 1, 1974, the same day when Kuala Lumpur was declared a Federal Territory. Until 1997, Rawang was the district capital; the capital has been moved to Bandar Baru Selayang. Gombak borders Kuala Lumpur to the southeast and the Genting Highlands to the east. Both Gombak and Kuala Lumpur, along with some other districts in Selangor, are situated within the Klang Valley. Other localities in Gombak district include Batu Arang, Kuang, Rawang, Kundang, Gombak Town, Selayang, Batu Caves and Hulu Kelang.
The main campus of the International Islamic University Malaysia (IIUM/UIAM) is also located here as well as the Batu Caves. Gombak is also home to an aboriginal Orang Asli settlement, and it is the site of the Orang Asli Museum.
Gombak River merges with the larger Klang River in Kuala Lumpur. The meeting place of the two rivers is the birthplace of Kuala Lumpur. At the center of the confluence is the Masjid Jamek.
Gombak (town) also refers to as a locality (town/area/suburb) in the northern and central portion of the Setapak subdistrict (both in Gombak and Kuala Lumpur). Before 1974, Gombak was a town before it became a district. Gombak was home to the settlements of the first Minangkabau immigrants in the 1800s and was established soon after. Old mosques in the Gombak area such as the Masjid Lama Batu 6 Gombak are still standing to this day. Today, Gombak can be referred to both the town and district itself but the locals usually refers Gombak as the town, not the district.
Administrative divisions
[edit]
Gombak District is divided into 4 mukims, which are:
Government
[edit]Gombak is partly administrated by two different local governments completely within it, which fall under the state jurisdiction, not the district:
- Ampang Jaya Municipal Council (Among Mukim Ulu Kelang of the district)
- Selayang Municipal Council (Most part of district except Mukim Ulu Kelang area)
Demographics
[edit]| Year | Pop. | ±% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1991 | 352,649 | — | ||
| 2000 | 537,525 | +52.4% | ||
| 2010 | 668,694 | +24.4% | ||
| 2020 | 942,336 | +40.9% | ||
| ||||
| Source: [5] | ||||
The following is based on Department of Statistics Malaysia 2010 census.[4]
| Ethnic groups in Gombak , 2010 census | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ethnicity | Population | Percentage |
| Bumiputera | 396,012 | 62.9% |
| Chinese | 147,488 | 23.4% |
| Indian | 76,773 | 12.2% |
| Others | 9,698 | 1.5% |
| Total | 629,971 | 100% |
Gombak has one of the largest Hui Muslim Communities in Malaysia. Nearly 60% of Hui Chinese live in Gombak.[6]
Education
[edit]National education is under the purview of the Gombak District Education Office. As of 2014, there were 53 national type primary schools, eight national type (Chinese) primary schools, seven national type (Tamil) primary schools, 30 national type secondary schools (SMK), two national type secondary boarding schools (SM Berasrama Penuh), two national type secondary Islam religious school (SM Agama) and two national type secondary vocational schools (Kolej Vokasional)[citation needed]
Tourist attractions
[edit]

Gombak has a large amount of recreational area and tourist attraction.
- Batu Caves
- Forest Research Institute Malaysia
- Batu Dam, Batu Caves
- Gua Damai Extreme Park, Batu Caves
- Batu Arang Heritage Town
- Orang Asli Museum, Gombak
- Hutan Lipur Bukit Lagong, Selayang
- Hutan Lipur Sungai Tua, Selayang
- Kancing Forest Park, Rawang
- Selayang Hot Spring, Selayang
- Commonwealth Forest Park, Rawang
- Templer Park, Rawang
- Tasik Biru Kundang, Kundang
- National Zoo of Malaysia
- Klang Gates Dam
- Batu Asah Waterfall, Hulu Kelang
- Ampang Forest Reserve, Hulu Kelang
- Selangor Fruit Valley, Batu Arang
Federal Parliament and State Assembly Seats
[edit]
List of Gombak district representatives in the Federal Parliament (Dewan Rakyat)
| Parliament | Seat Name | Member of Parliament | Party |
|---|---|---|---|
| P97 | Selayang | William Leong Jee Keen | Pakatan Harapan (PKR) |
| P98 | Gombak | Amirudin Shari | Pakatan Harapan (PKR) |
| P99 | Ampang | Rodziah Ismail | Pakatan Harapan (PKR) |
| P106 | Damansara | Gobind Singh Deo | Pakatan Harapan (DAP) |
| P107 | Sungai Buloh | Ramanan Ramakrishnan | Pakatan Harapan (PKR) |
