Infinite-order apeirogonal tiling
 From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
| Infinite-order apeirogonal tiling | |
|---|---|
 Poincaré disk model of the hyperbolic plane | |
| Type | Hyperbolic regular tiling |
| Vertex configuration | ∞∞ |
| Schläfli symbol | {∞,∞} |
| Wythoff symbol | ∞ | ∞ 2 ∞ ∞ | ∞ |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | [∞,∞], (*∞∞2) [(∞,∞,∞)], (*∞∞∞) |
| Dual | self-dual |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive, edge-transitive, face-transitive |
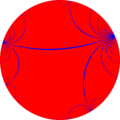
The infinite-order apeirogonal tiling is a regular tiling of the hyperbolic plane. It has Schläfli symbol of {∞,∞}, which means it has countably infinitely many apeirogons around all its ideal vertices.
Symmetry
[edit]This tiling represents the fundamental domains of *∞∞ symmetry.
Uniform colorings
[edit]This tiling can also be alternately colored in the [(∞,∞,∞)] symmetry from 3 generator positions.
| Domains | 0 | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
 symmetry: [(∞,∞,∞)] |  t0{(∞,∞,∞)} |  t1{(∞,∞,∞)} |  t2{(∞,∞,∞)} |
Related polyhedra and tiling
[edit]The union of this tiling and its dual can be seen as orthogonal red and blue lines here, and combined define the lines of a *2∞2∞ fundamental domain.
| Paracompact uniform tilings in [∞,∞] family | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
= = | = = | = = | = = | = = | = | = |
 |  |  | 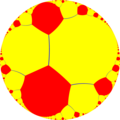 |  |  |  |
| {∞,∞} | t{∞,∞} | r{∞,∞} | 2t{∞,∞}=t{∞,∞} | 2r{∞,∞}={∞,∞} | rr{∞,∞} | tr{∞,∞} |
| Dual tilings | ||||||
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| V∞∞ | V∞.∞.∞ | V(∞.∞)2 | V∞.∞.∞ | V∞∞ | V4.∞.4.∞ | V4.4.∞ |
| Alternations | ||||||
| [1+,∞,∞] (*∞∞2) | [∞+,∞] (∞*∞) | [∞,1+,∞] (*∞∞∞∞) | [∞,∞+] (∞*∞) | [∞,∞,1+] (*∞∞2) | [(∞,∞,2+)] (2*∞∞) | [∞,∞]+ (2∞∞) |
 |  |  |  |  | 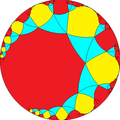 | |
| h{∞,∞} | s{∞,∞} | hr{∞,∞} | s{∞,∞} | h2{∞,∞} | hrr{∞,∞} | sr{∞,∞} |
| Alternation duals | ||||||
 |  |  |  | |||
| V(∞.∞)∞ | V(3.∞)3 | V(∞.4)4 | V(3.∞)3 | V∞∞ | V(4.∞.4)2 | V3.3.∞.3.∞ |
| Paracompact uniform tilings in [(∞,∞,∞)] family | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| (∞,∞,∞) h{∞,∞} | r(∞,∞,∞) h2{∞,∞} | (∞,∞,∞) h{∞,∞} | r(∞,∞,∞) h2{∞,∞} | (∞,∞,∞) h{∞,∞} | r(∞,∞,∞) r{∞,∞} | t(∞,∞,∞) t{∞,∞} |
| Dual tilings | ||||||
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| V∞∞ | V∞.∞.∞.∞ | V∞∞ | V∞.∞.∞.∞ | V∞∞ | V∞.∞.∞.∞ | V∞.∞.∞ |
| Alternations | ||||||
| [(1+,∞,∞,∞)] (*∞∞∞∞) | [∞+,∞,∞)] (∞*∞) | [∞,1+,∞,∞)] (*∞∞∞∞) | [∞,∞+,∞)] (∞*∞) | [(∞,∞,∞,1+)] (*∞∞∞∞) | [(∞,∞,∞+)] (∞*∞) | [∞,∞,∞)]+ (∞∞∞) |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Alternation duals | ||||||
 |  |  |  |  |  | |
| V(∞.∞)∞ | V(∞.4)4 | V(∞.∞)∞ | V(∞.4)4 | V(∞.∞)∞ | V(∞.4)4 | V3.∞.3.∞.3.∞ |
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- John Horton Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strauss, The Symmetries of Things 2008, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5 (Chapter 19, The Hyperbolic Archimedean Tessellations)
- "Chapter 10: Regular honeycombs in hyperbolic space". The Beauty of Geometry: Twelve Essays. Dover Publications. 1999. ISBN 0-486-40919-8. LCCN 99035678.
External links
[edit]- Weisstein, Eric W. "Hyperbolic tiling". MathWorld.
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Poincaré hyperbolic disk". MathWorld.
- Hyperbolic and Spherical Tiling Gallery Archived 2013-03-24 at the Wayback Machine
- KaleidoTile 3: Educational software to create spherical, planar and hyperbolic tilings
- Hyperbolic Planar Tessellations, Don Hatch


