Butolame

 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
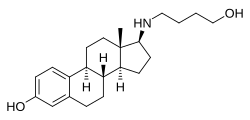
| Other names | 17β-((4-Hydroxybutyl)amino)estradiol; 17β-[(4-Hydroxybutyl)amino]estra-1,3,5(10)-trien-3-ol |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H33NO2 |
| Molar mass | 343.511 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Butolame, also known as 17β-((4-hydroxybutyl)amino)estradiol, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen and a 17β-aminoestrogen with anticoagulant effects that was first described in 1993 and was never marketed.[1][2][3]
References
[edit]- ^ Negwer M, Scharnow HG (2001). Organic-chemical drugs and their synonyms: (an international survey). Wiley-VCH. p. 2352. ISBN 978-3-527-30247-5.
- ^ Lemini C, Rubio-Póo C, Silva G, García-Mondragón J, Zavala E, Mendoza-Patiño N, et al. (October 1993). "Anticoagulant and estrogenic effects of two new 17 beta-aminoestrogens, butolame [17 beta-(4-hydroxy-1-butylamino)-1,3,5(10)-estratrien-3-ol] and pentolame [17 beta-(5-hydroxy-1-pentylamino)-1,3,5(10)-estratrien-3-ol]". Steroids. 58 (10): 457–461. doi:10.1016/0039-128x(93)90002-5. PMID 8256254. S2CID 54381037.
- ^ Jaimez R, Cooney A, Jackson K, Lemus AE, Lemini C, Cárdenas M, et al. (May 2000). "In vivo estrogen bioactivities and in vitro estrogen receptor binding and transcriptional activities of anticoagulant synthetic 17beta-aminoestrogens". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 73 (1–2): 59–66. doi:10.1016/s0960-0760(00)00053-4. PMID 10822025. S2CID 40211307.