List of Gombak district representatives in the State Legislative Assembly (Dewan Undangan Negeri)
| Parliament | State | Seat Name | State Assemblyman | Party |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P97 | N13 | Kuang | Mohd Rafiq Mohd Abdulah | Perikatan Nasional (BERSATU) |
| P97 | N14 | Rawang | Chua Wei Kiat | Pakatan Harapan (PKR) |
| P97 | N15 | Taman Templer | Anfal Saari | Pakatan Harapan (AMANAH) |
| P98 | N16 | Sungai Tua | Amirudin Shari | Pakatan Harapan (PKR) |
| P98 | N17 | Gombak Setia | Hilman Idham | Perikatan Nasional (BERSATU) |
| P98 | N18 | Hulu Kelang | Mohamed Azmin Ali | Perikatan Nasional (BERSATU) |
| P99 | N19 | Bukit Antarabangsa | Mohd Kamri Kamaruddin | Pakatan Harapan (PKR) |
| P99 | N20 | Lembah Jaya | Syed Ahmad Syed Abdul Rahman Alhadad | Pakatan Harapan (PKR) |
| P106 | N37 | Bukit Lanjan | Pua Pei Ling | Pakatan Harapan (PKR) |
| P107 | N38 | Paya Jaras | Mohd. Khairuddin Othman | Pakatan Harapan (PKR) |
Transportation
[edit]By rail
[edit] KTM Komuter (commuter rail services):
KTM Komuter (commuter rail services): - 1 Batu Caves-Pulau Sebang Line:
- KC05 Batu Caves
- 2 Tanjung Malim-Port Klang Line:
- KA07 Kepong Sentral
- KA08 Sungai Buloh
- KA09 Kuang
- KA10 Rawang
- 1 Batu Caves-Pulau Sebang Line:
 KTM ETS (inter-city rail services):
KTM ETS (inter-city rail services):  Rapid KL (rapid transit):
Rapid KL (rapid transit): - 5 LRT Kelana Jaya Line
- KJ1 Gombak
- 12 MRT Putrajaya Line
- PY04 Sungai Buloh
- PY08 Sri Damansara Barat
- 5 LRT Kelana Jaya Line
By car
[edit]The Gombak district is served by the following expressways:
 FT 1 Federal Route 1 is the main thoroughfare going through Rawang town, Selayang and Batu Caves.
FT 1 Federal Route 1 is the main thoroughfare going through Rawang town, Selayang and Batu Caves. FT 68 Federal Route 68, also known as Jalan Gombak, runs through here before terminating in Bentong, Pahang.
FT 68 Federal Route 68, also known as Jalan Gombak, runs through here before terminating in Bentong, Pahang. North–South Expressway Northern Route runs through Gombak district, providing exits to 114 Sungai Buloh North, 115 Rawang South and 116 Rawang.
North–South Expressway Northern Route runs through Gombak district, providing exits to 114 Sungai Buloh North, 115 Rawang South and 116 Rawang. East Coast Expressway and Kuala Lumpur–Karak Expressway are the district's main gateway to the east coast states of Pahang, Terengganu and Kelantan.
East Coast Expressway and Kuala Lumpur–Karak Expressway are the district's main gateway to the east coast states of Pahang, Terengganu and Kelantan. Kuala Lumpur–Kuala Selangor Expressway connects Ijok near Kuala Selangor to Templer's Park near Rawang with exits to 2505 Kundang, 2506 Kuang and 2508 Templer Park are runs through Gombak district.
Kuala Lumpur–Kuala Selangor Expressway connects Ijok near Kuala Selangor to Templer's Park near Rawang with exits to 2505 Kundang, 2506 Kuang and 2508 Templer Park are runs through Gombak district. Guthrie Corridor Expressway also runs through Gombak district, providing exits to 115 Rawang South and 3501 Kuang.
Guthrie Corridor Expressway also runs through Gombak district, providing exits to 115 Rawang South and 3501 Kuang.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Portal Rasmi PDT Gombak Perutusan Pegawai Daerah Gombak". www2.selangor.gov.my. Archived from the original on 2019-07-15. Retrieved 2017-12-23.
- ^ "Portal Rasmi PDT Gombak Orang Besar Daerah Gombak". www2.selangor.gov.my. Archived from the original on 2019-05-29. Retrieved 2017-12-23.
- ^ "Portal Rasmi PDT Gombak Profil Gombak". www2.selangor.gov.my. Archived from the original on 2017-06-26. Retrieved 2017-12-23.
- ^ a b "Population Distribution and Basic Demographic Characteristics, 2010" (PDF). Department of Statistics, Malaysia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 May 2014. Retrieved 19 April 2012.
- ^ "Key Findings of Population and Housing Census of Malaysia 2020" (pdf) (in Malay and English). Department of Statistics, Malaysia. ISBN 978-967-2000-85-3.
- ^ Hailong, Ma (2017). The History of Chinese Muslims' Migration into Malaysia (PDF). King Faisal Center for Research and Islamic Studies. p. 27.